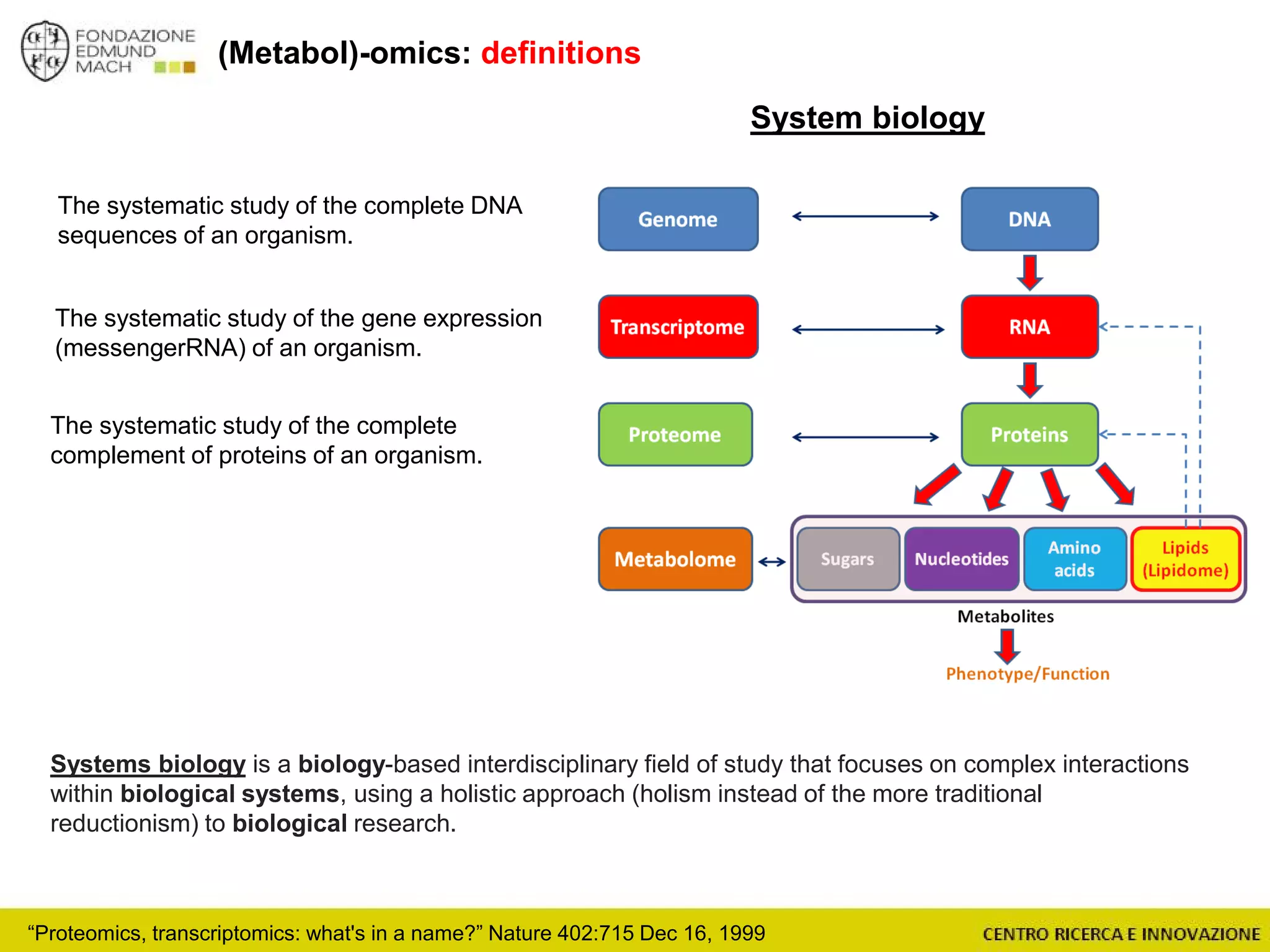
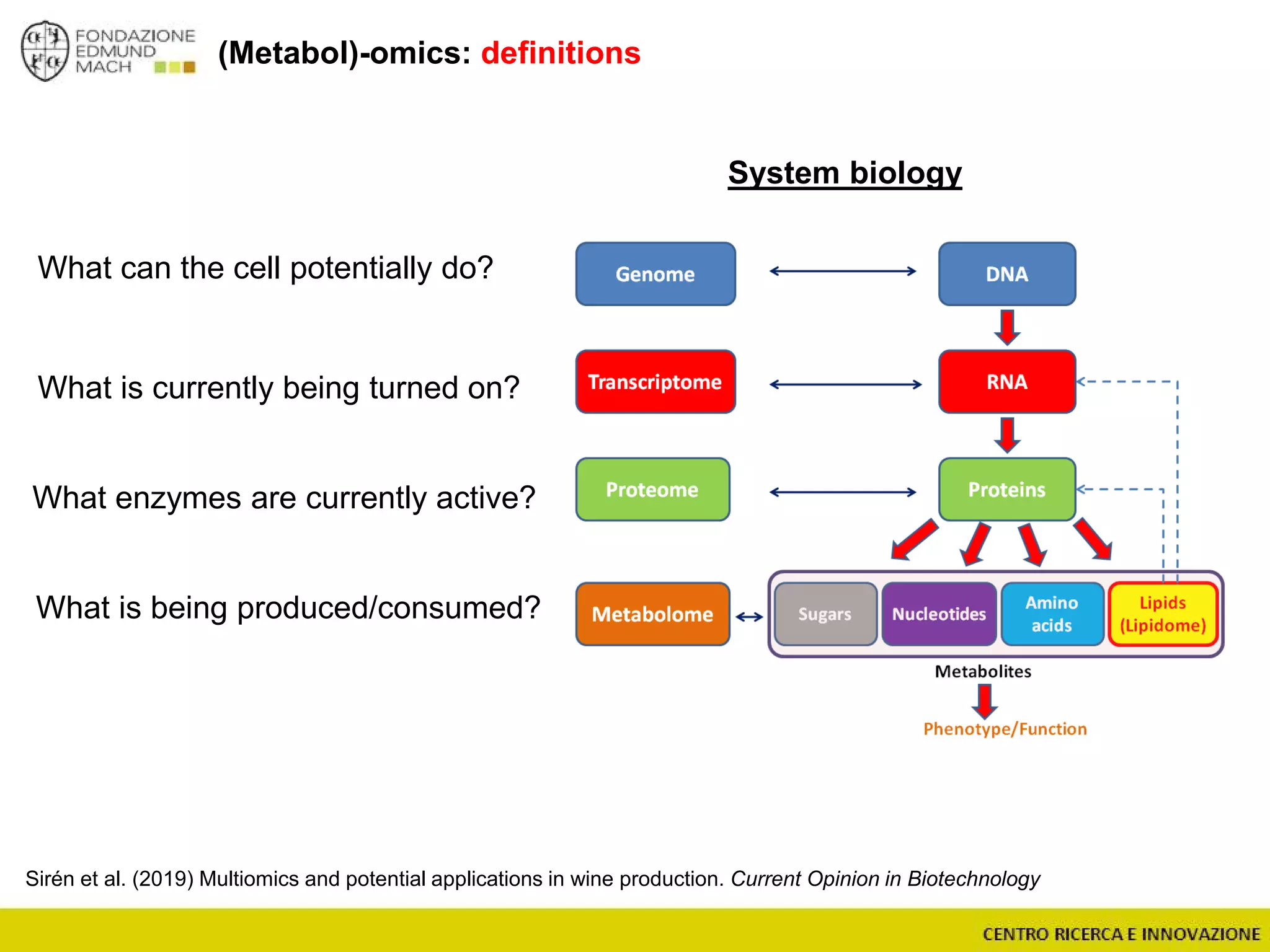
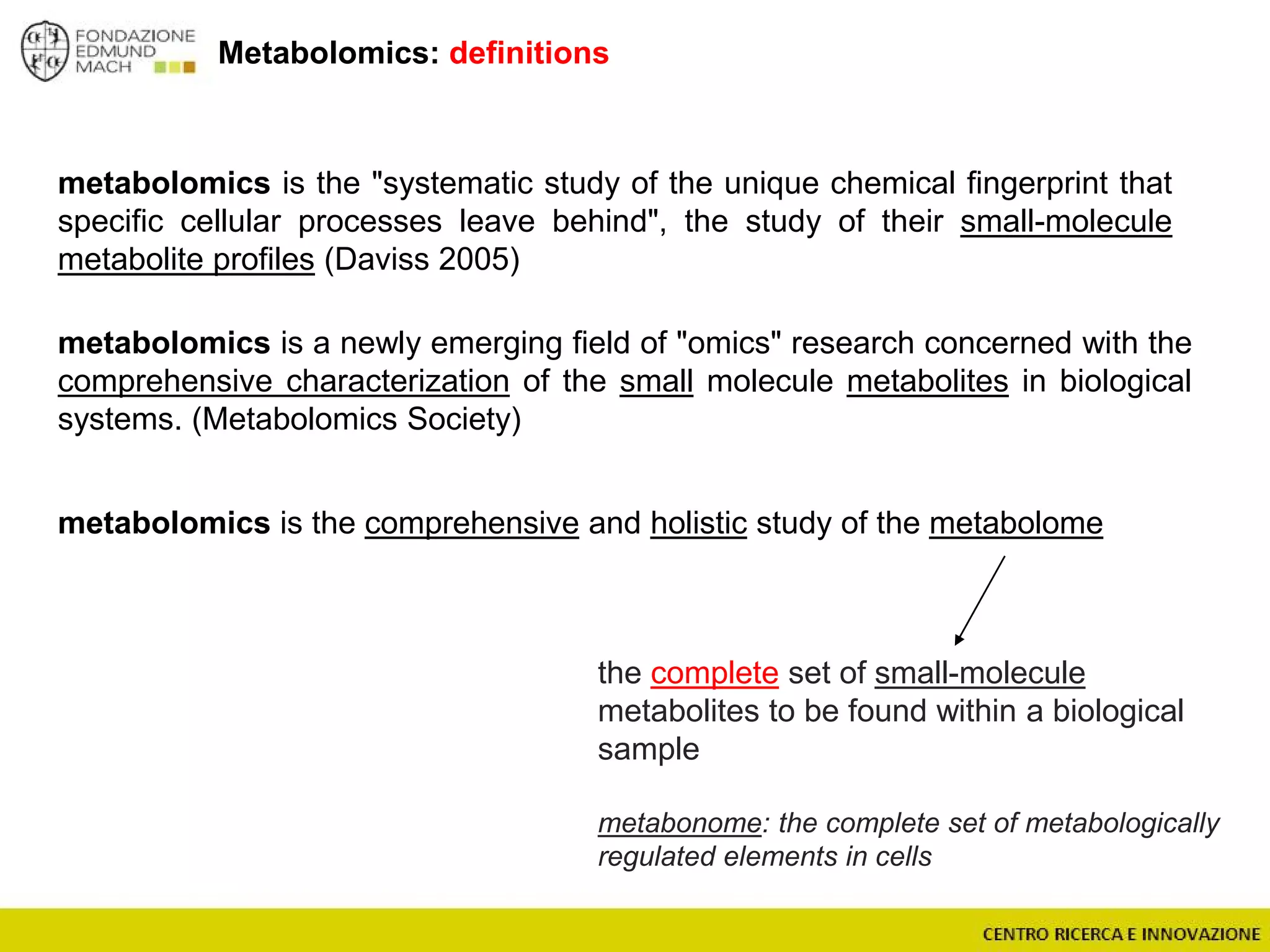
