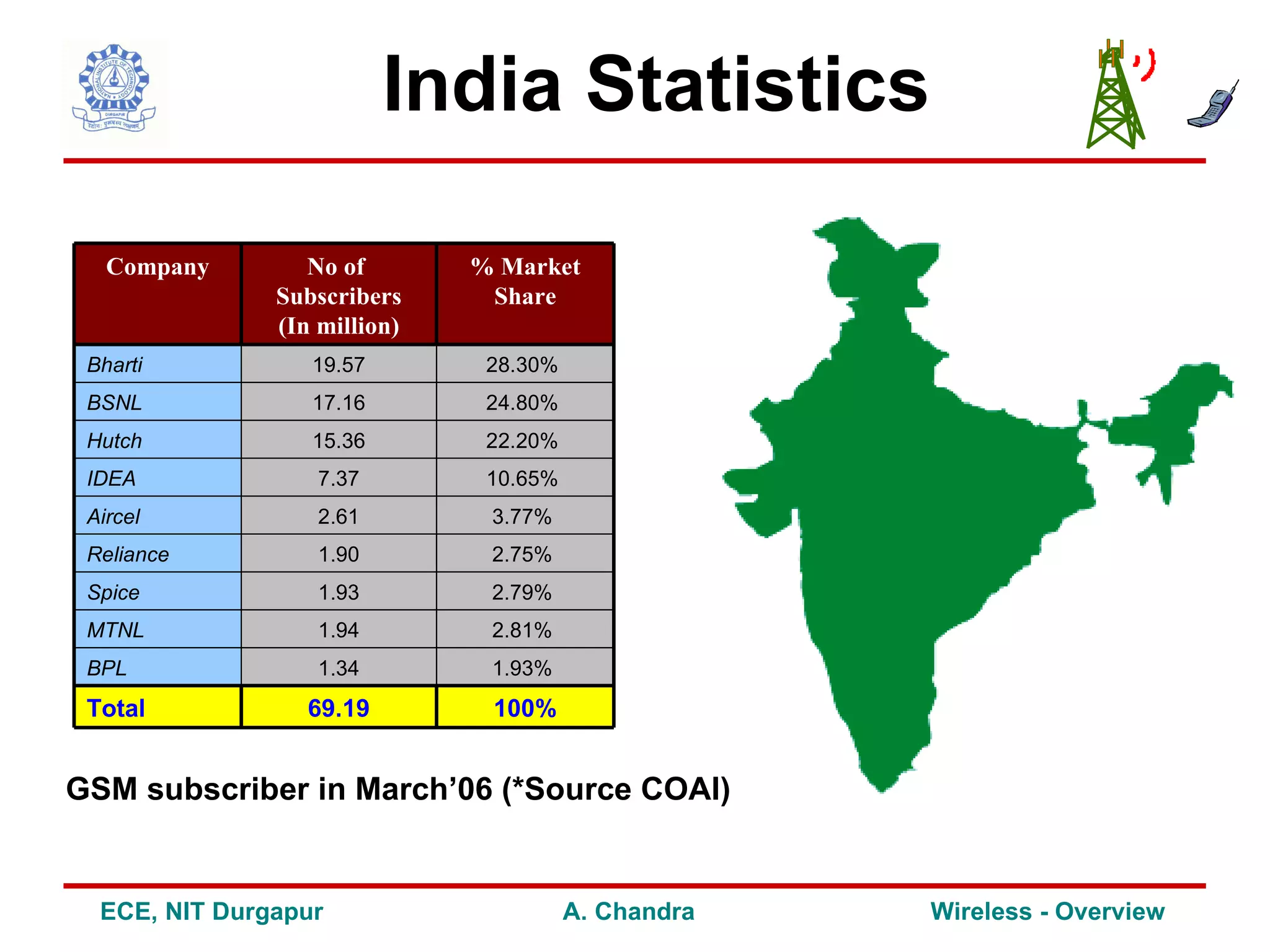
The document provides an overview of wireless communication, including:
