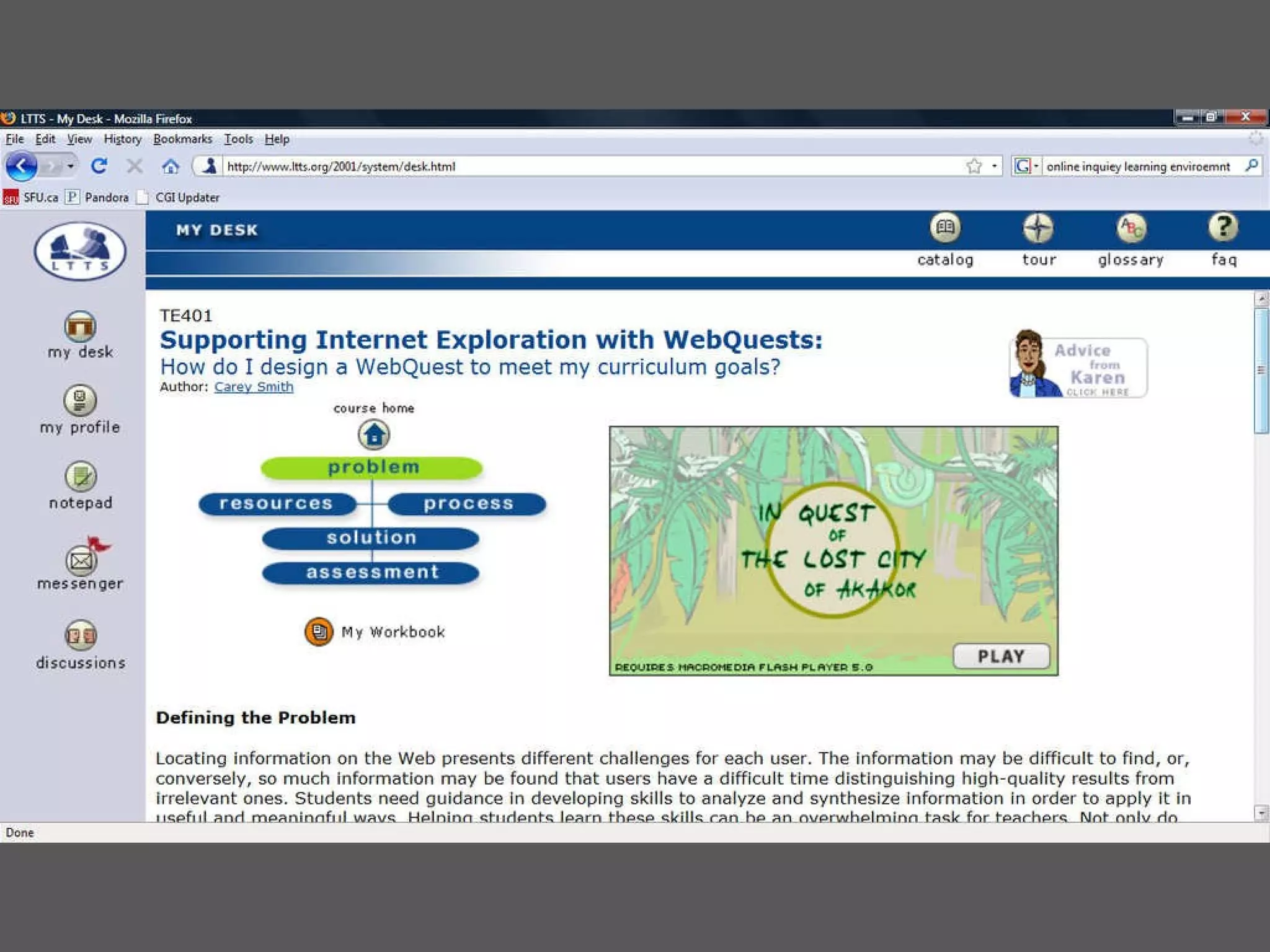
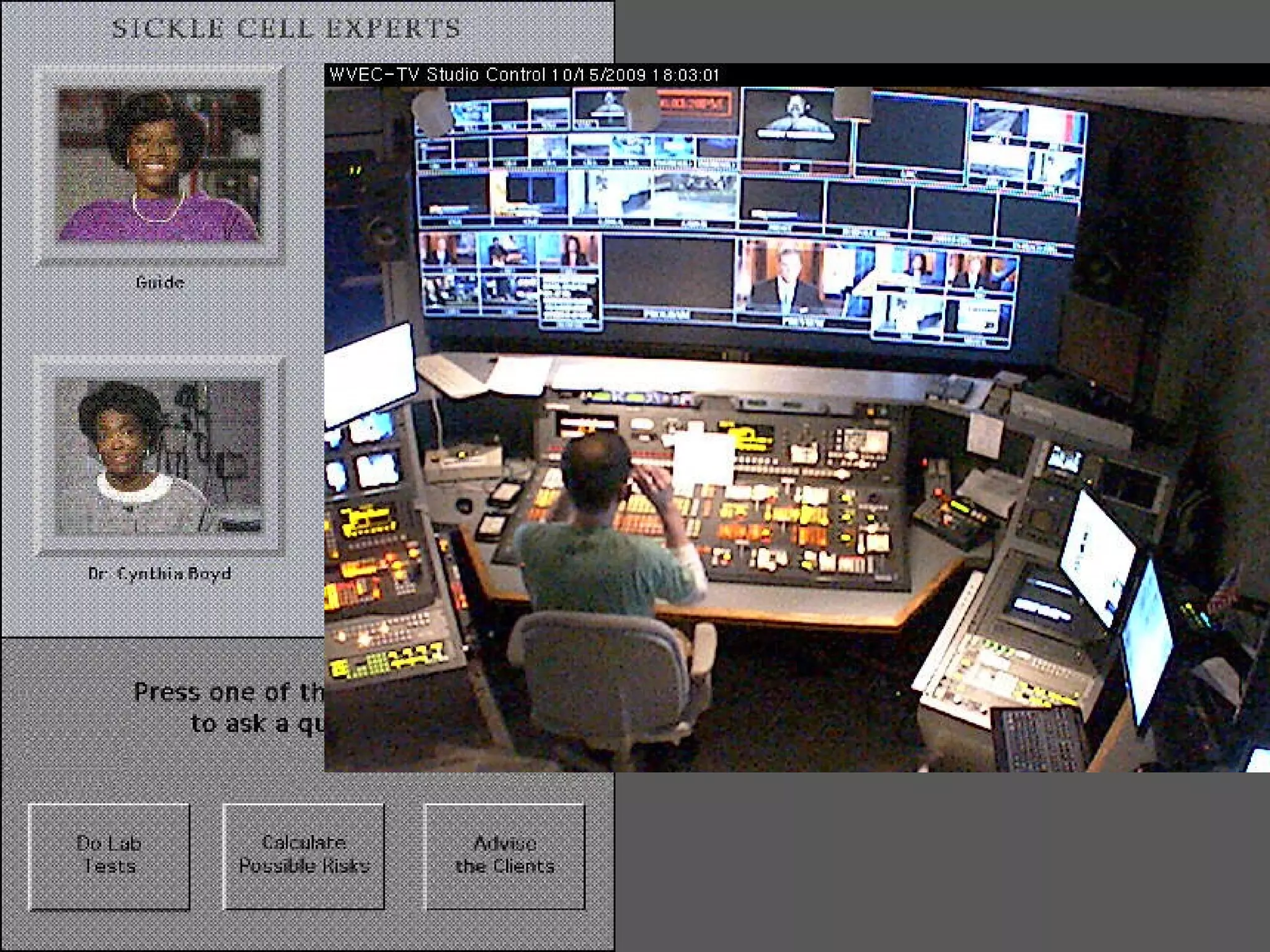
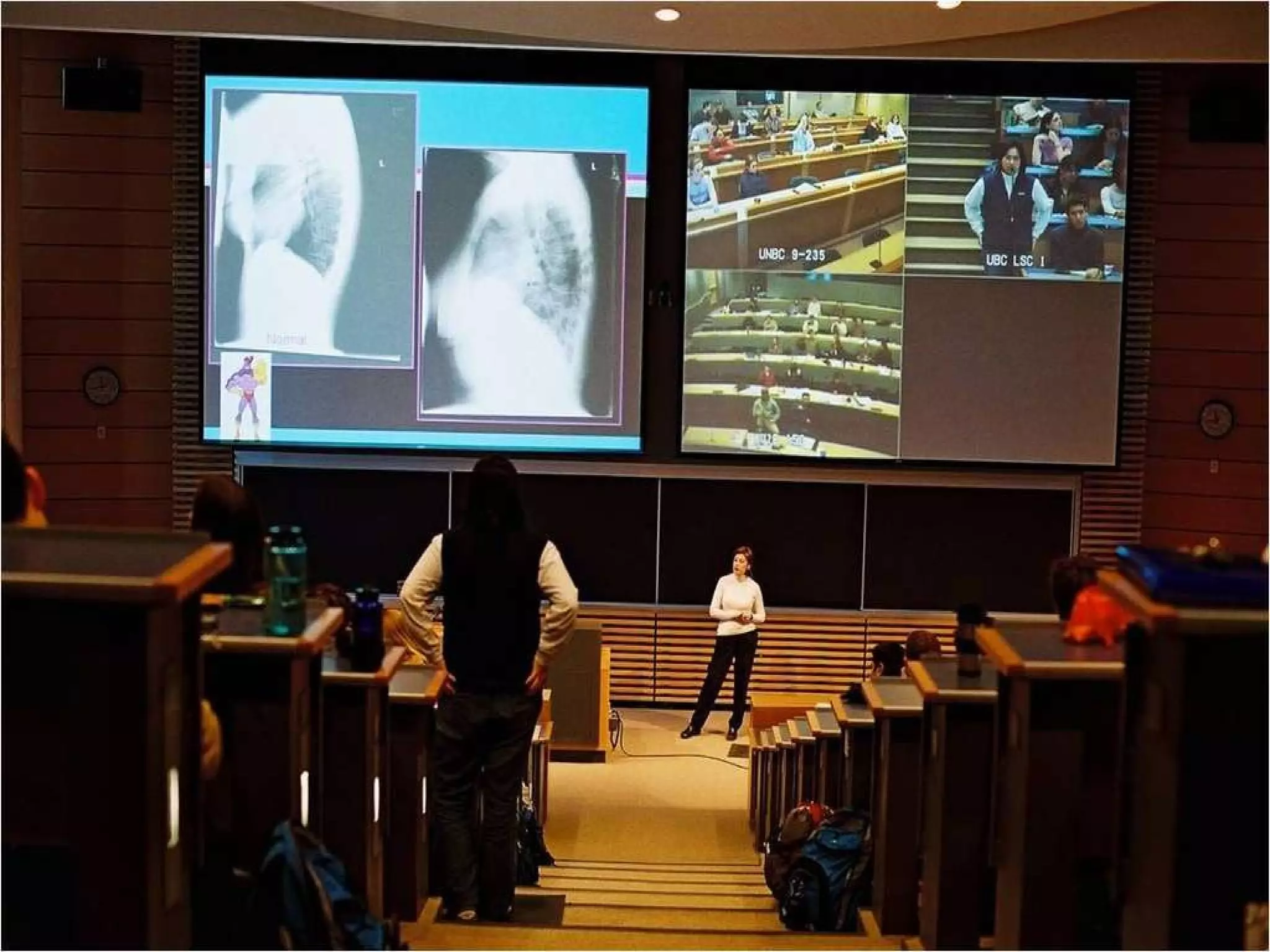
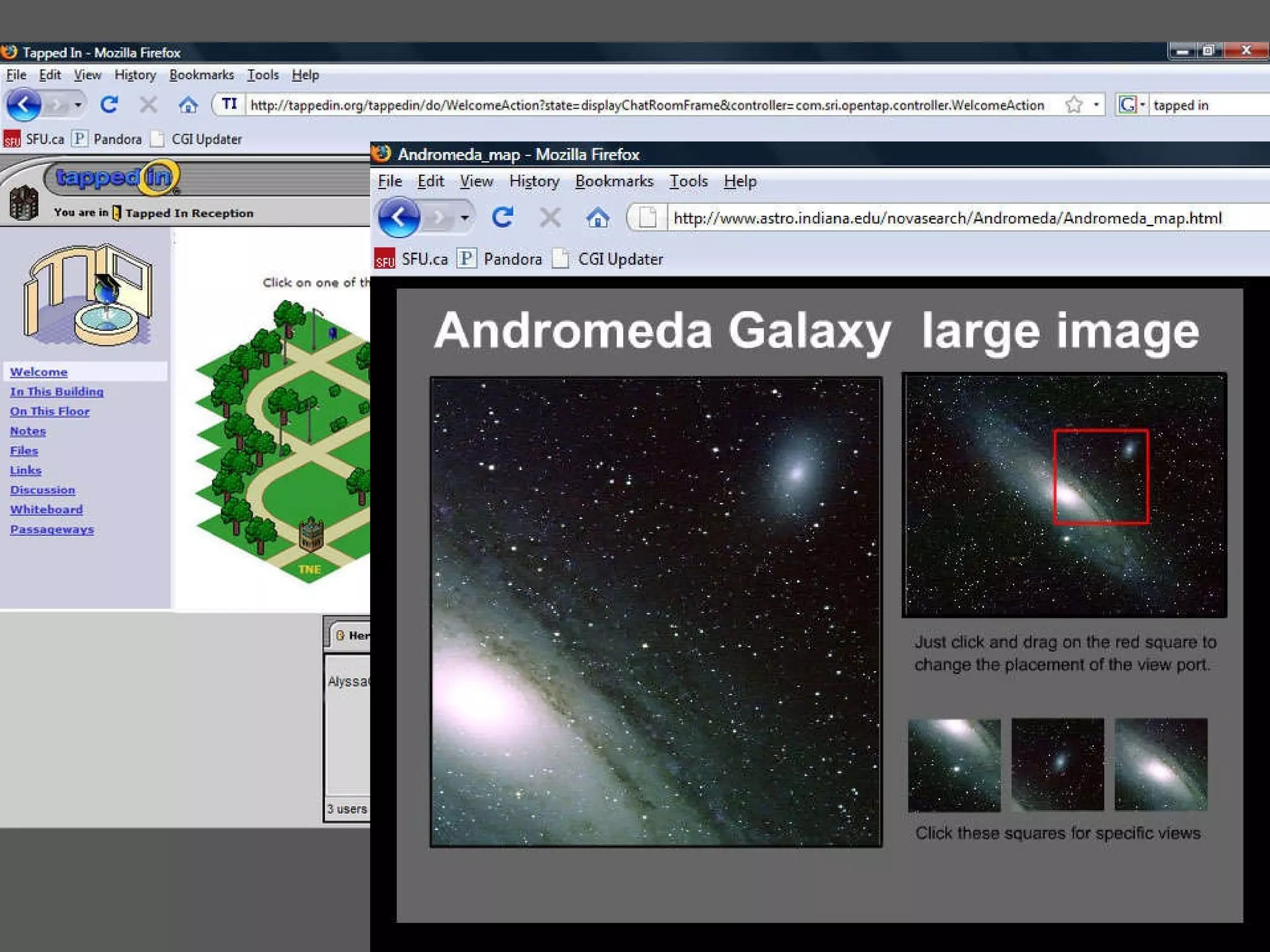
This document discusses designing learning spaces in physical and virtual settings. It provides definitions of learning spaces and analyzes how their design has evolved from fixed and formal to being more dynamic and flexible to support greater movement and collaboration. The document outlines key questions in learning space design around intentional pedagogical alignment and user experience. It presents five socio-constructivist principles for designing spaces that promote learner interaction, engagement, real-world contexts, participation, and evolution. Examples of applying these principles in physical and virtual spaces are provided.