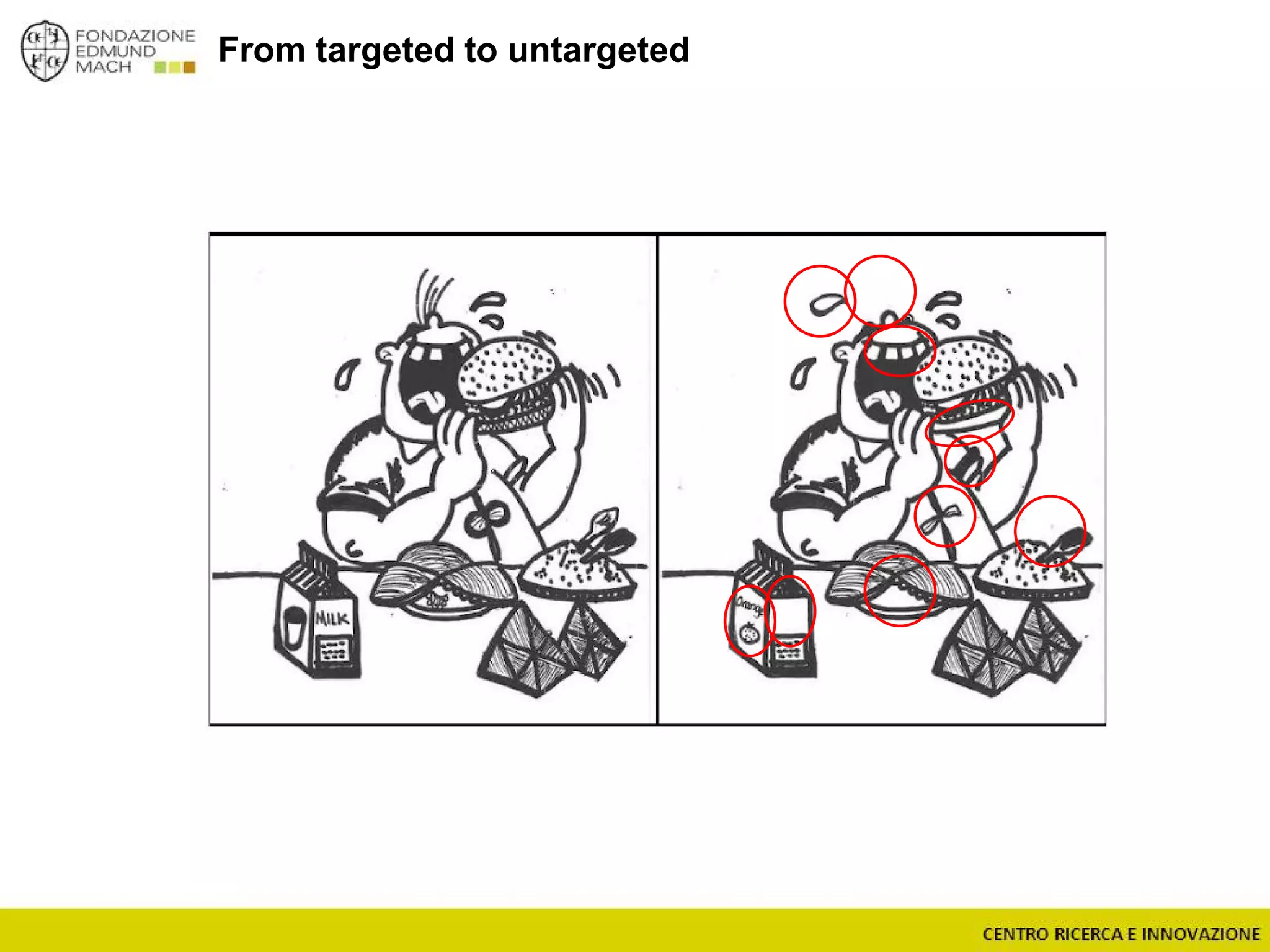
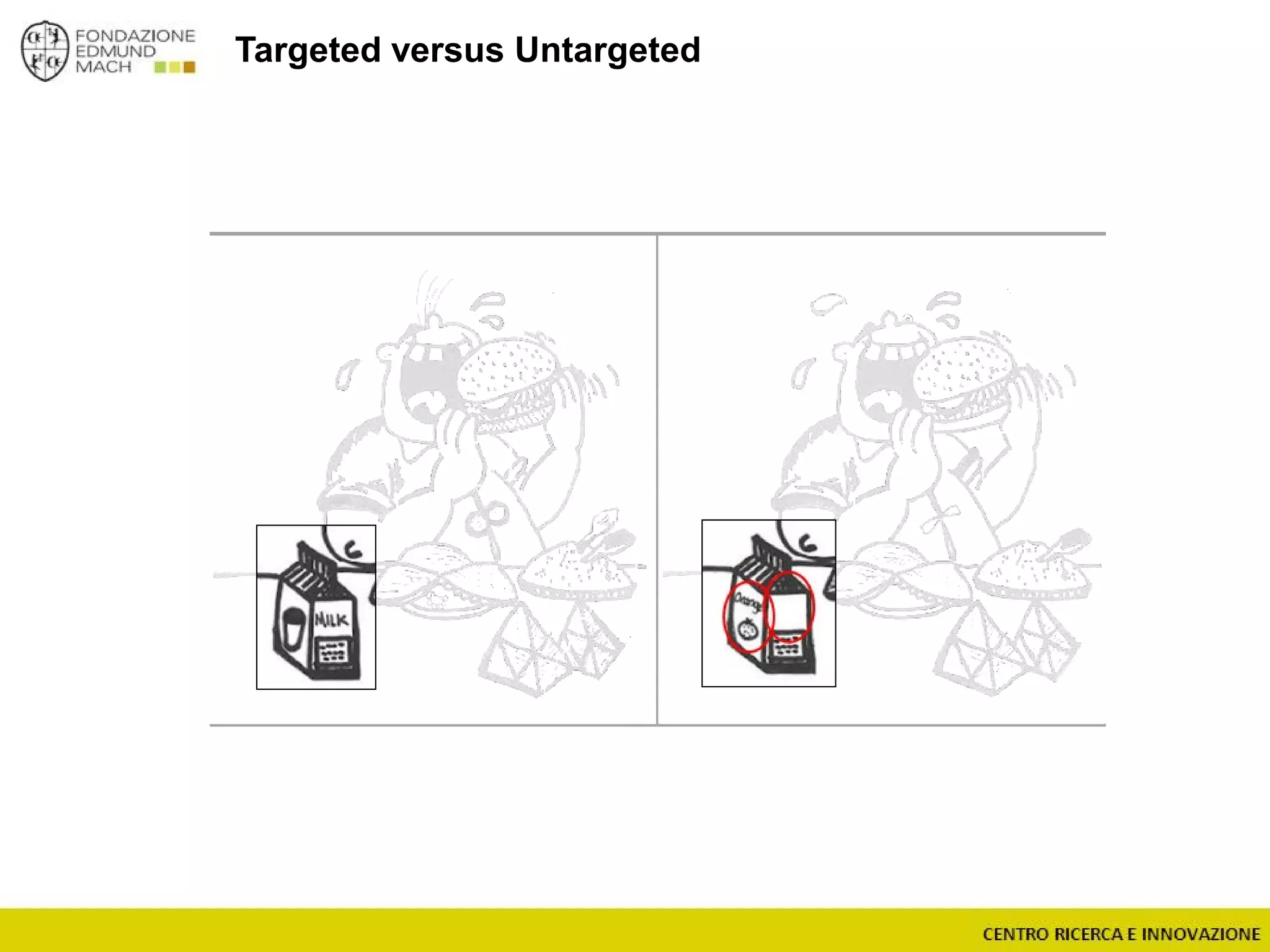
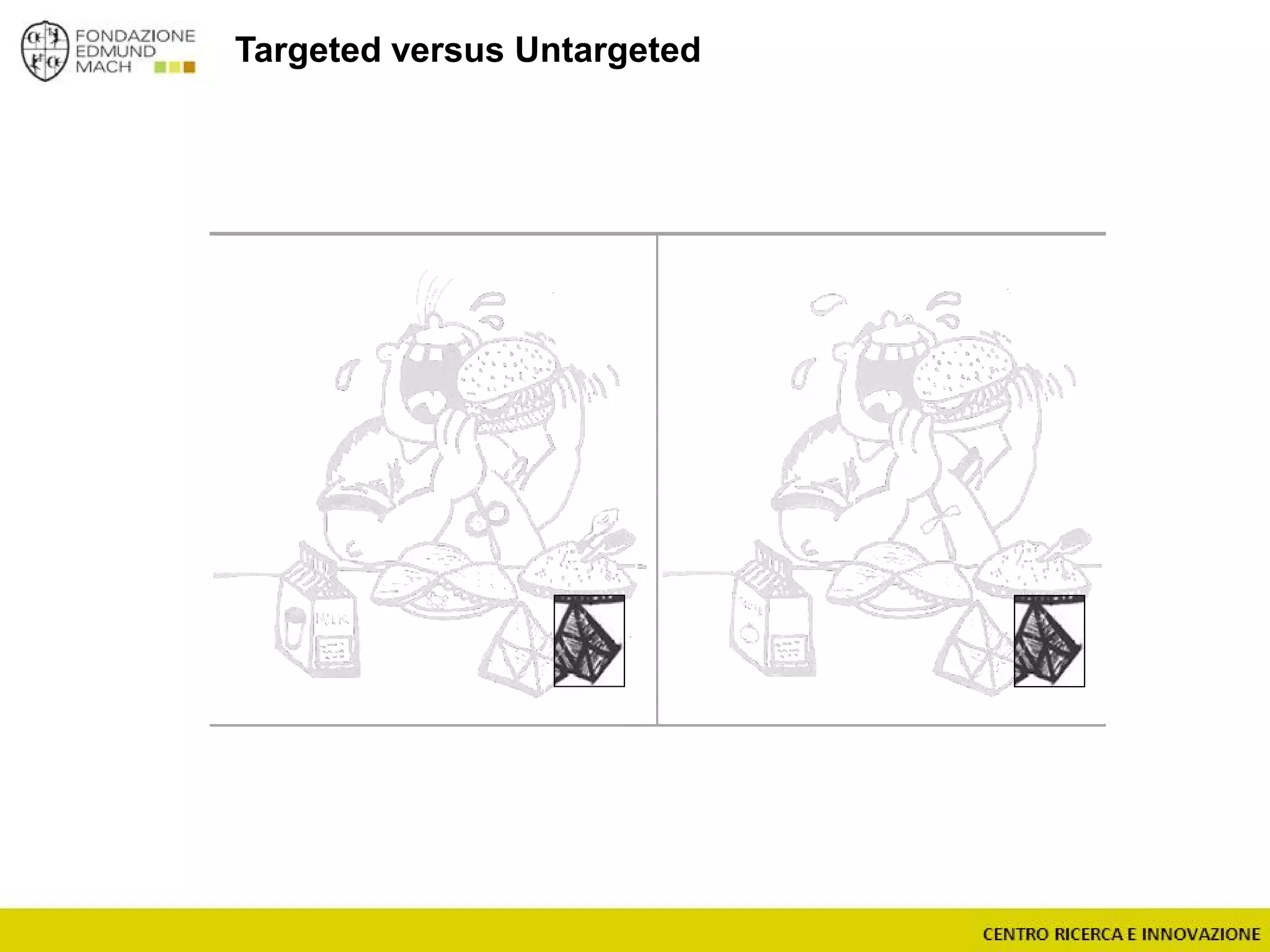
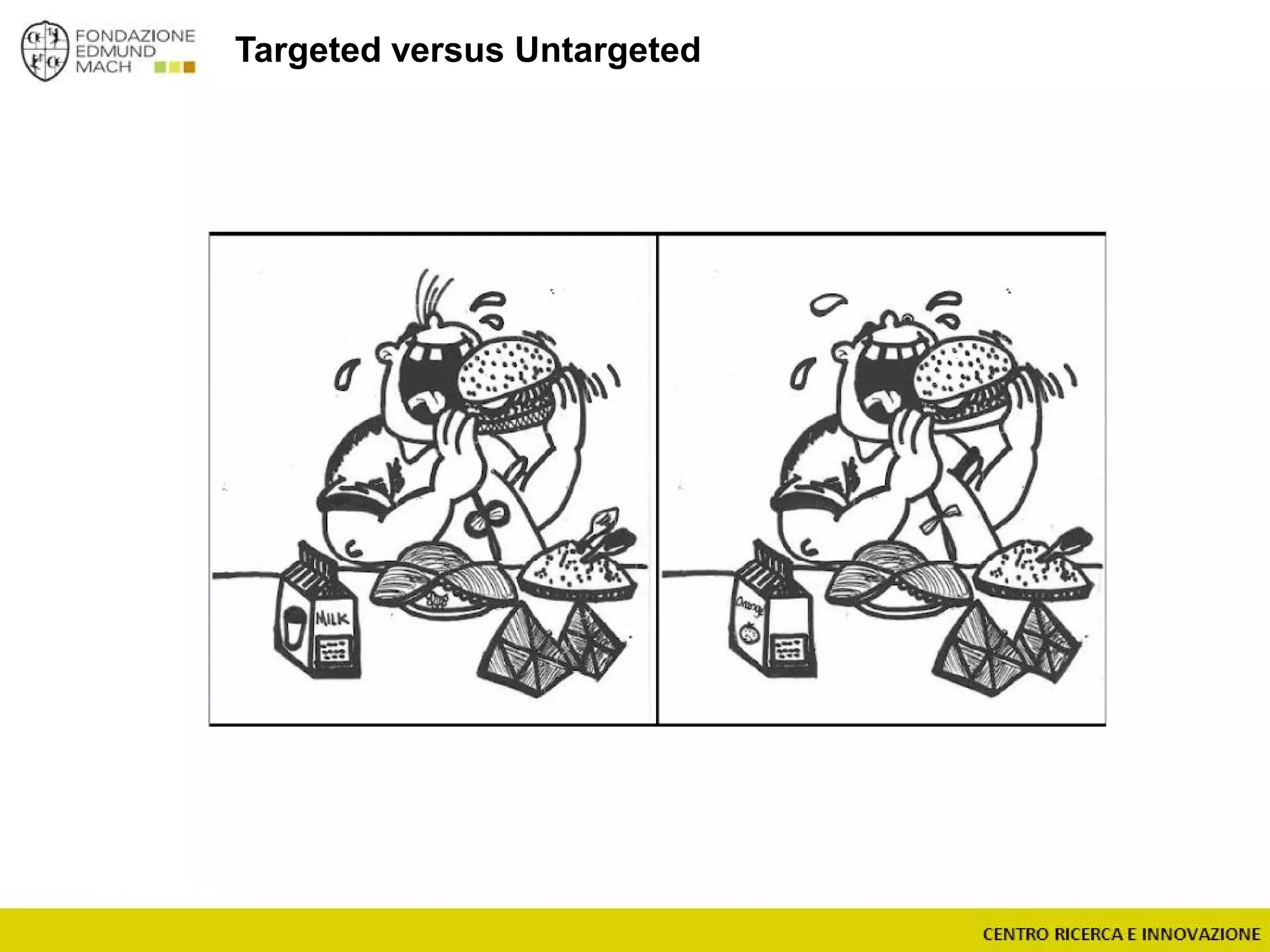