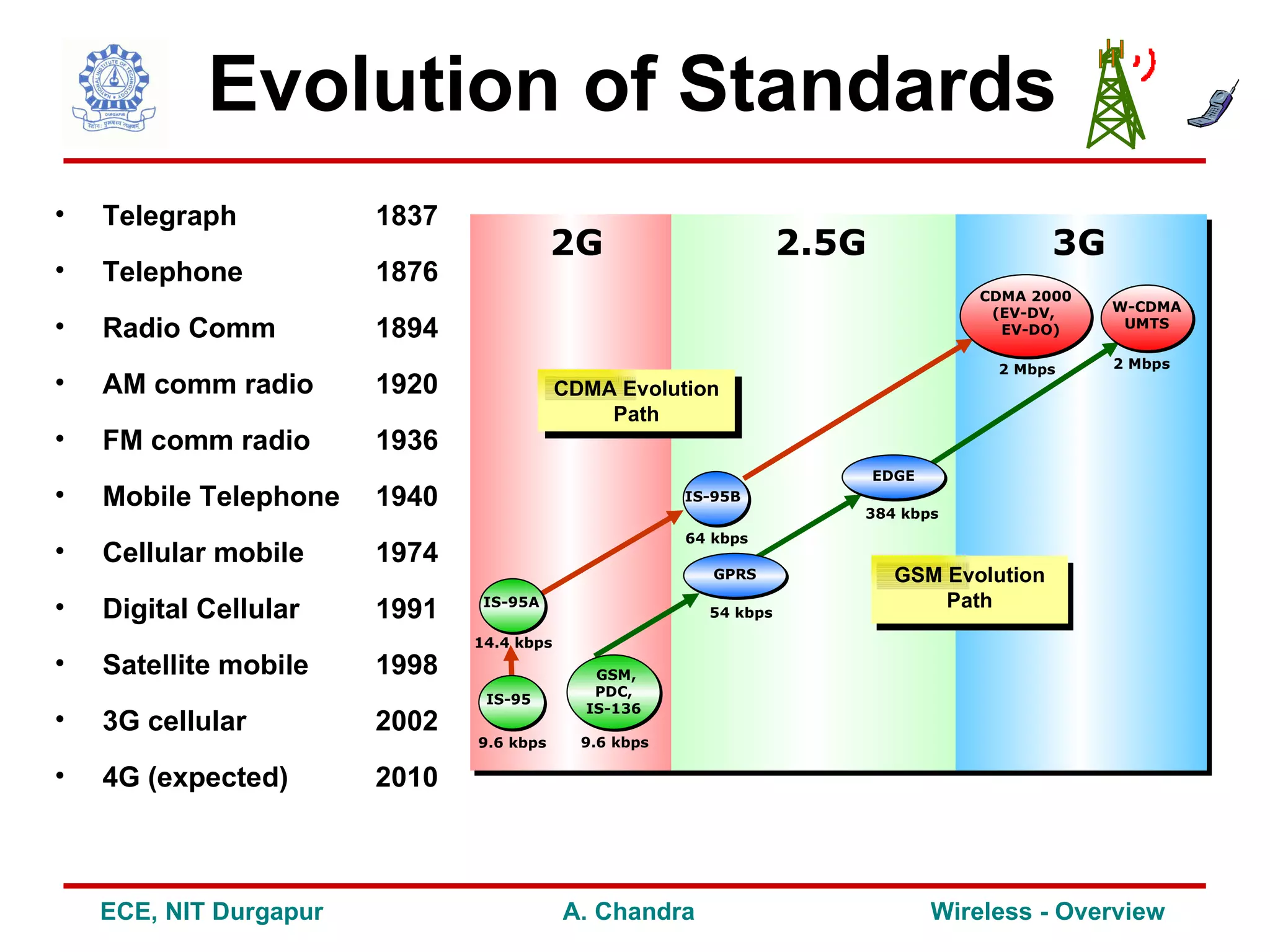
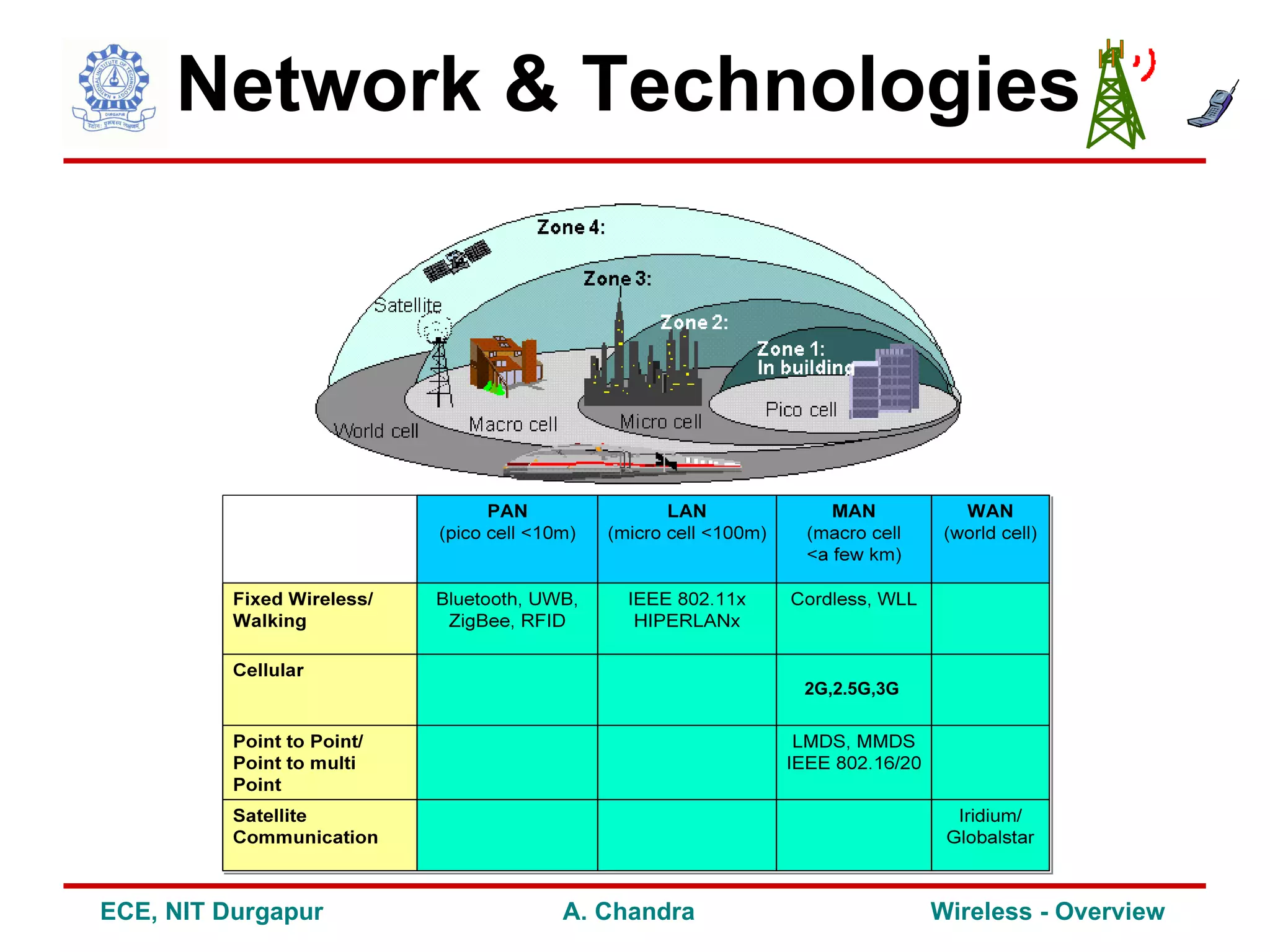
1) It discusses the evolution of wireless standards