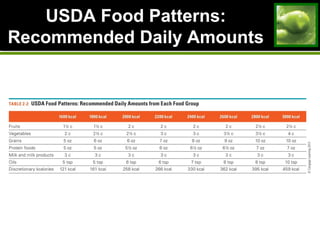
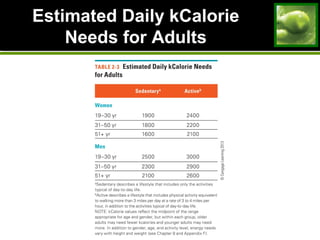
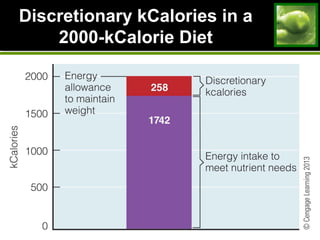
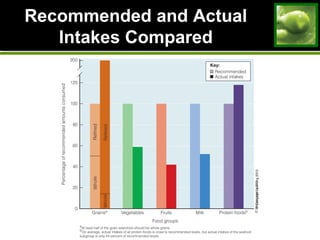
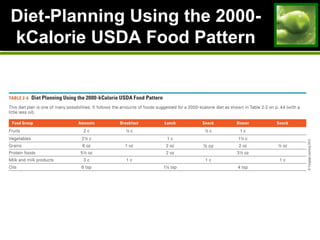
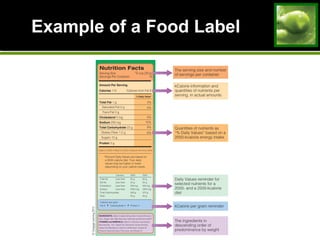
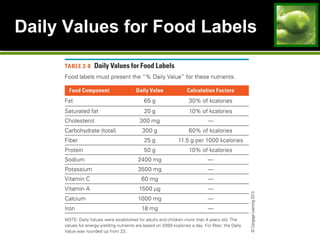
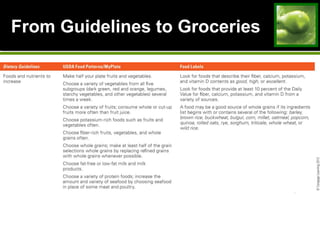
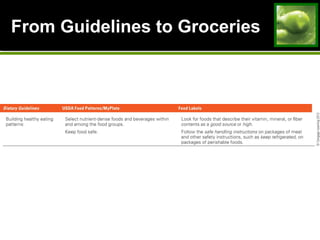
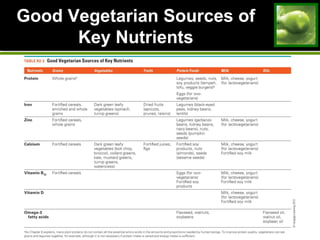
This document discusses principles and guidelines for planning a healthy diet, including adequacy, balance, nutrient density, moderation, and variety. It describes USDA Food Patterns and tools like MyPlate that can help plan diets meeting recommended daily amounts from major food groups. Food labels are explained which provide information on ingredients, serving sizes, nutrition facts, and claims. Special considerations for vegetarian diets are outlined like meeting protein, iron, zinc, calcium, vitamin B12, and omega-3 needs through food sources. Overall healthy, varied food choices following dietary guidelines promote optimal nutrition.