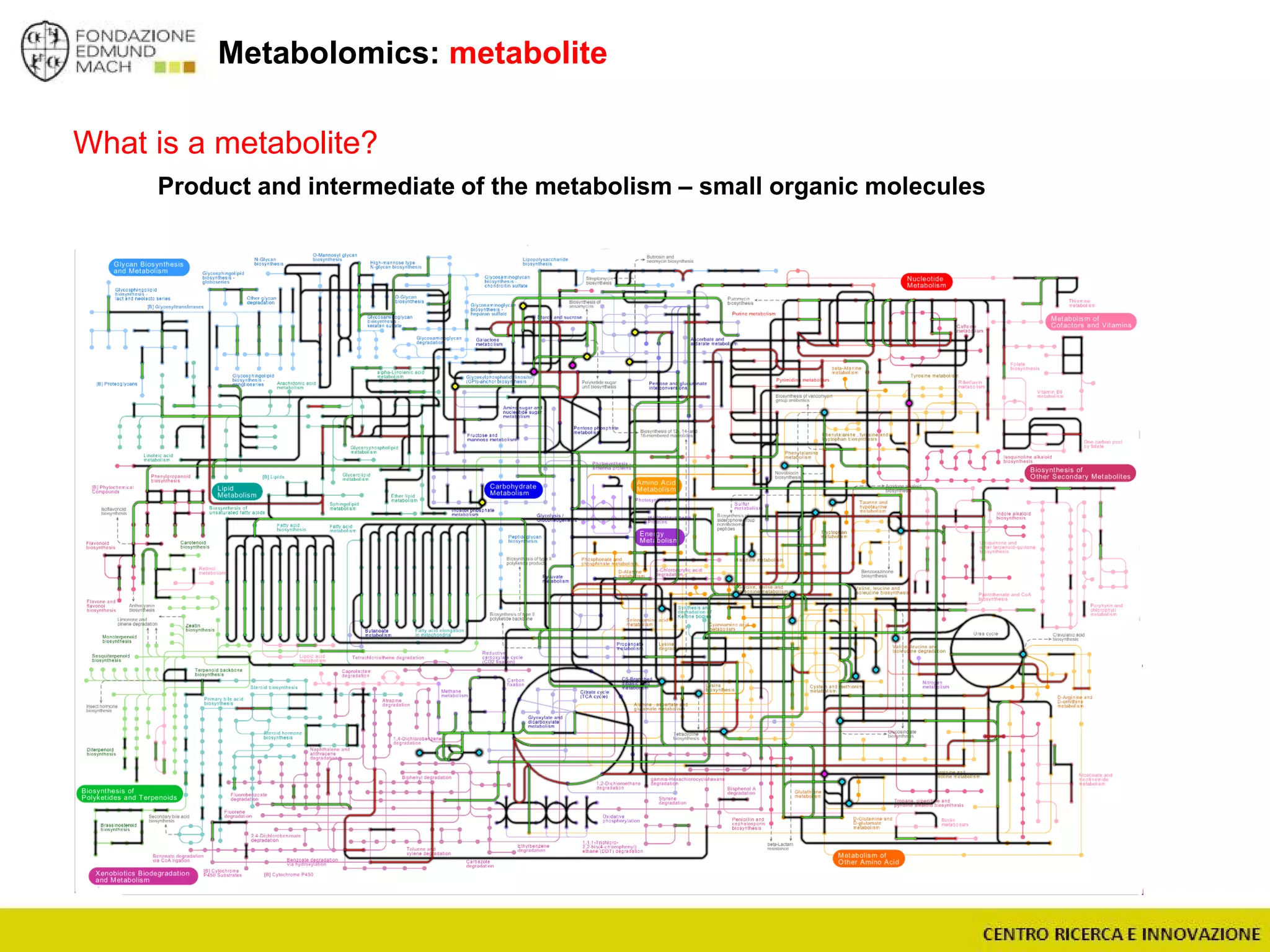
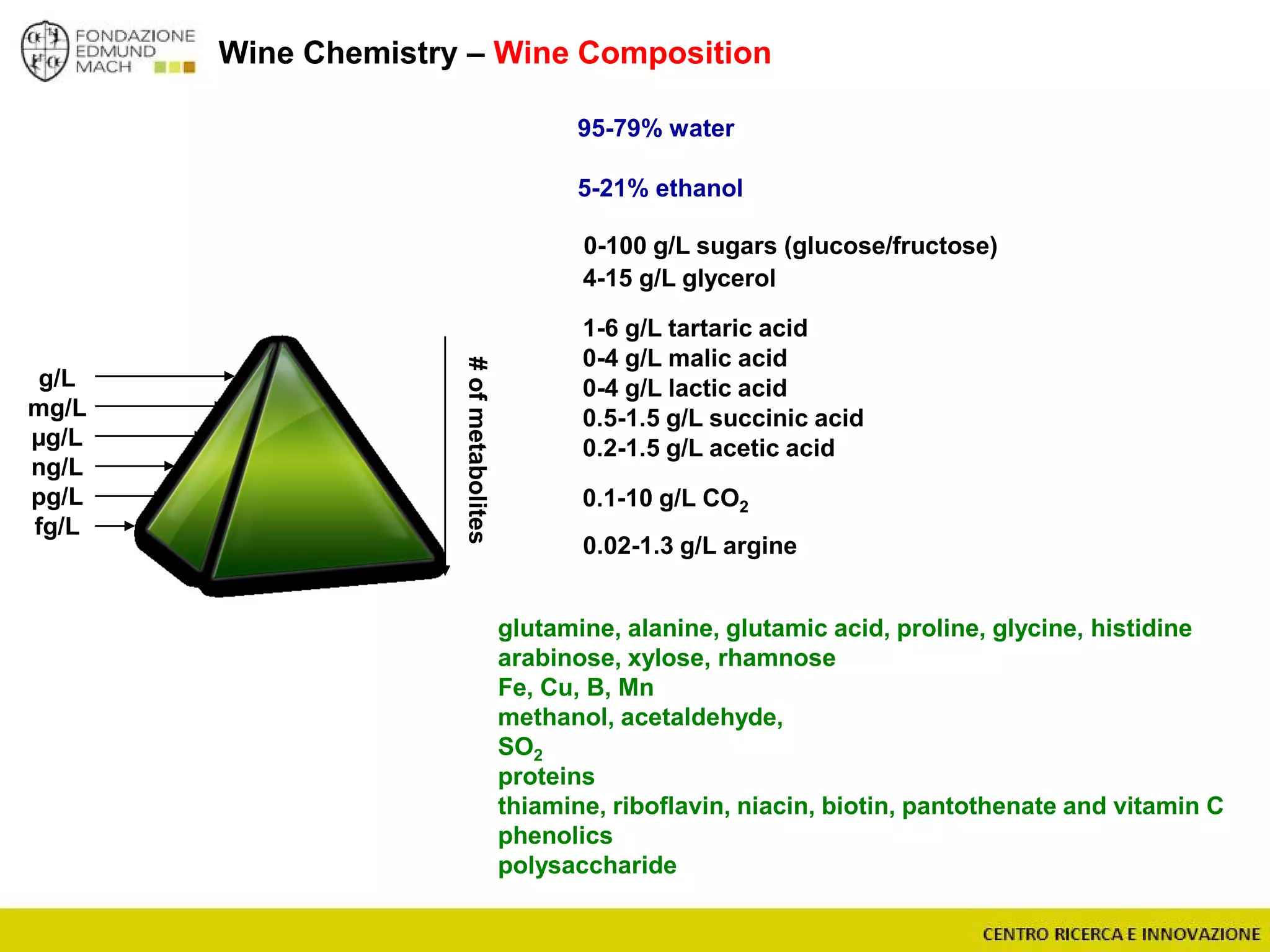
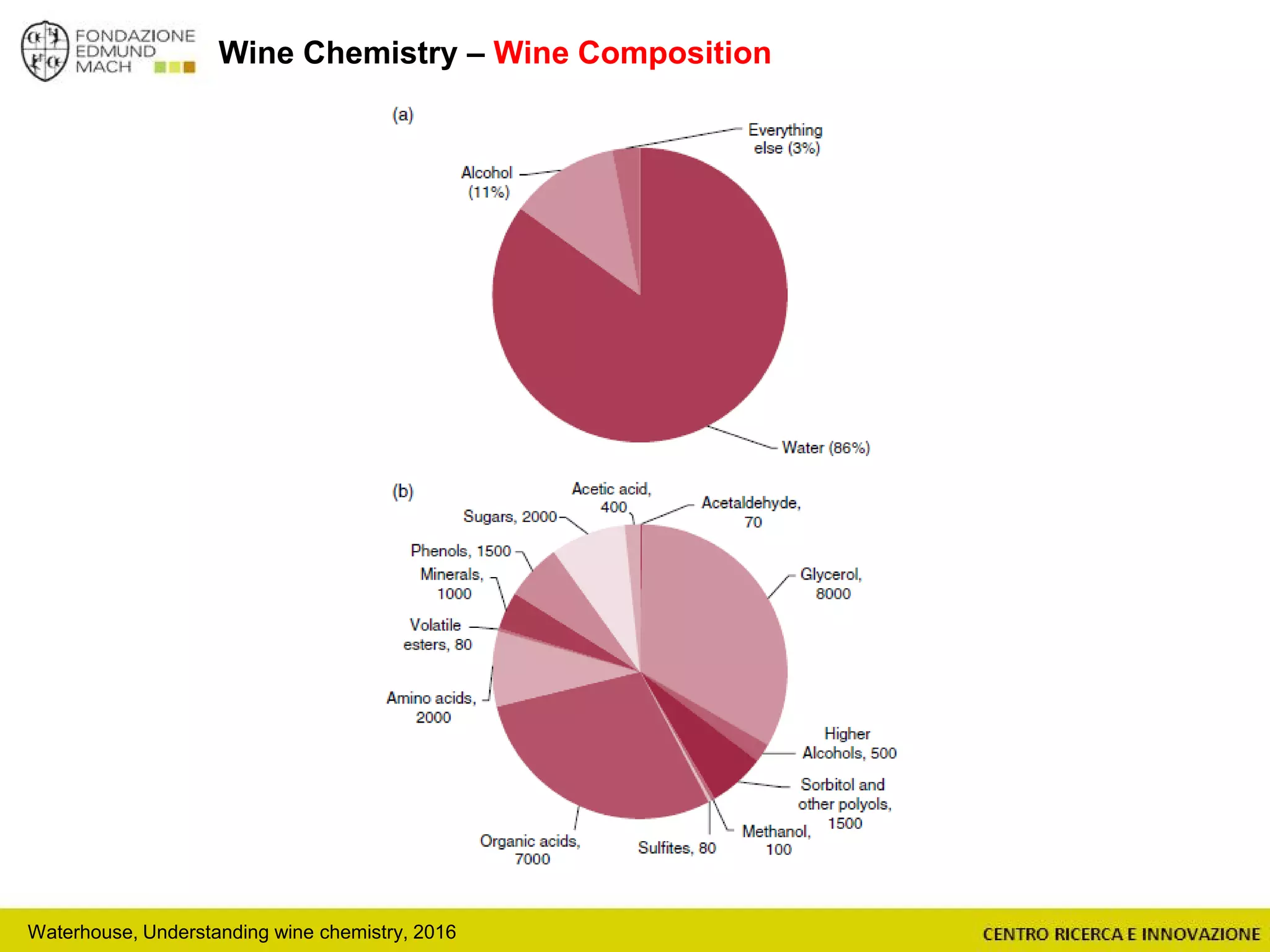