from telegraph to 4G cellular and highlights key technologies like 2G, 3G, WiFi and Bluetooth.
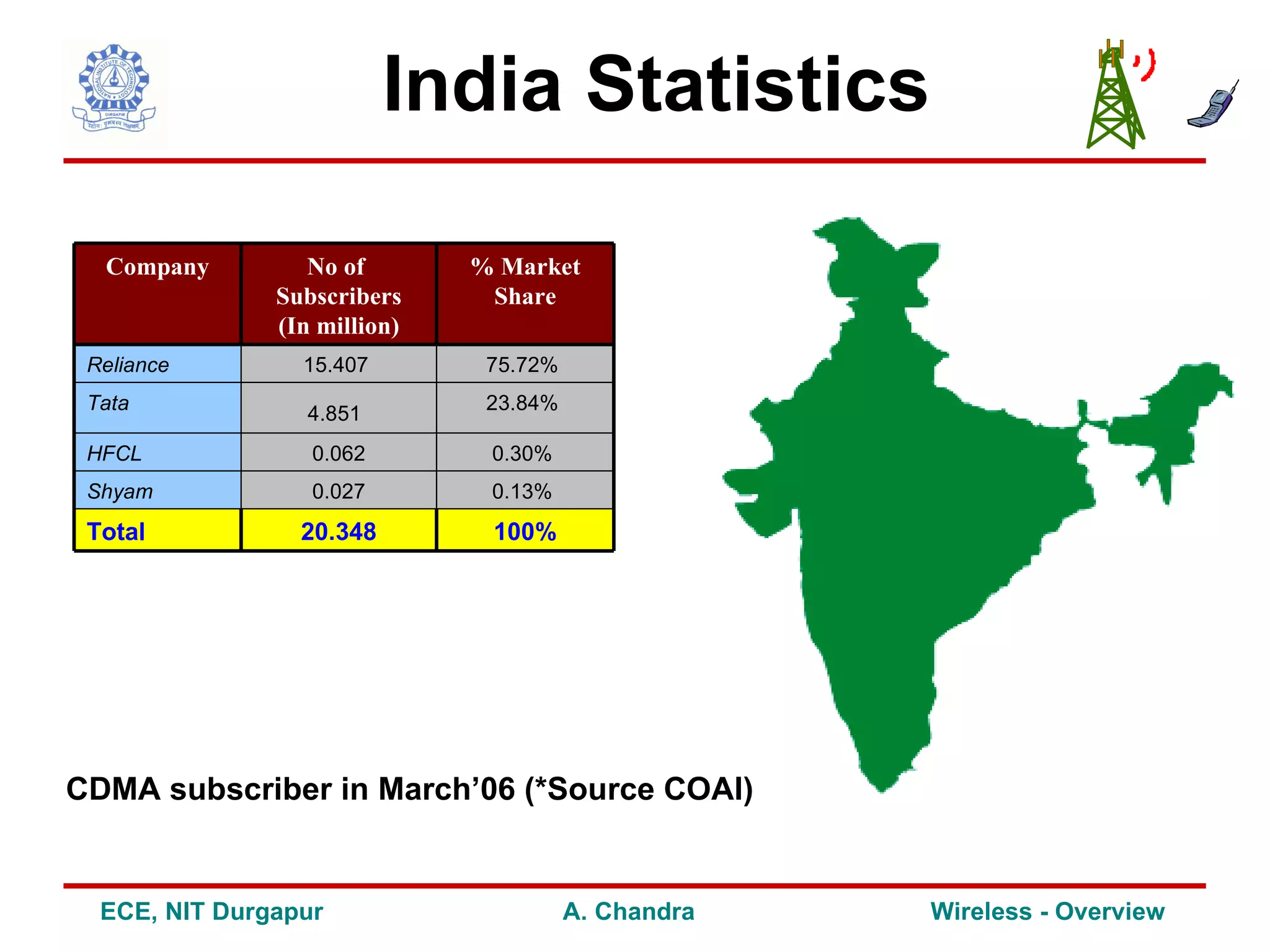
