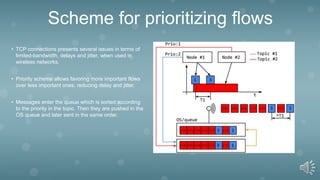
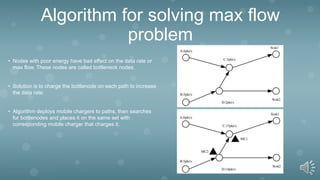
The document discusses using mobile robots in wireless sensor networks. It first outlines the purpose of studying current developments in mobile robots and wireless sensor networks to choose reliable implementation methods. It then discusses several key areas of research: using the MQTT protocol to simplify software and reduce resource usage; a priority scheme for flows to reduce delay and jitter; and an algorithm to solve the max flow problem by deploying mobile chargers to bottleneck nodes. The conclusion states that MQTT simplifies development and maintenance, flow prioritization reduces jitter, and the bottleneck algorithm can effectively increase max flow at sinks.