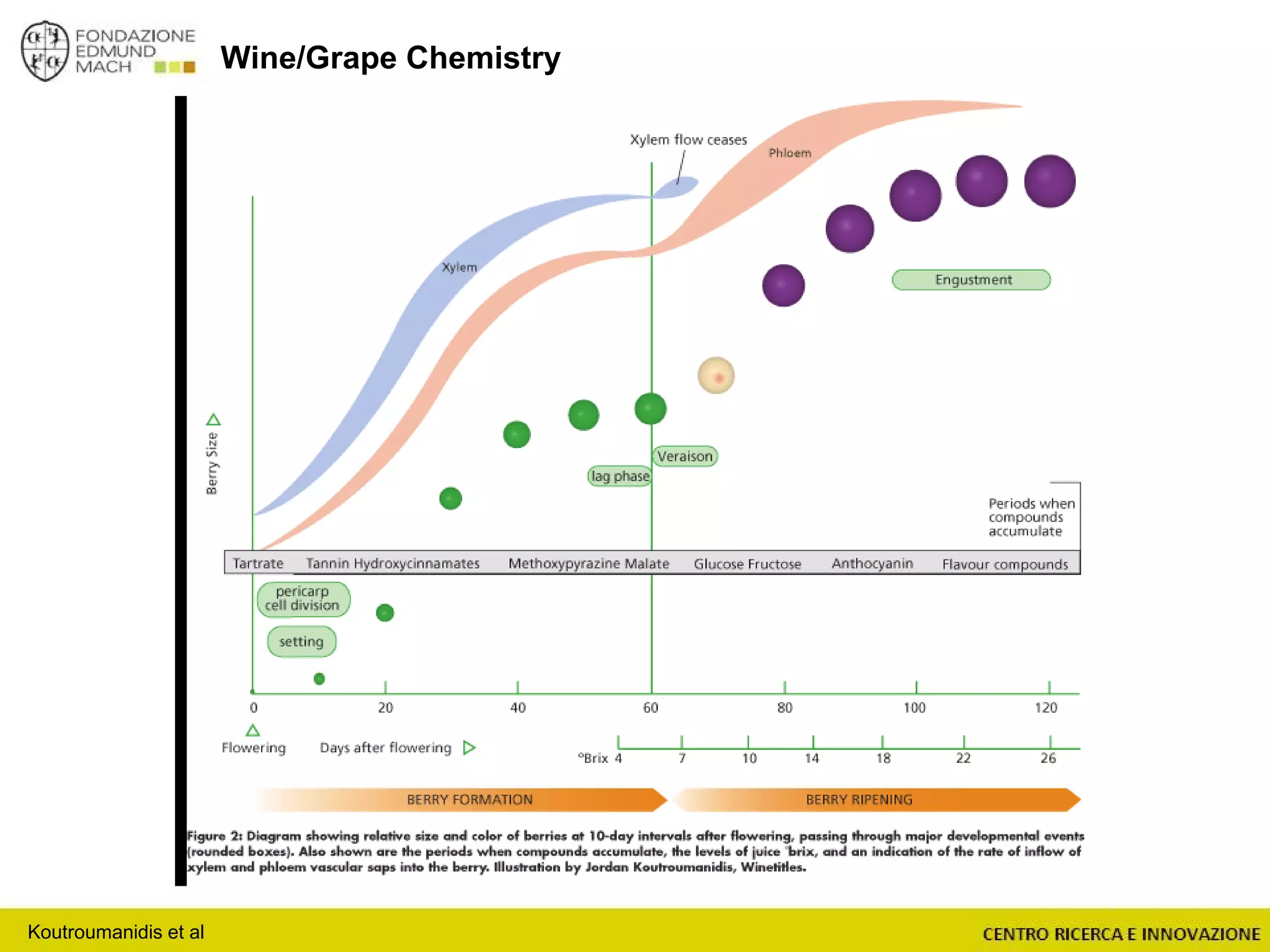
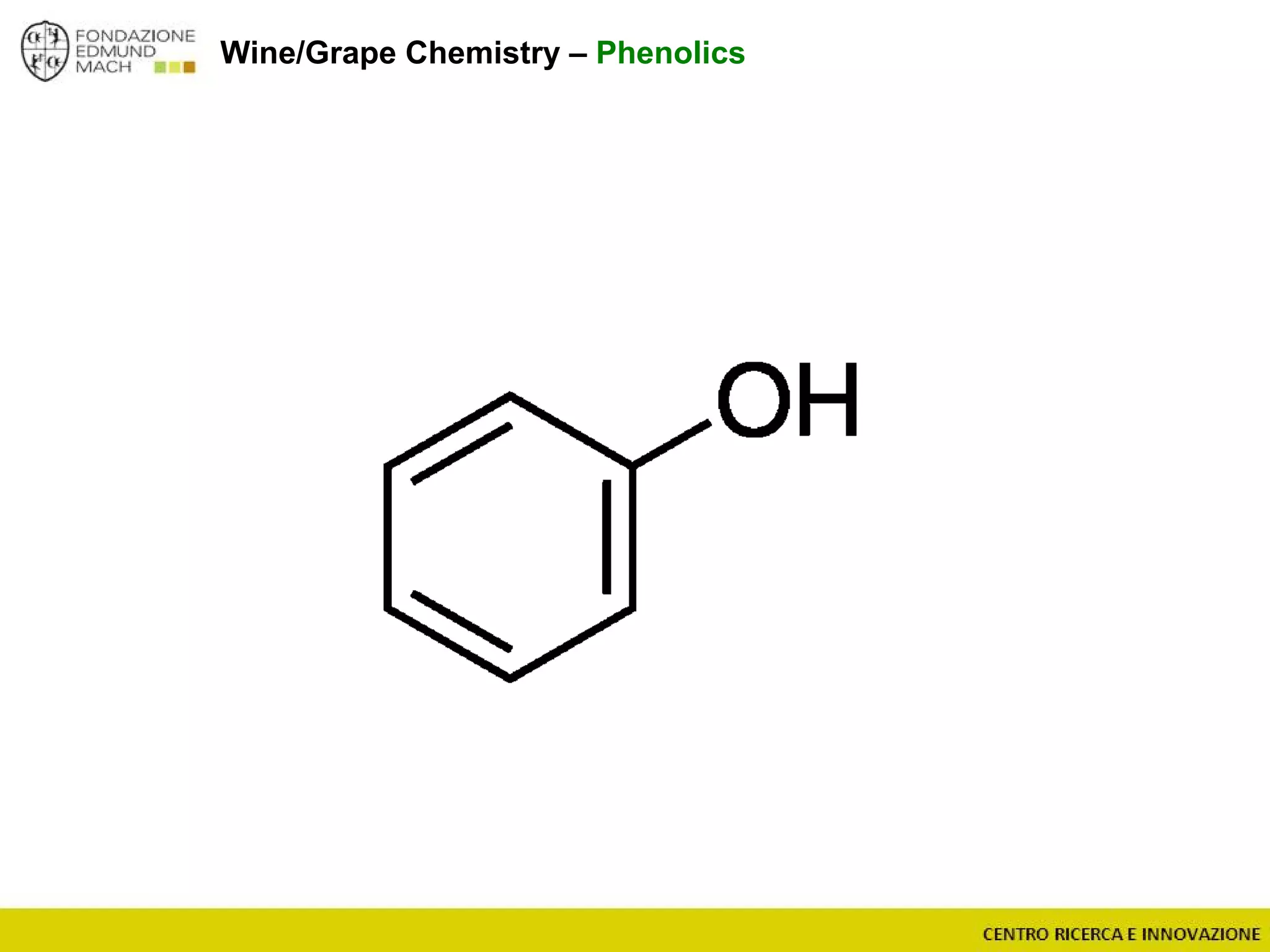
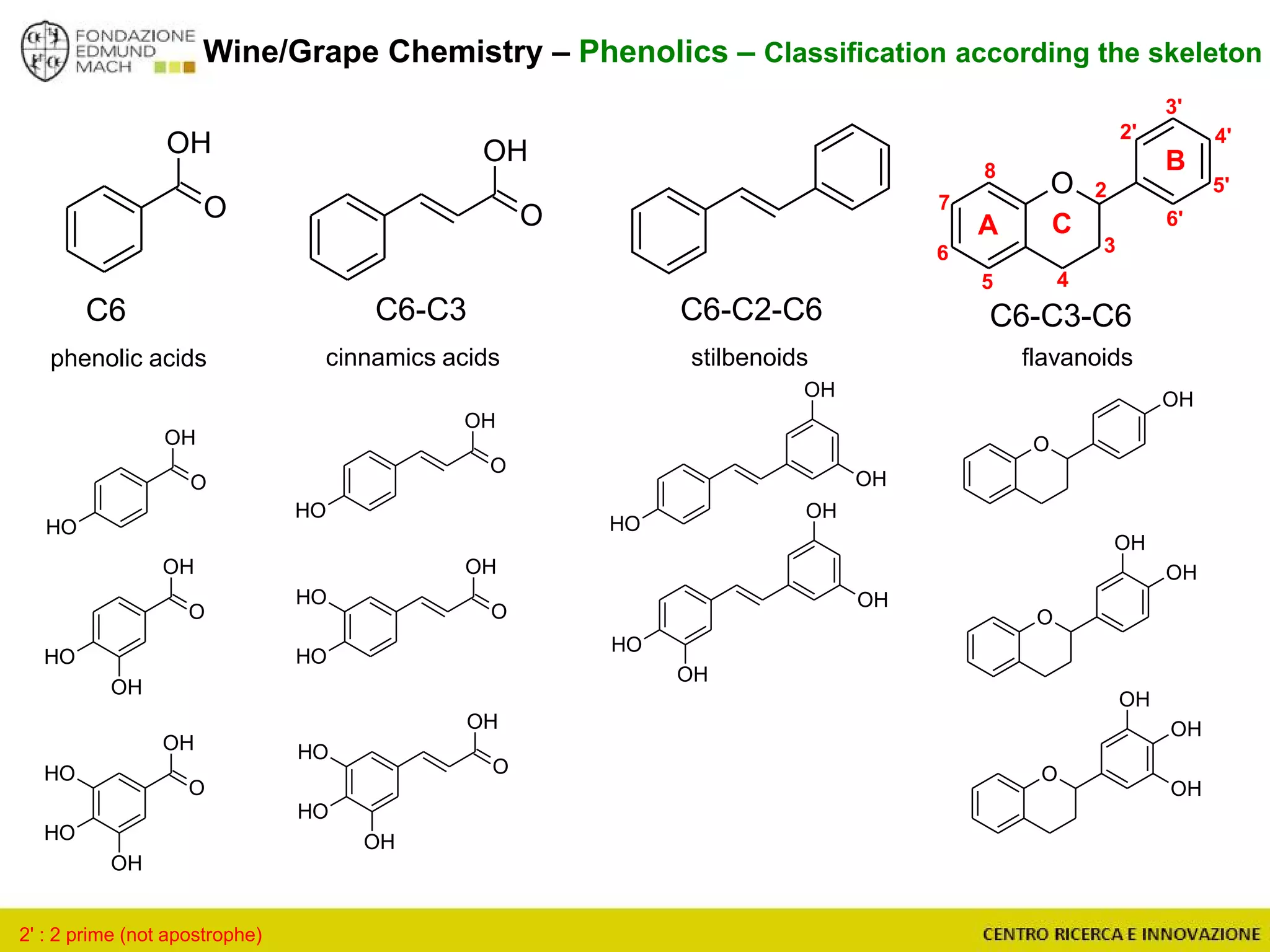
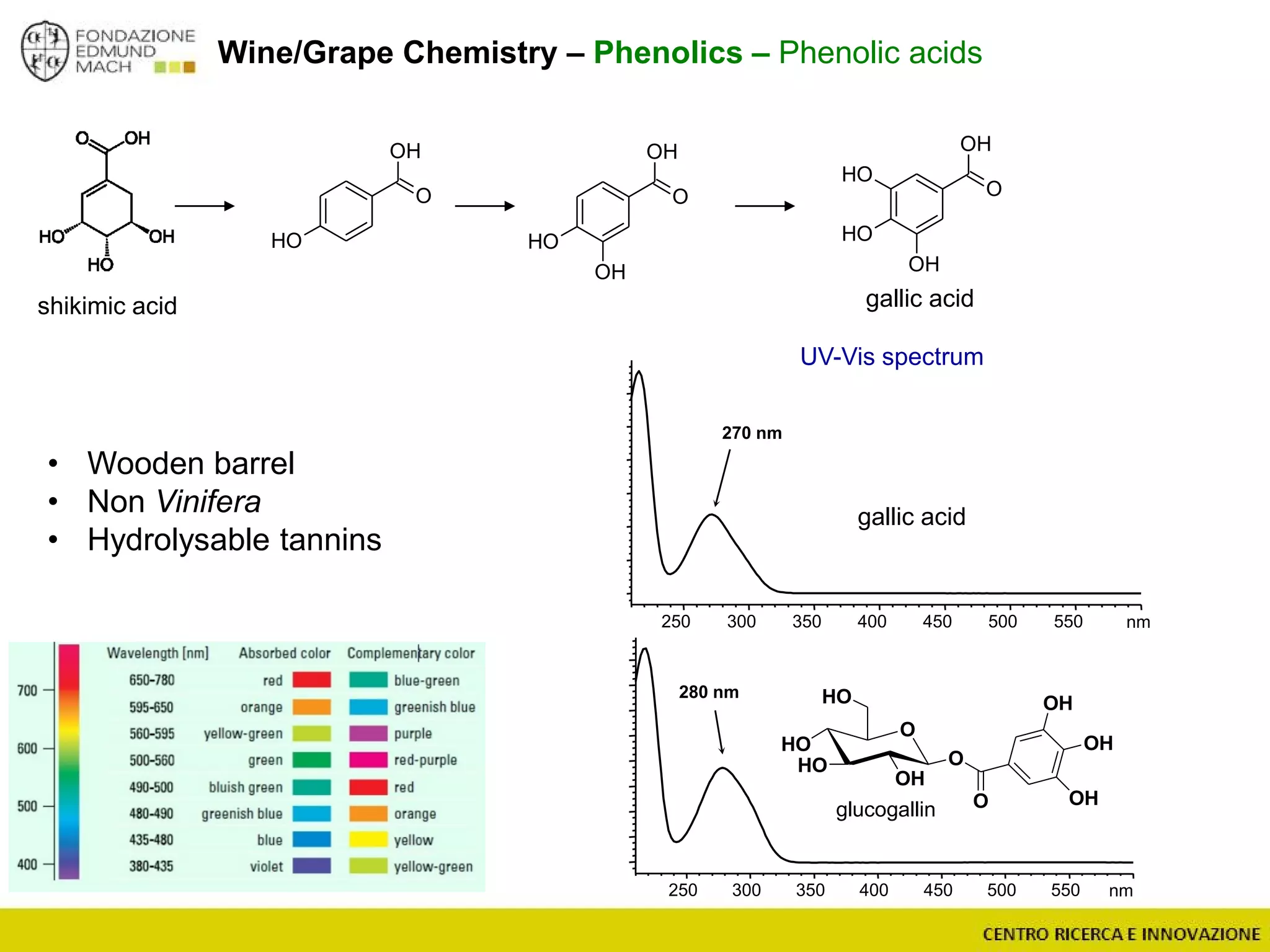