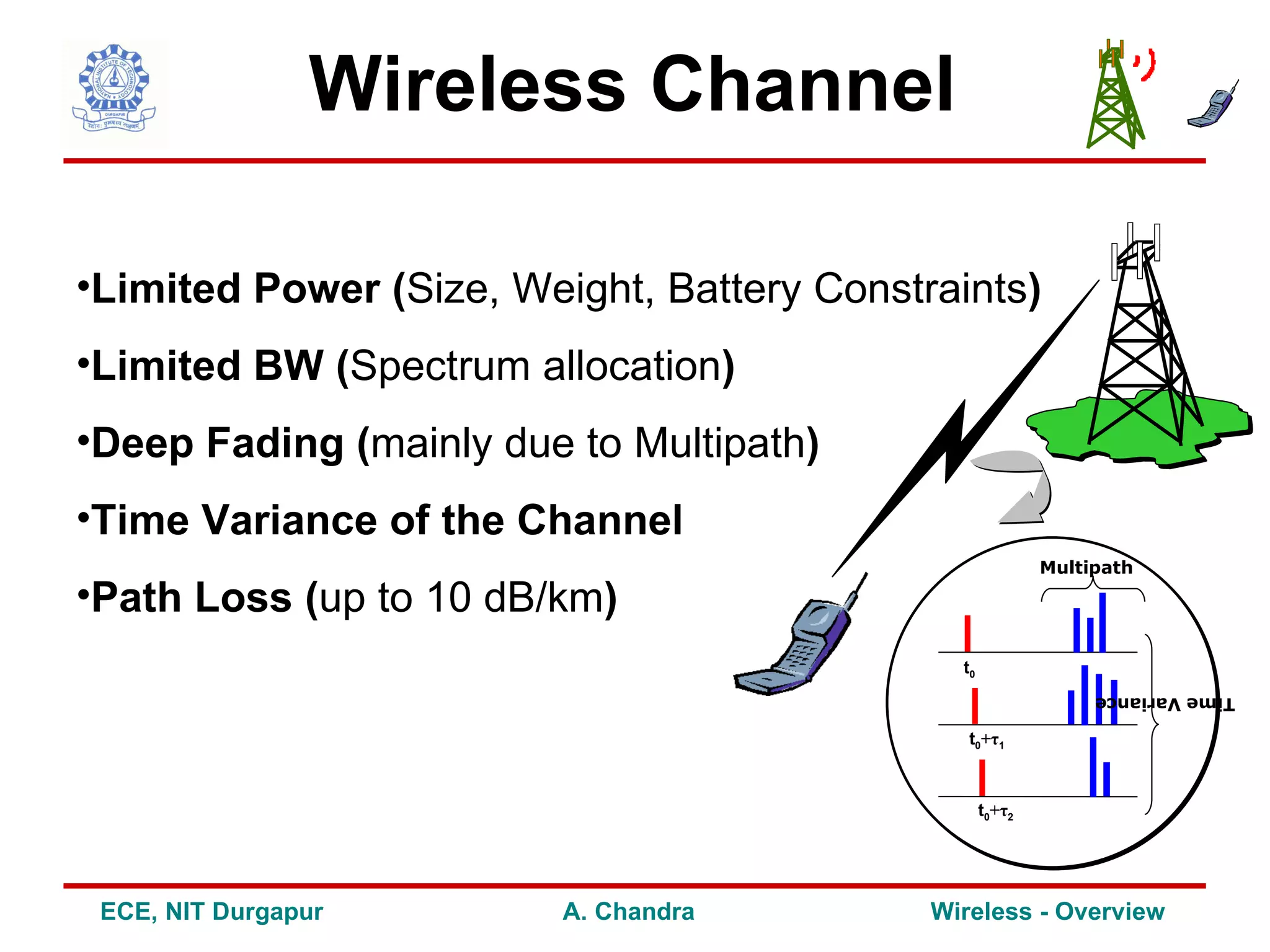
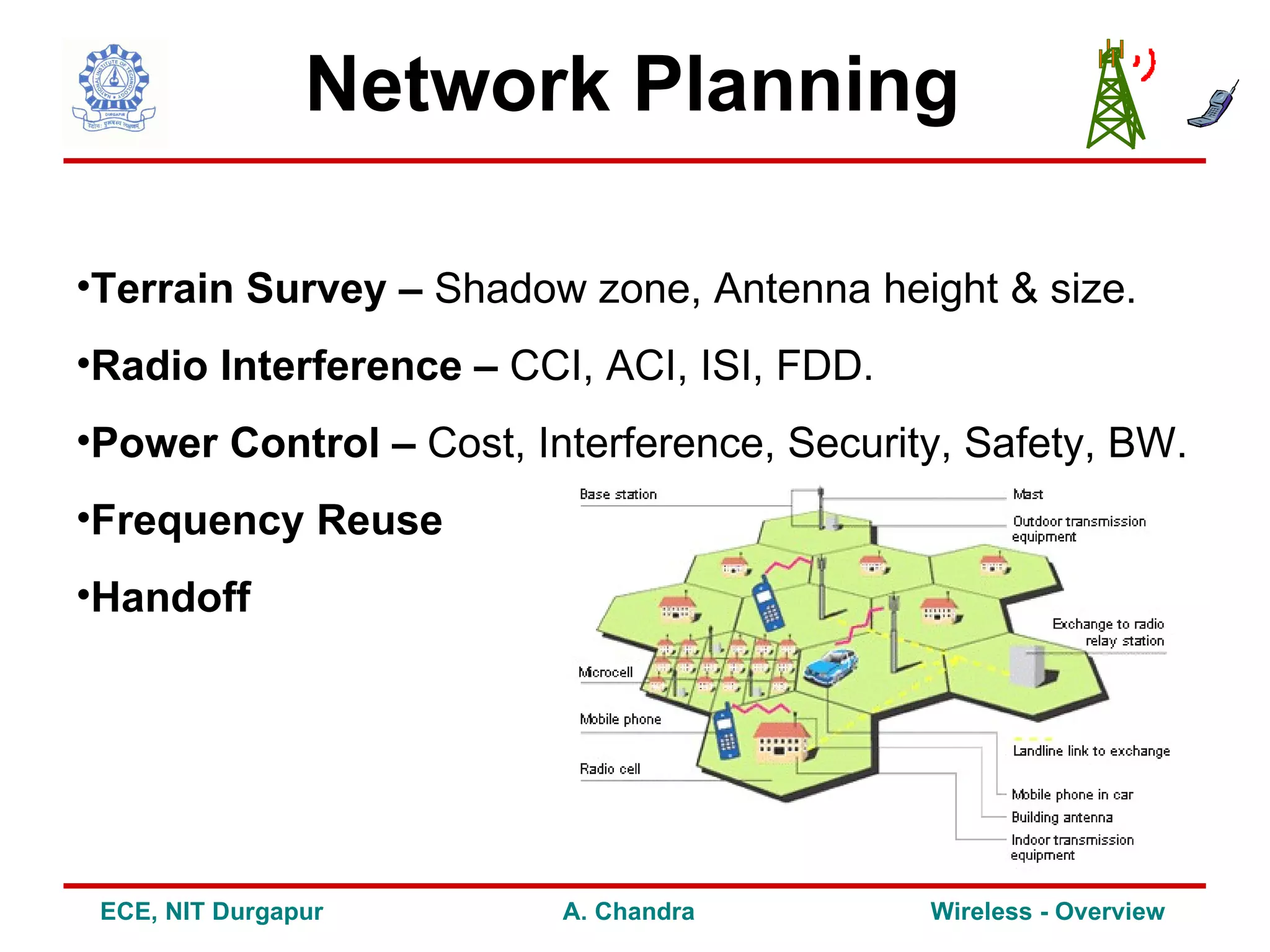
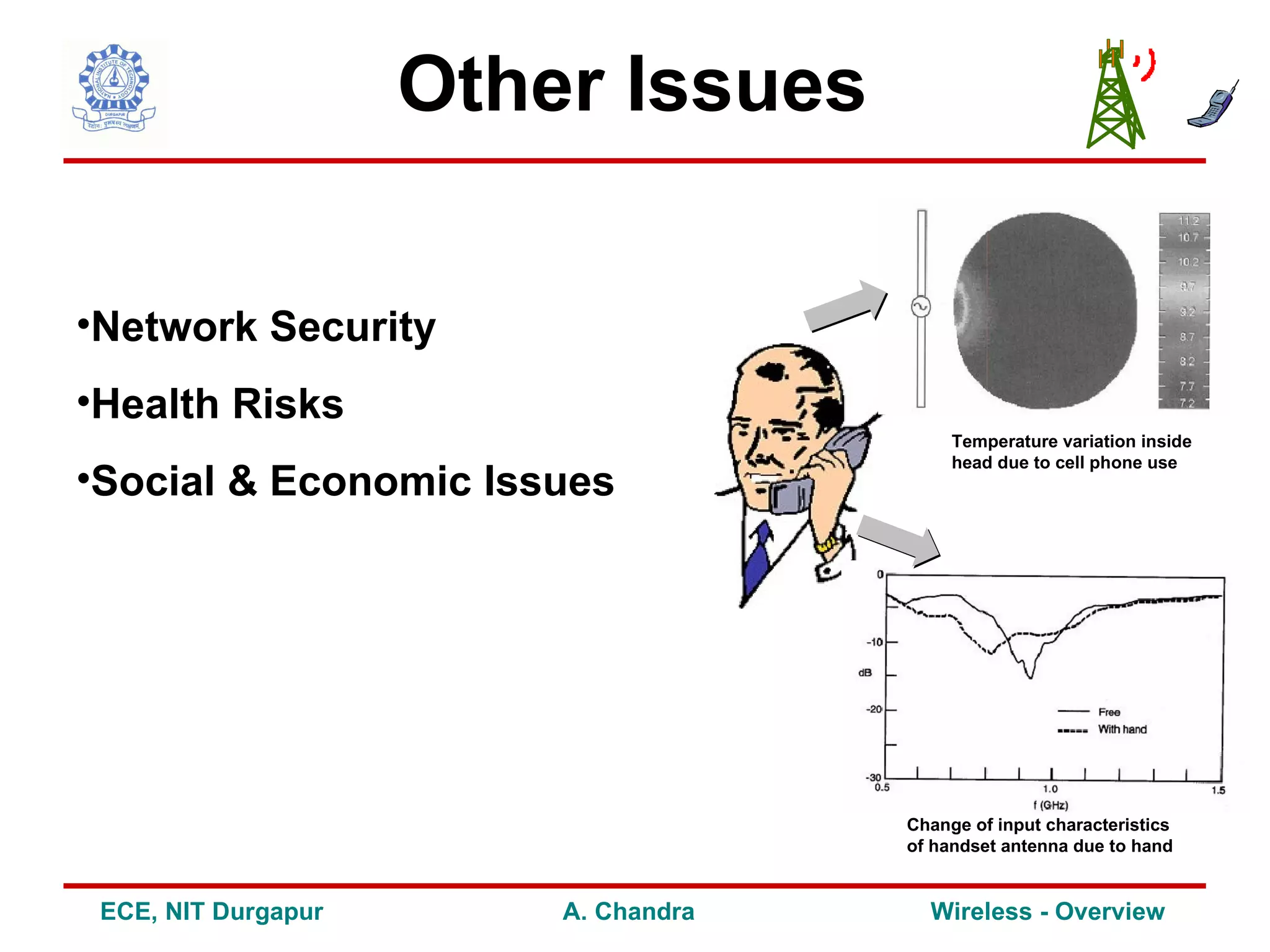