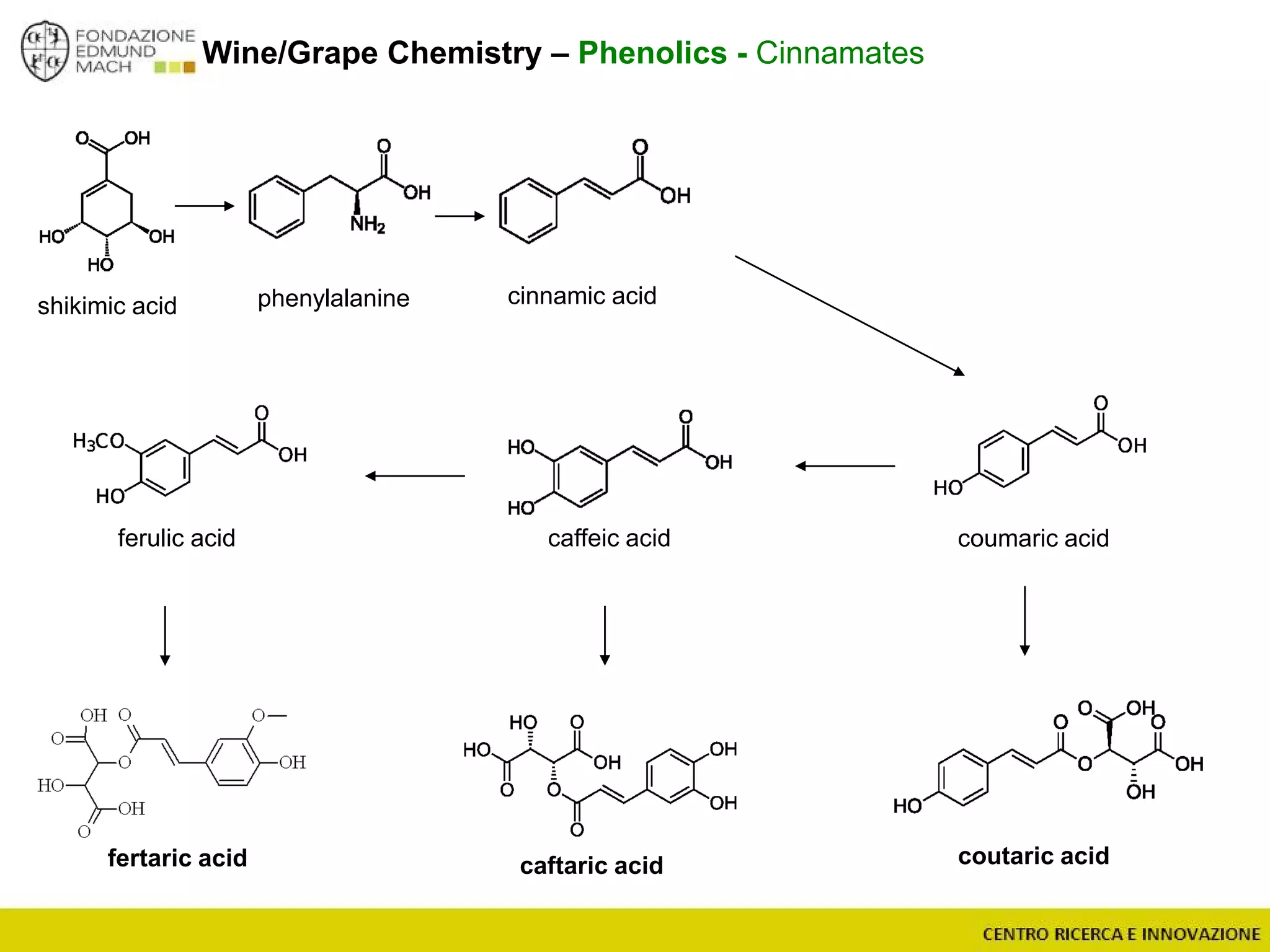
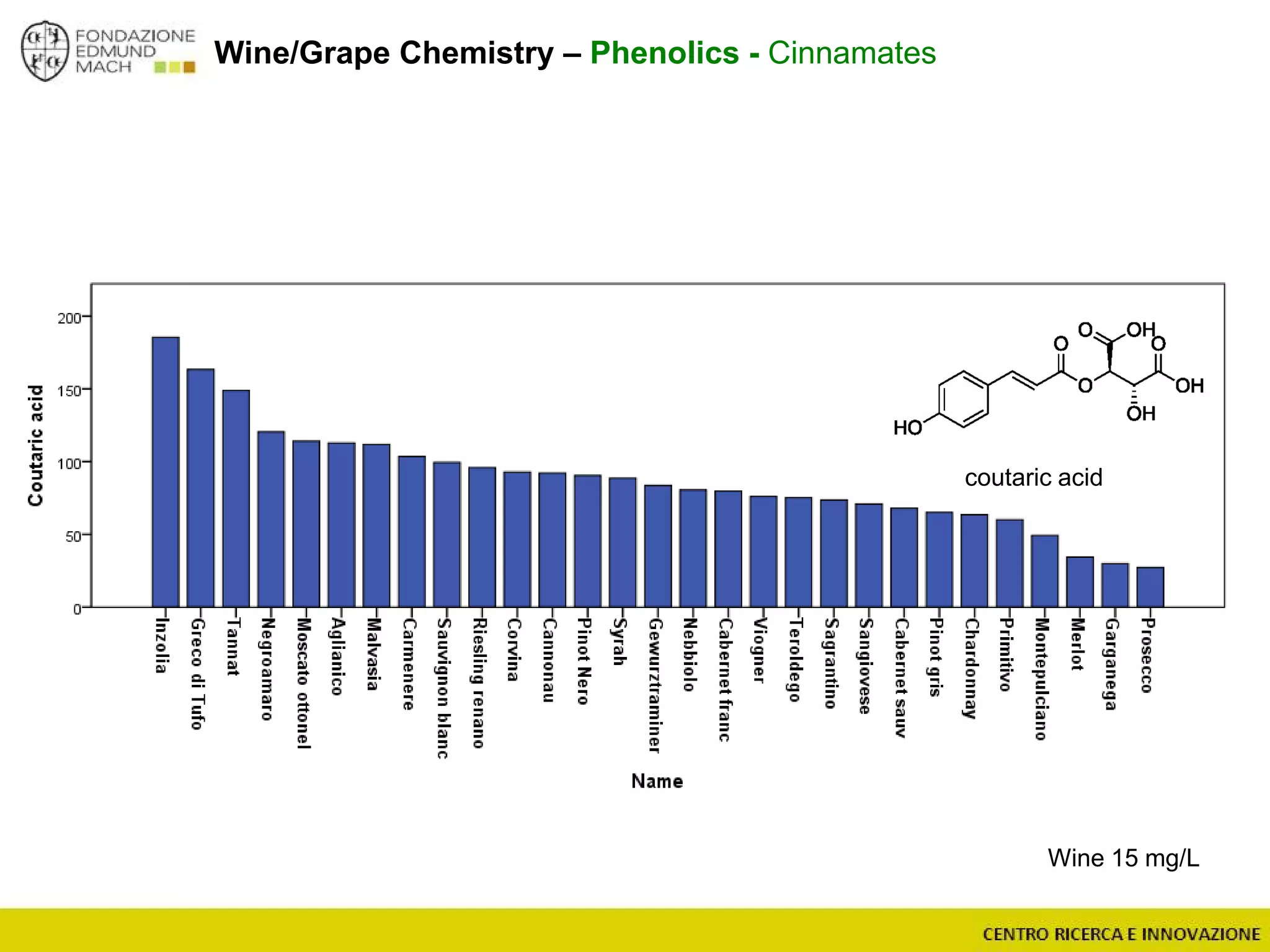
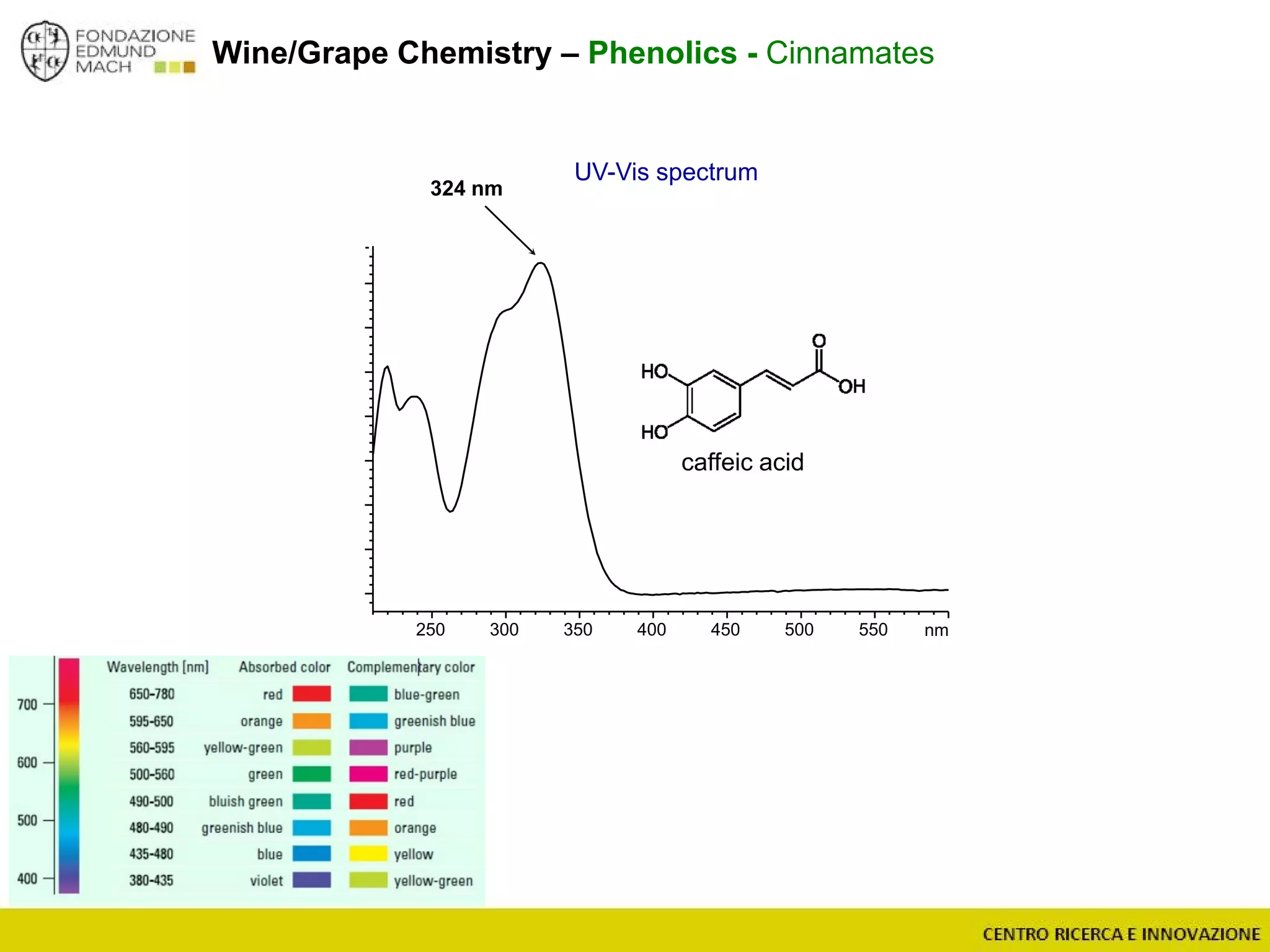