2) It outlines some of the challenges in wireless communication such as limitations of the wireless channel, issues around standardization, network planning and other concerns.
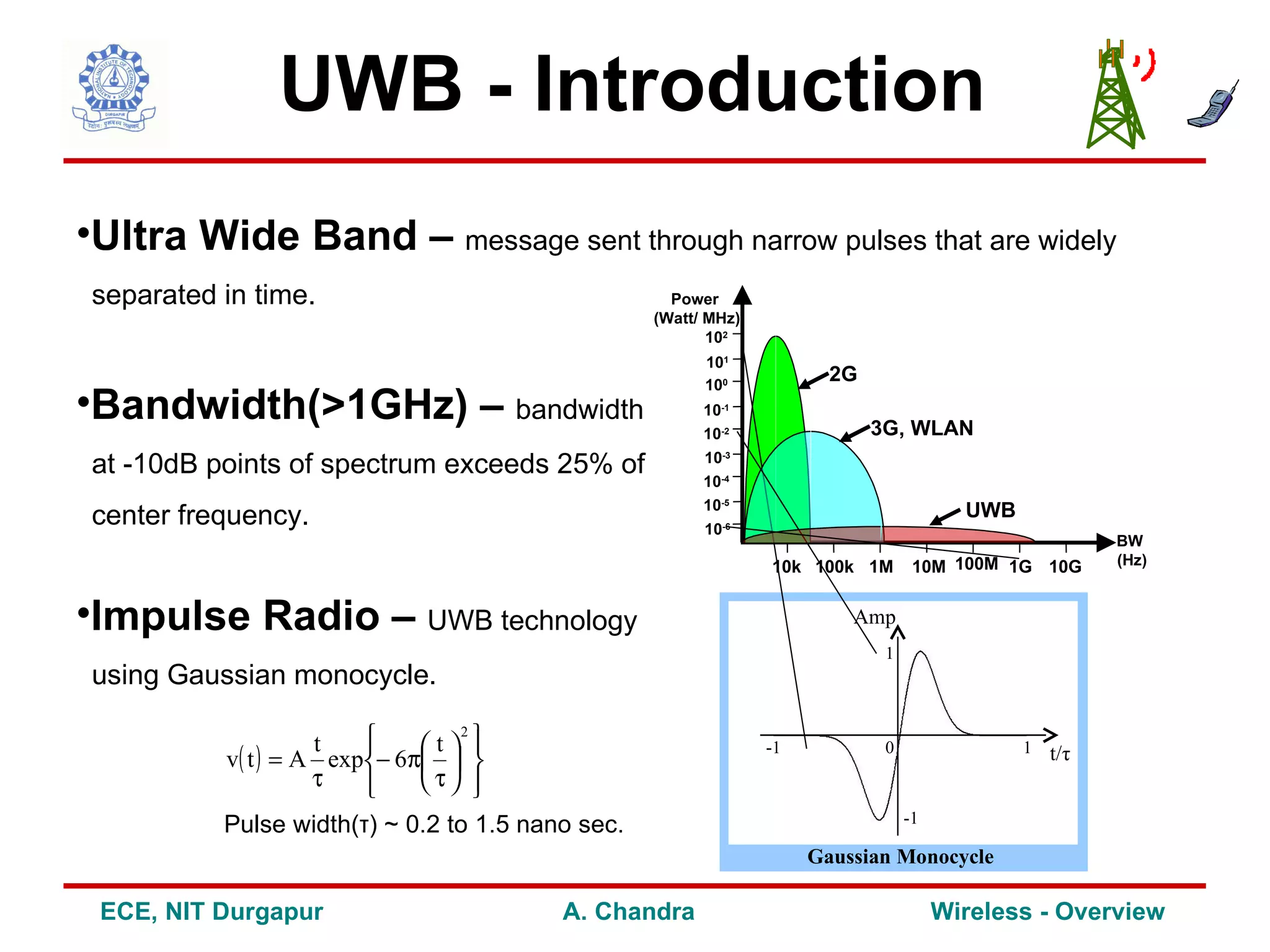
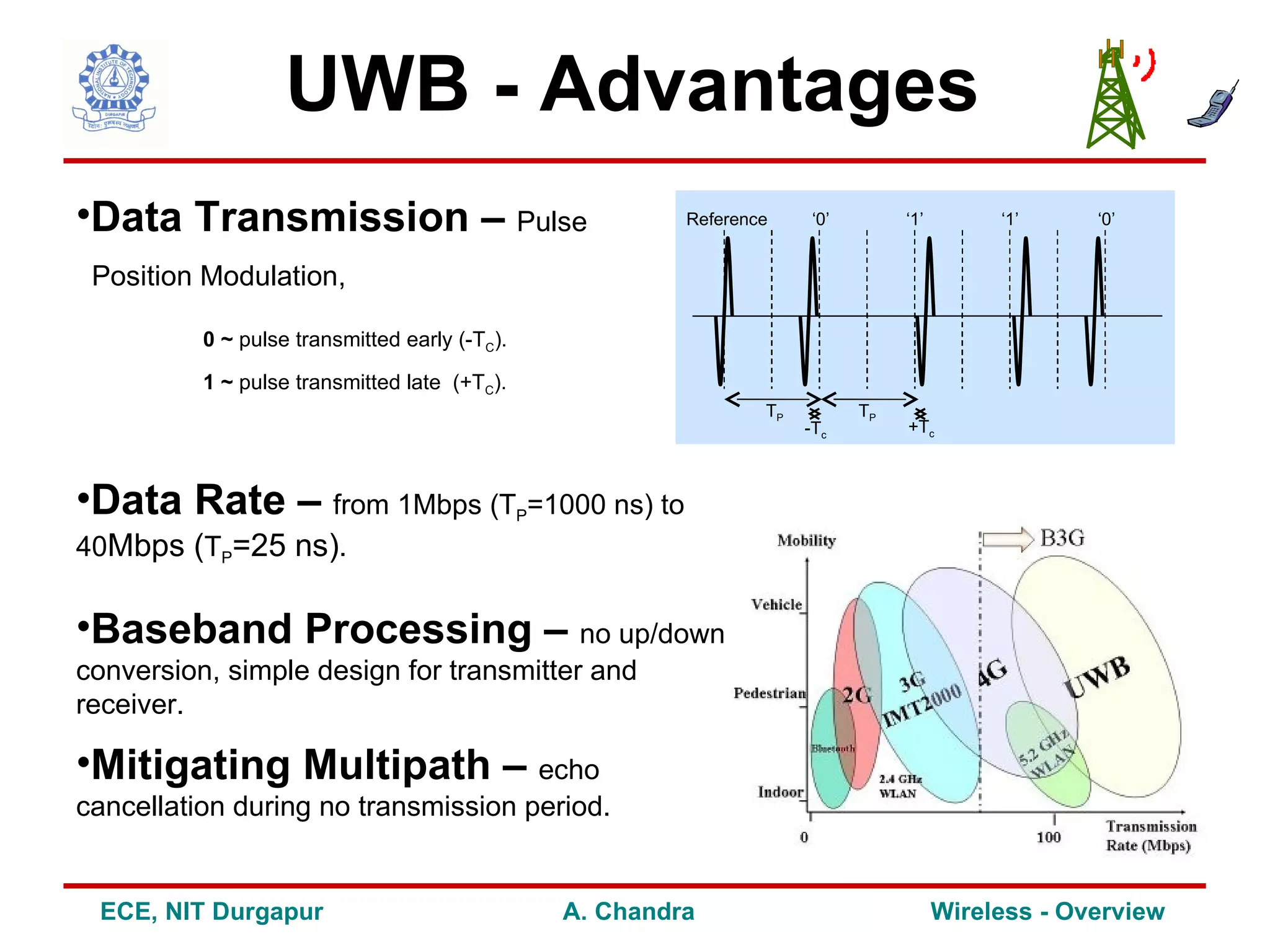