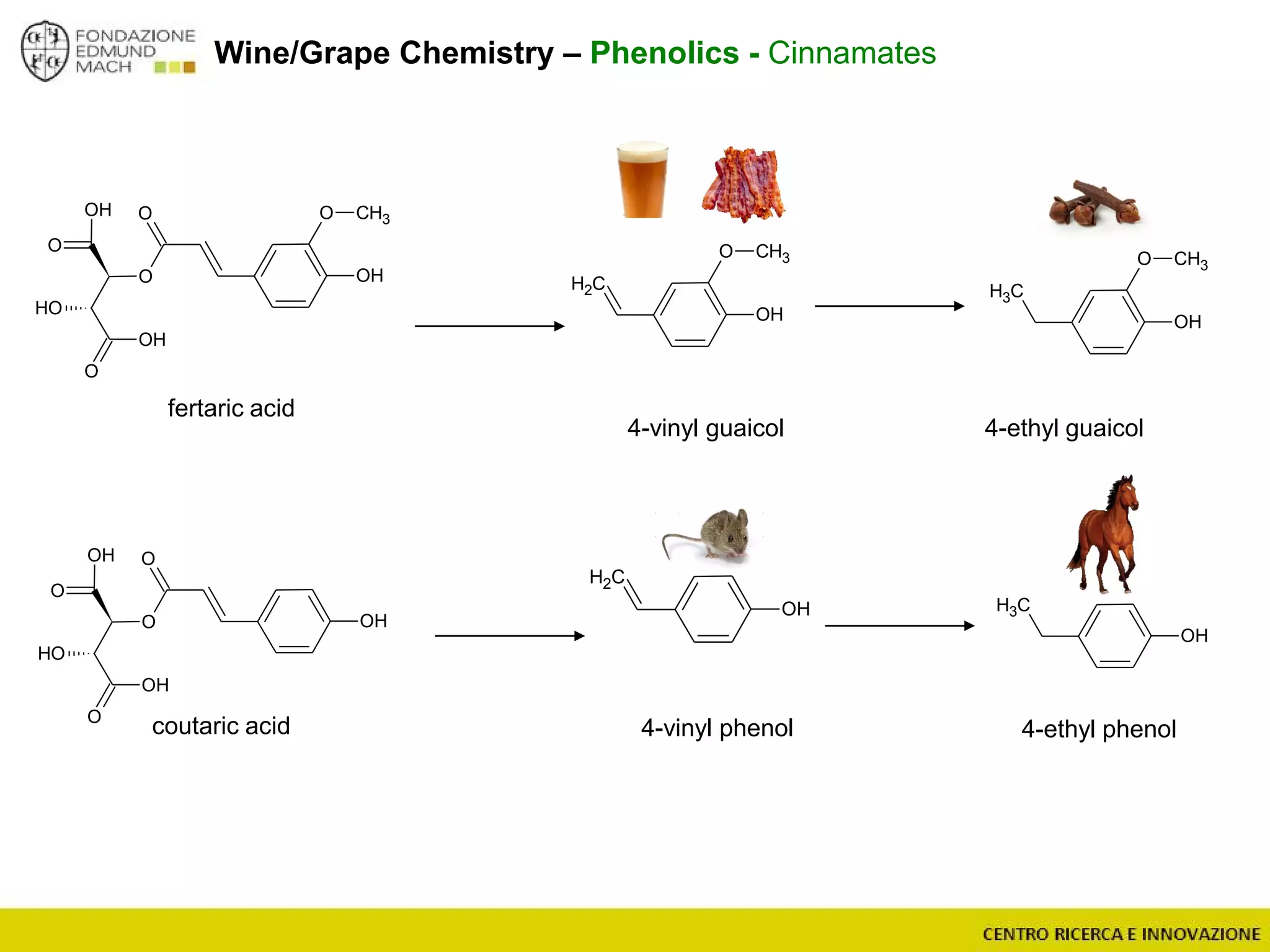
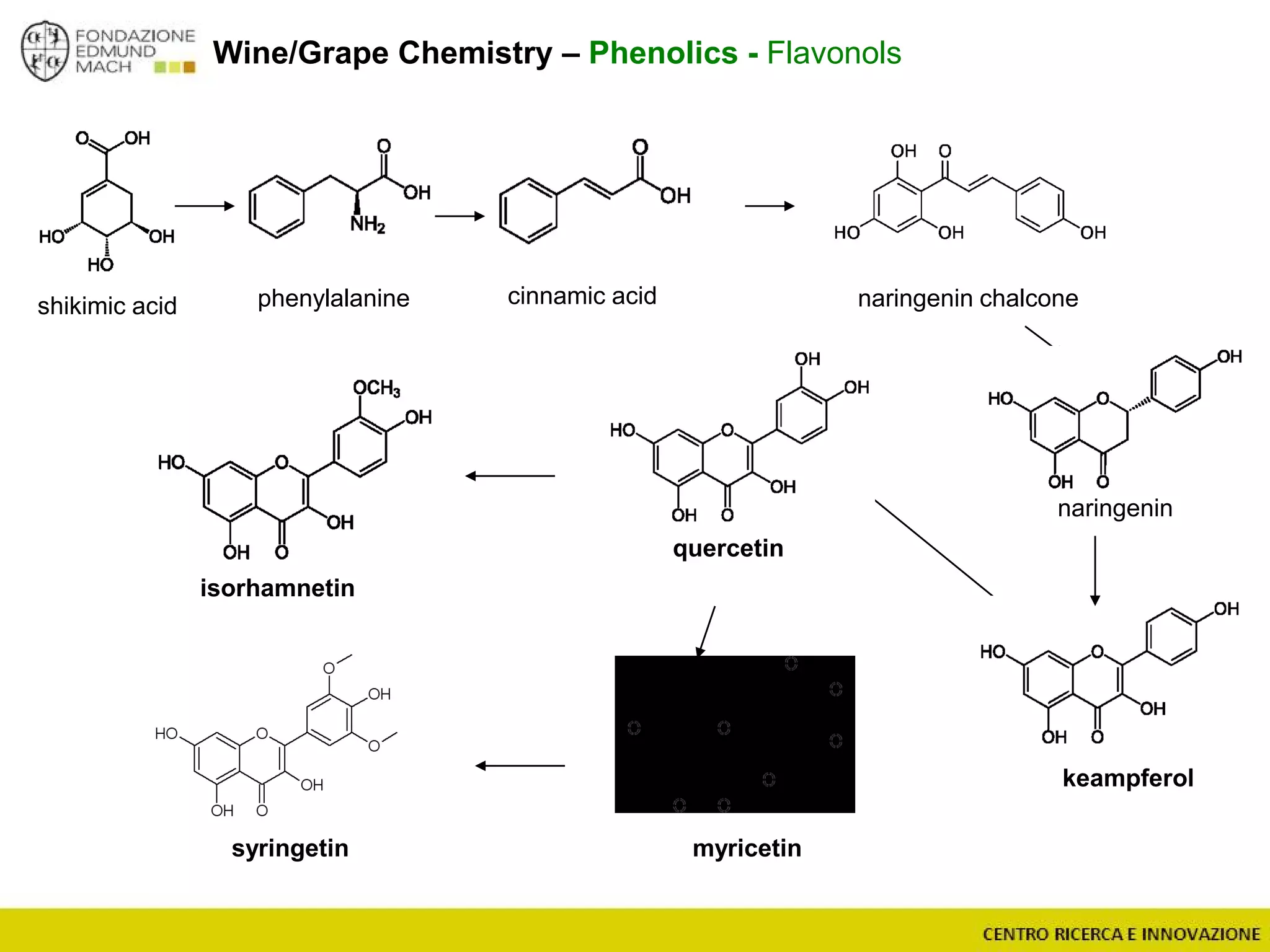
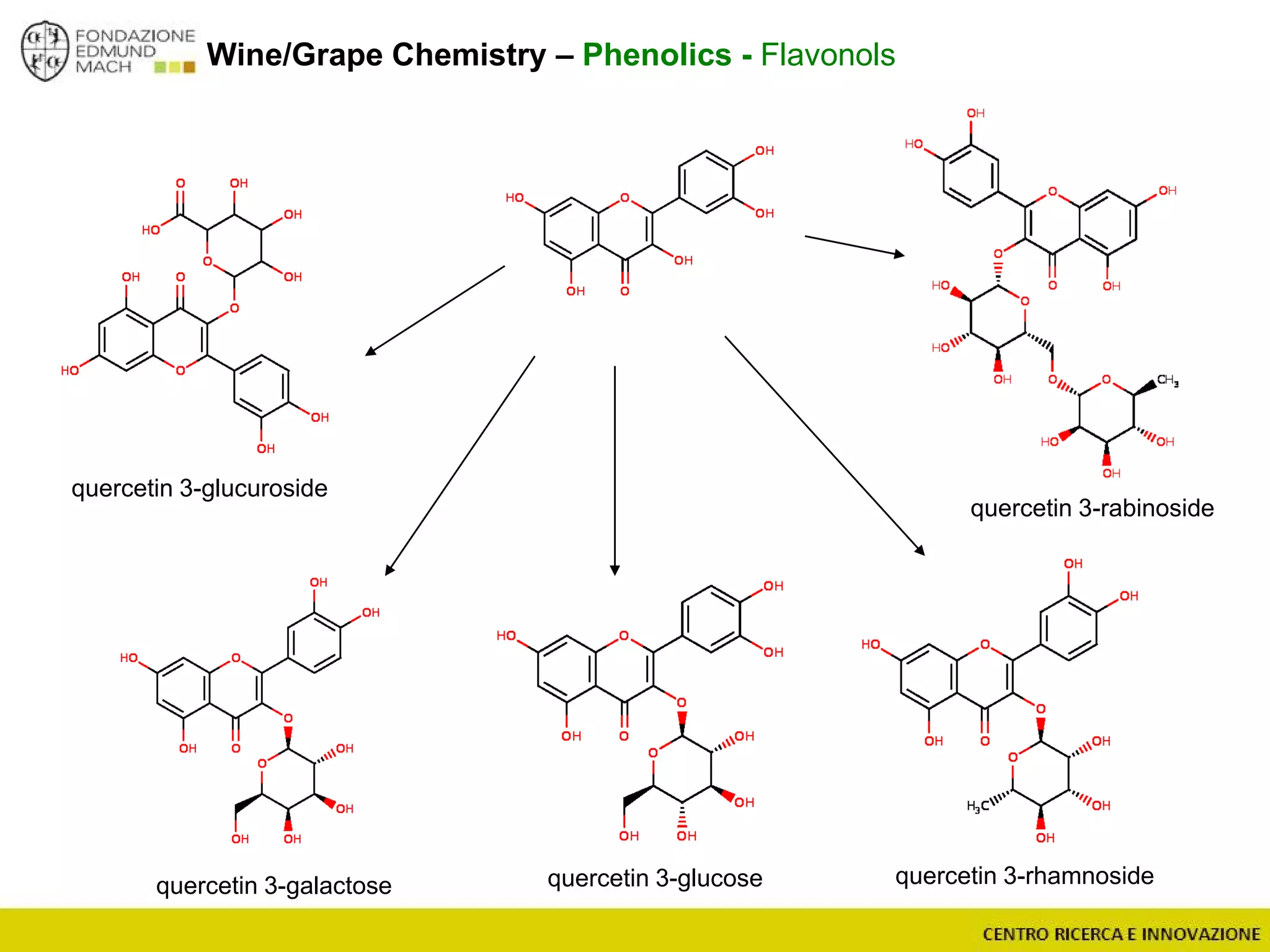
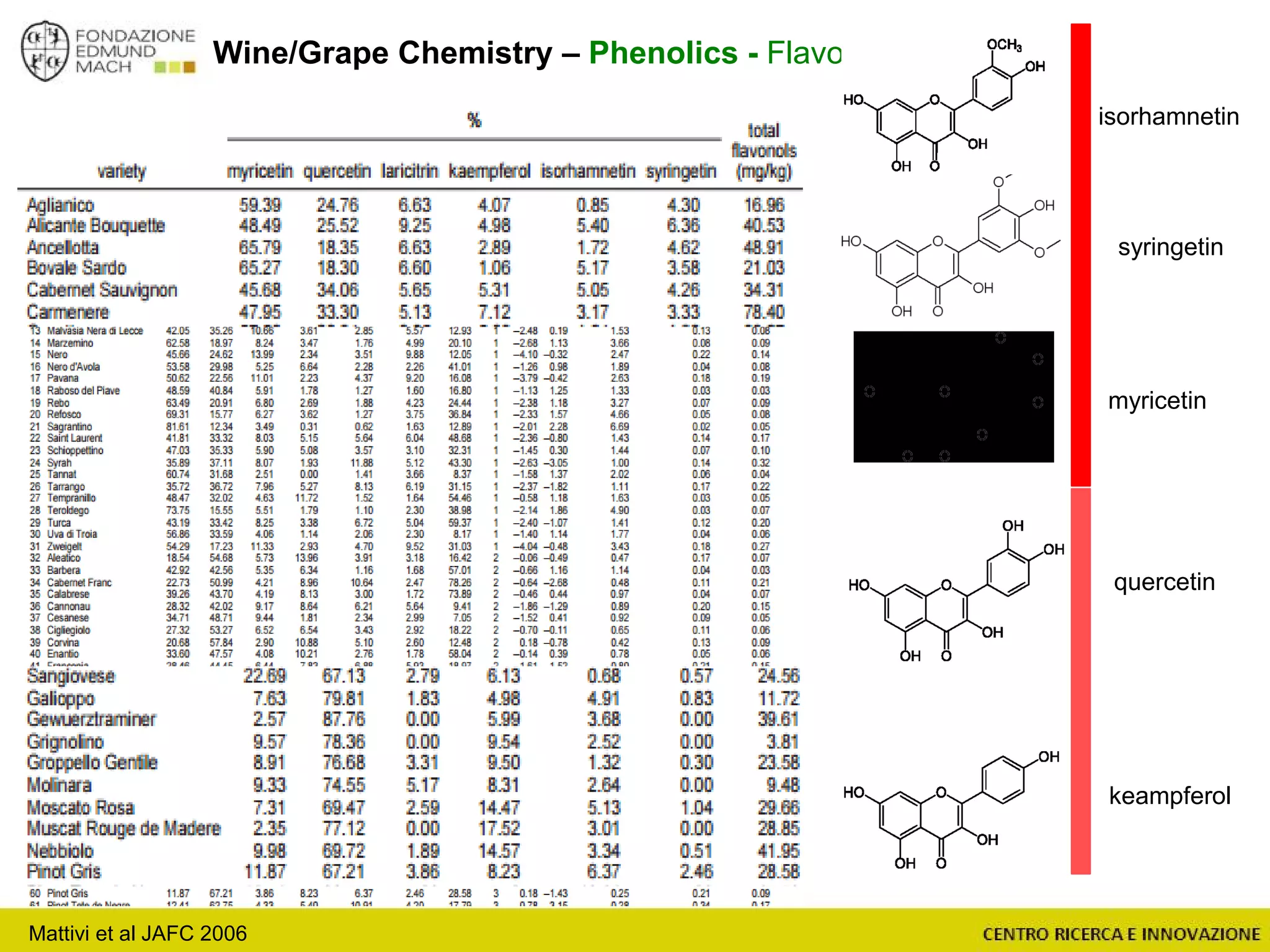