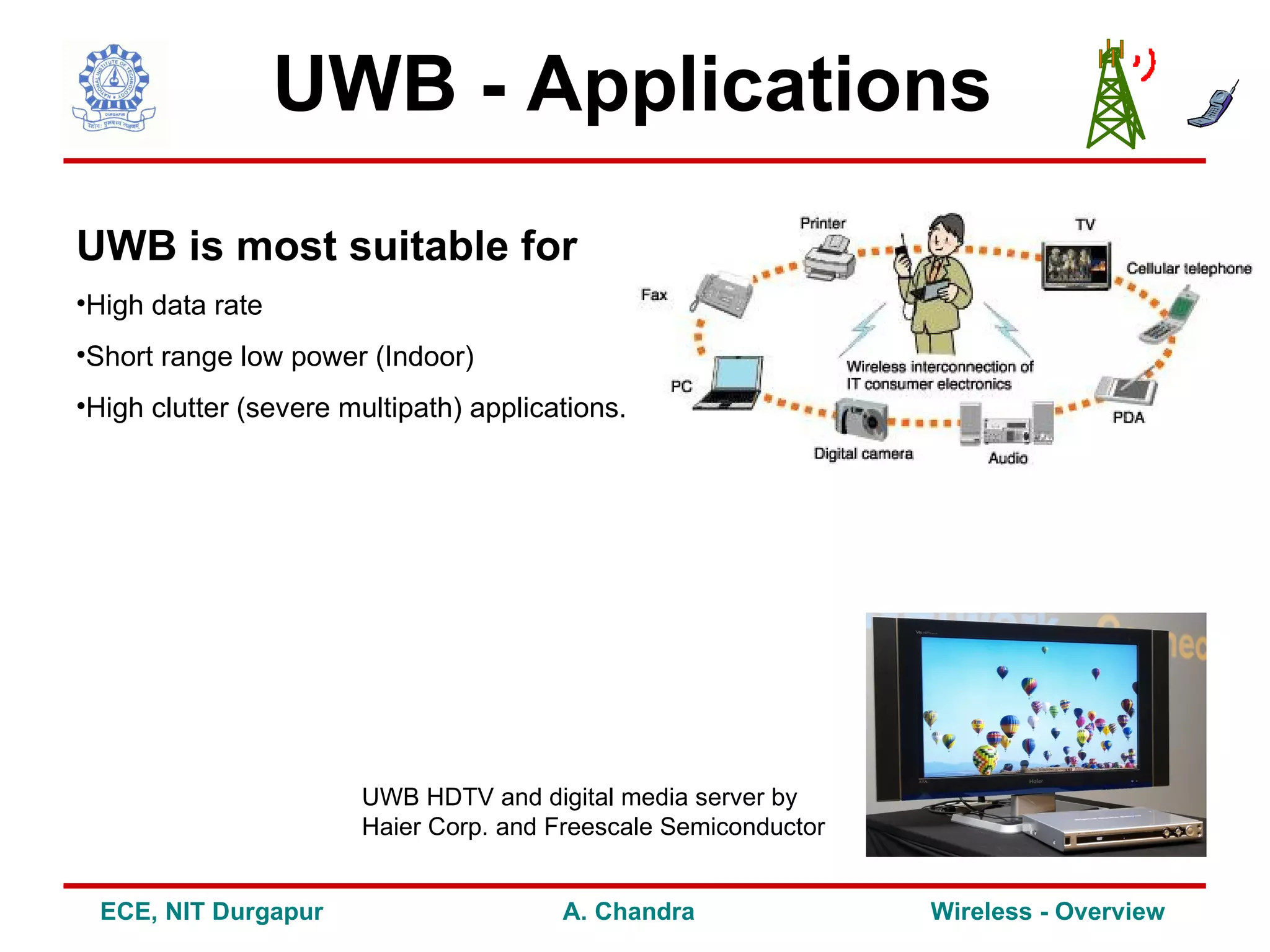
3) It explores future trends and research areas in wireless including technologies like UWB, OFDM and MIMO that can help address challenges and enhance capacity, data rates and performance.