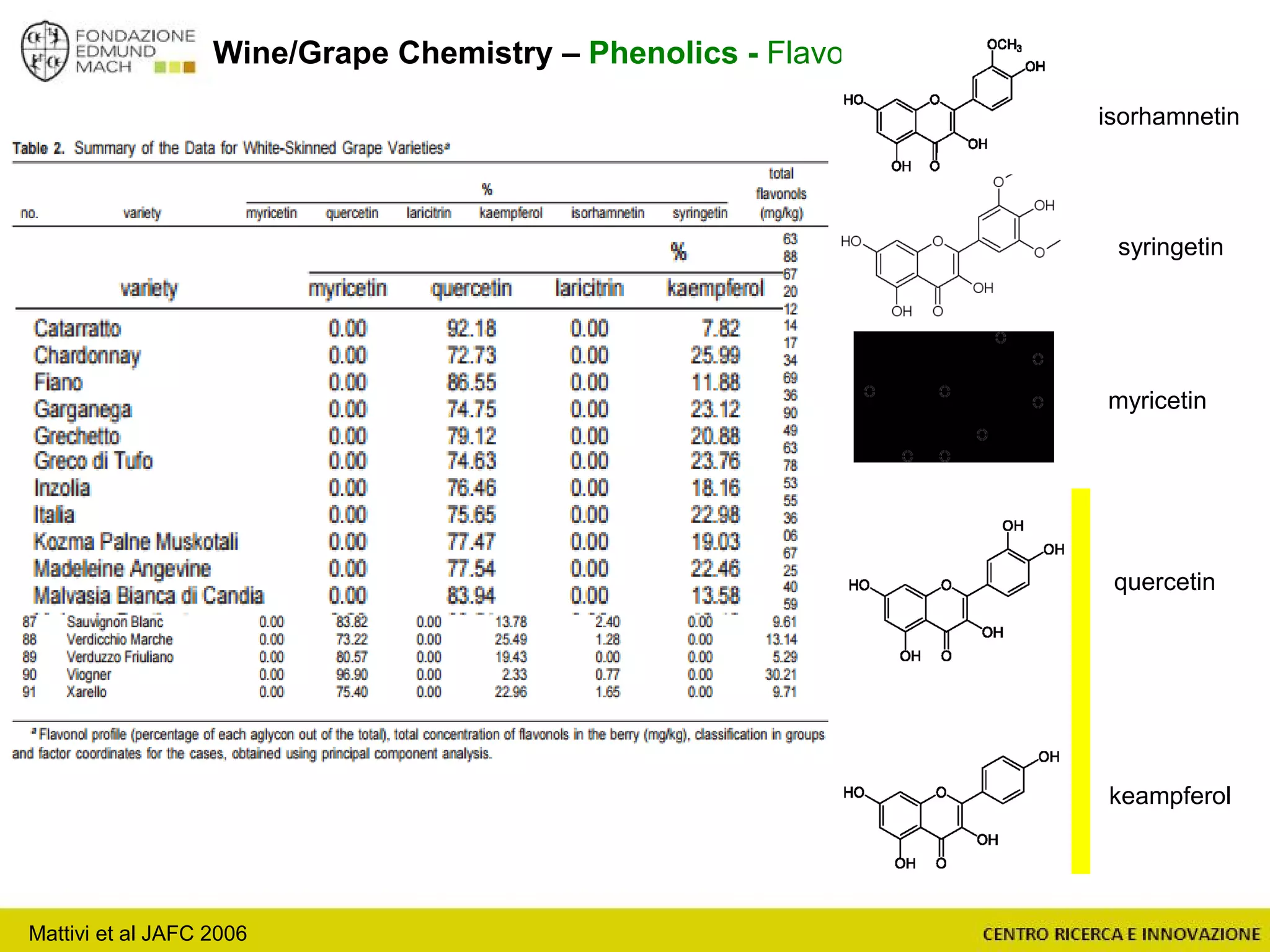
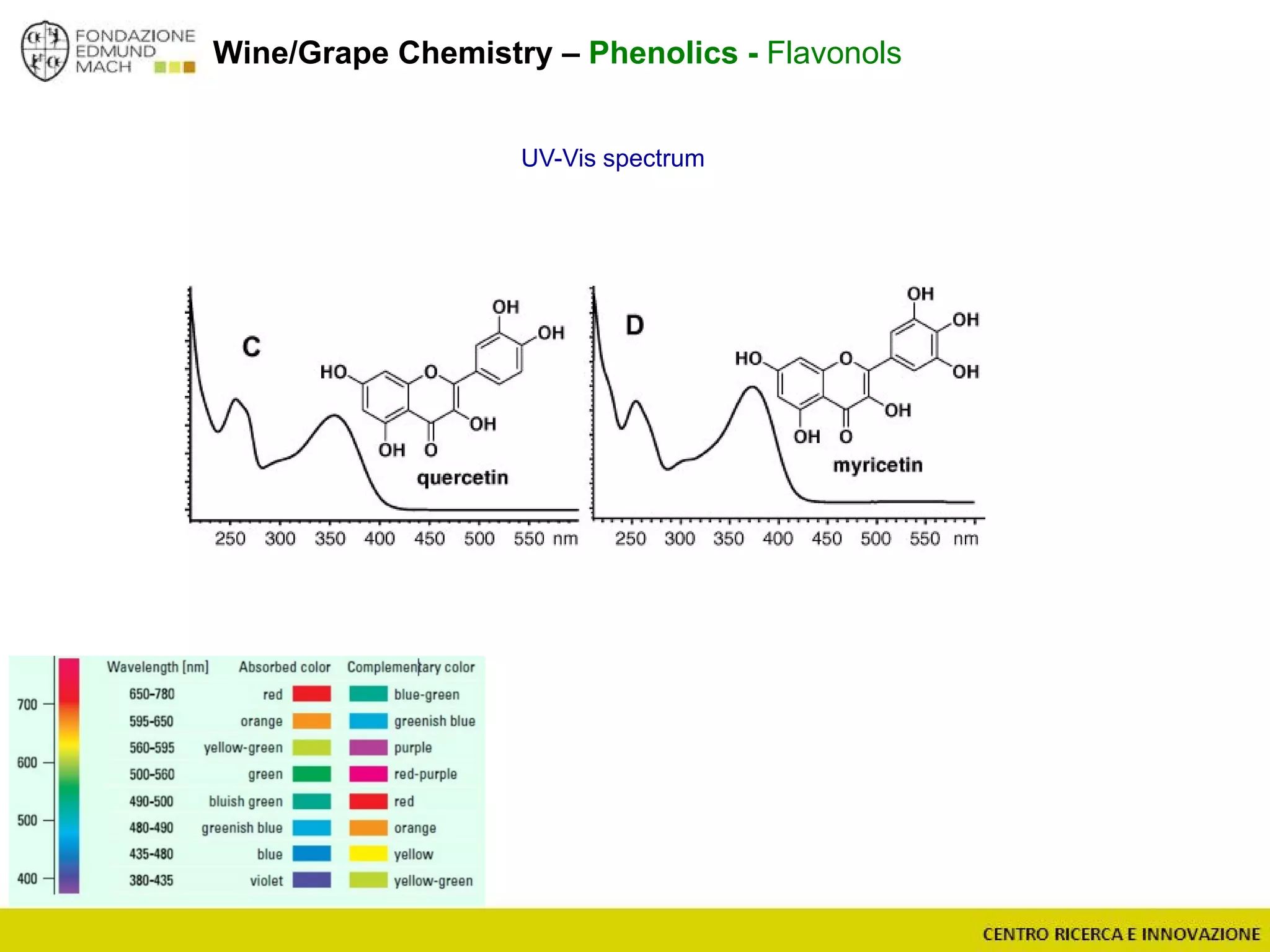
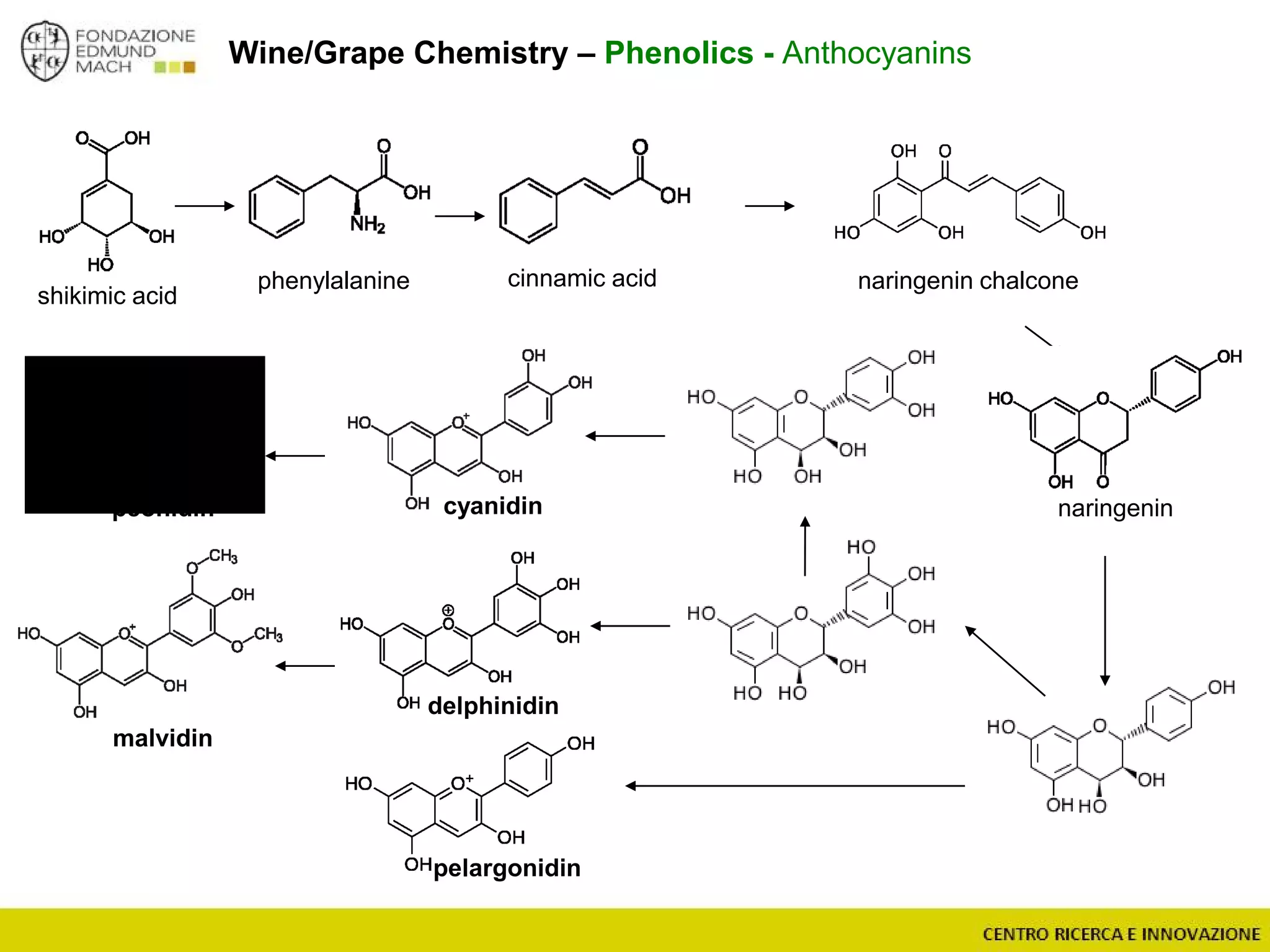
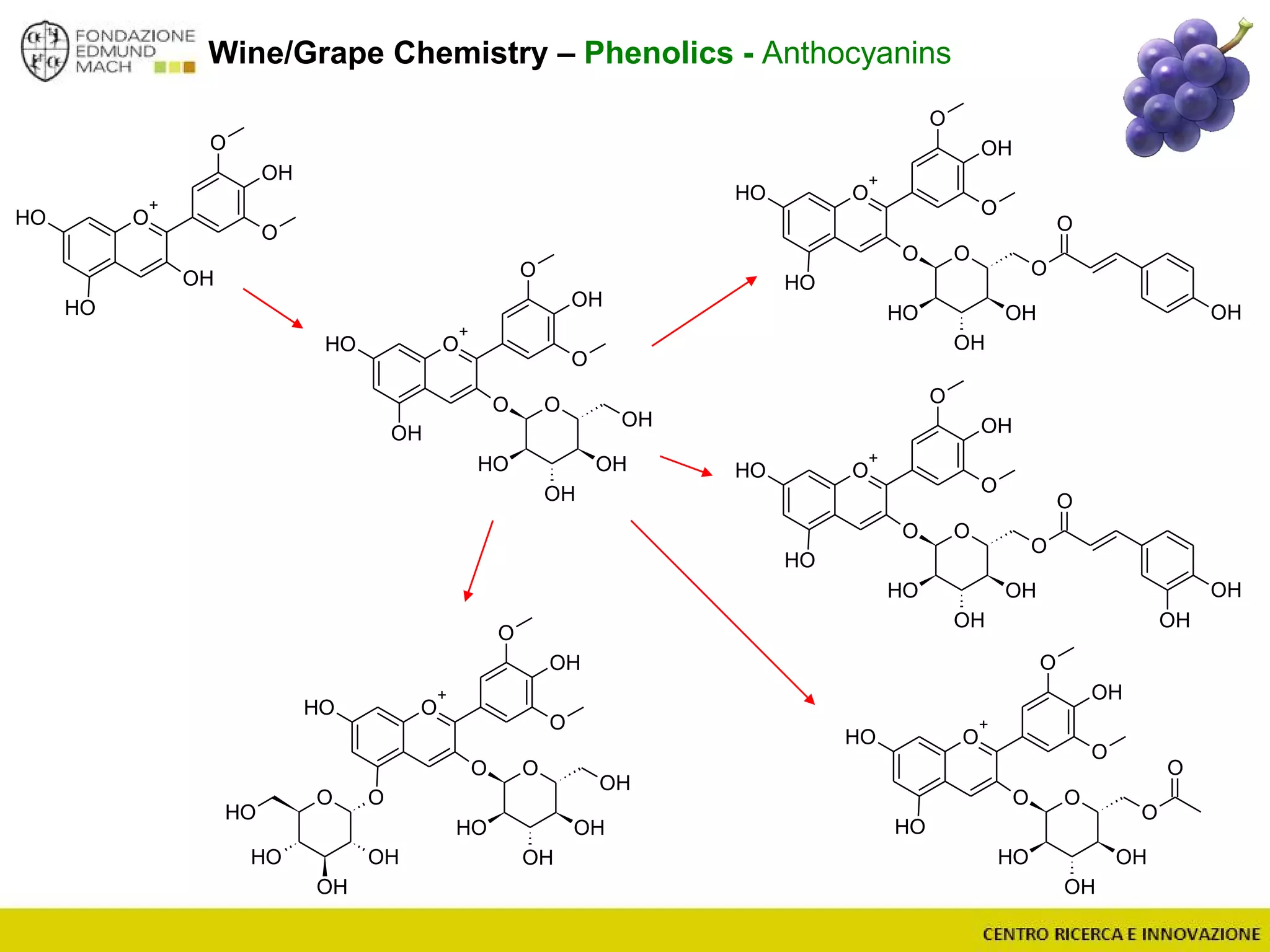
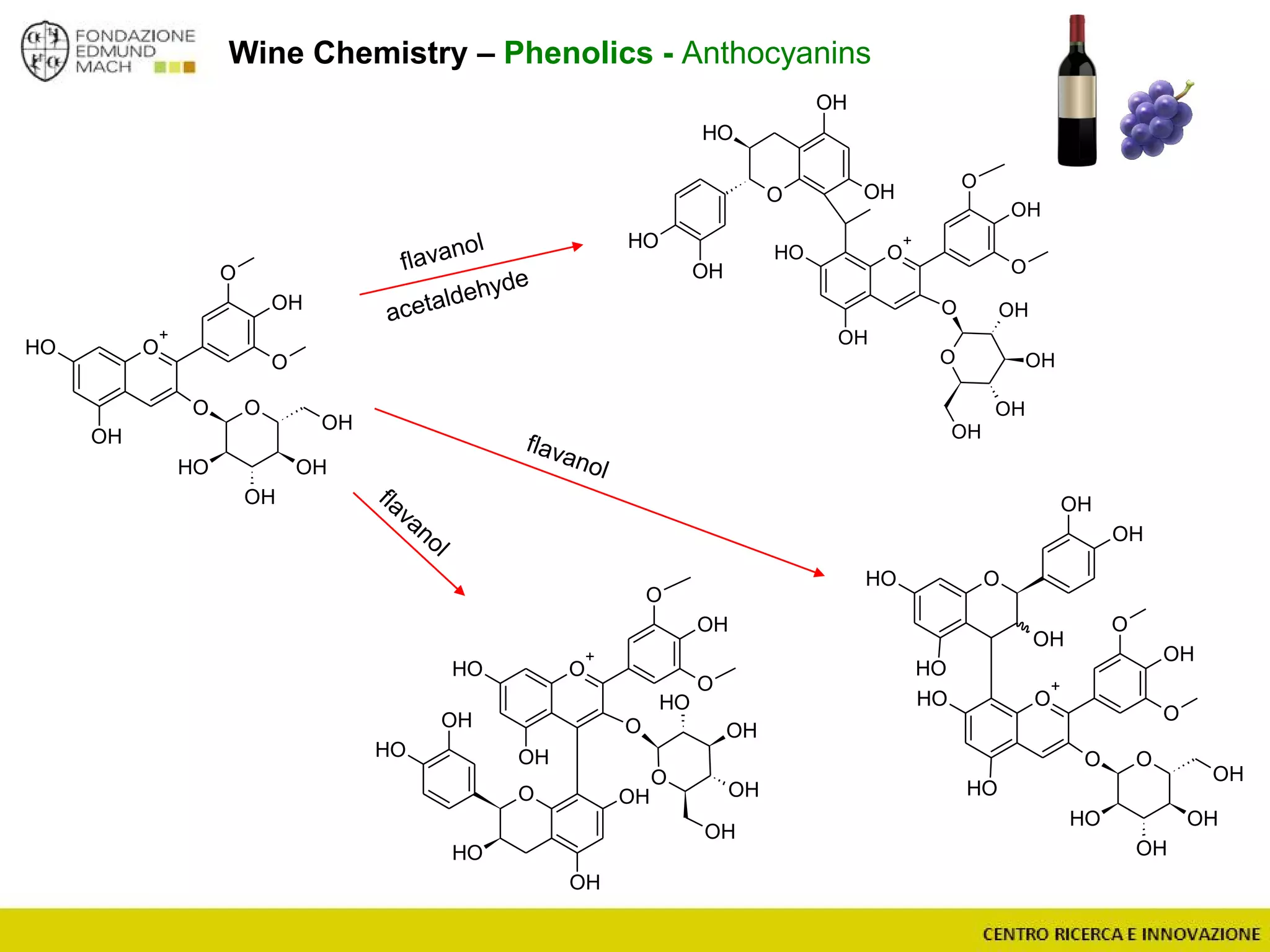
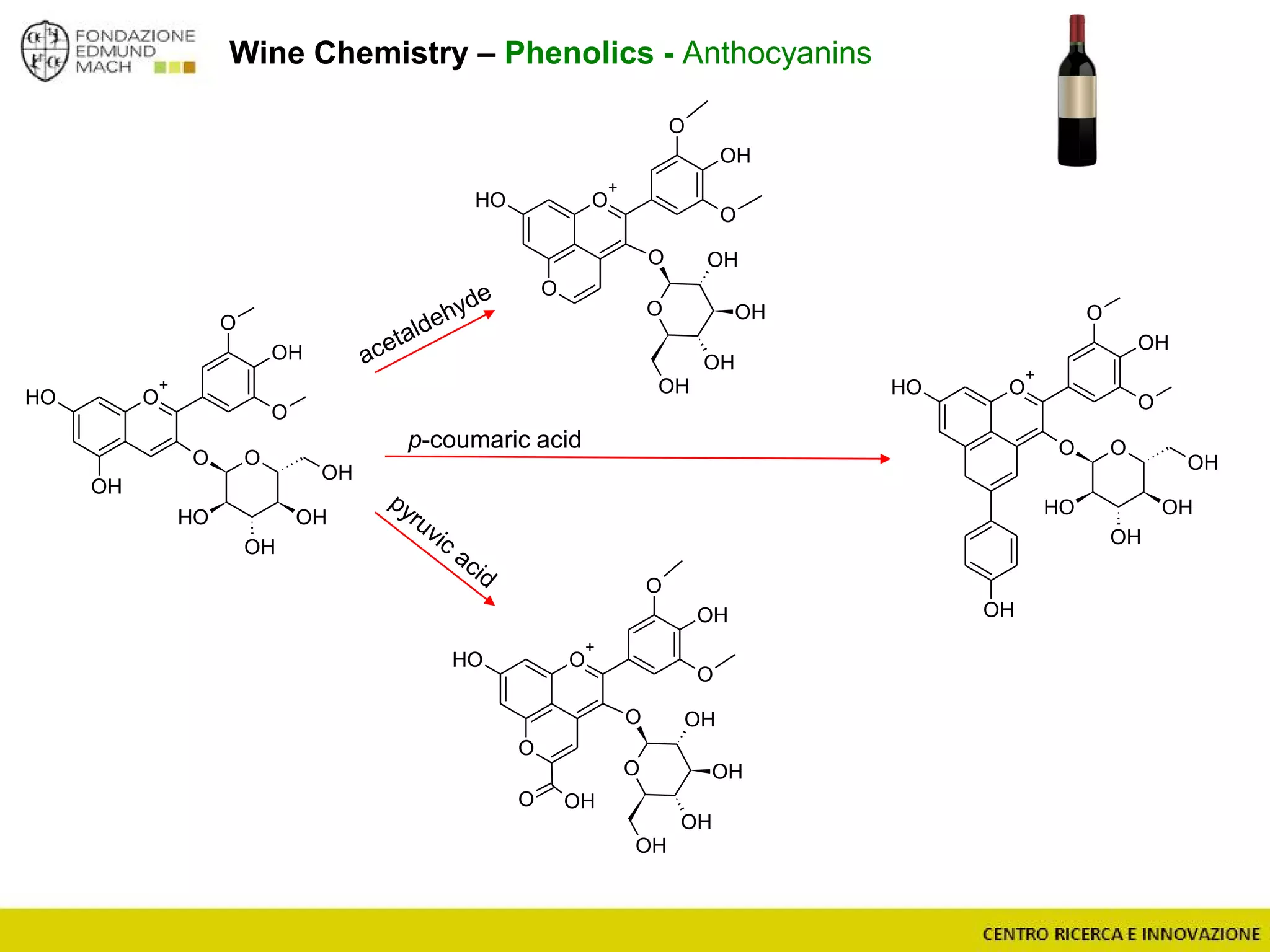
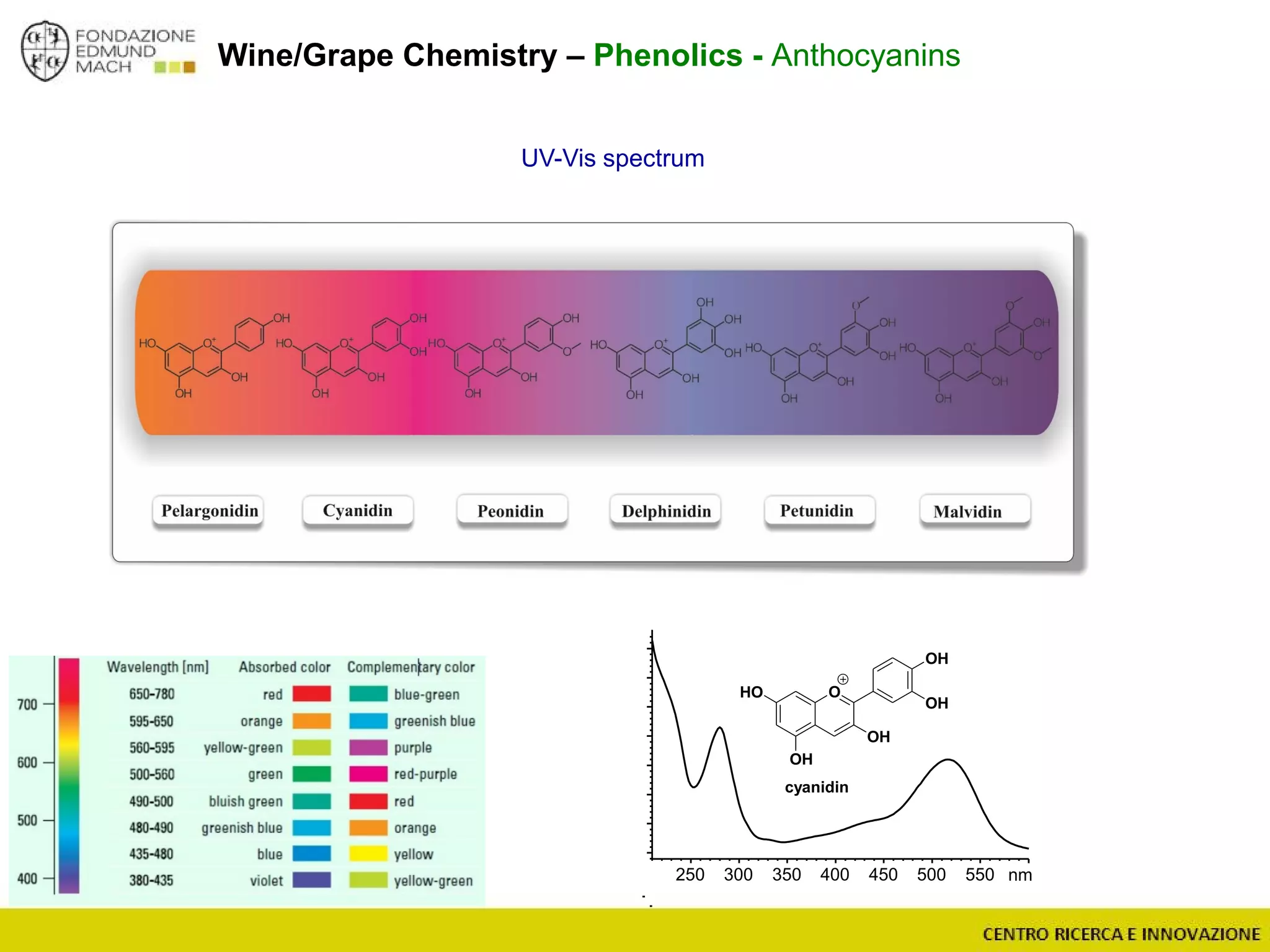
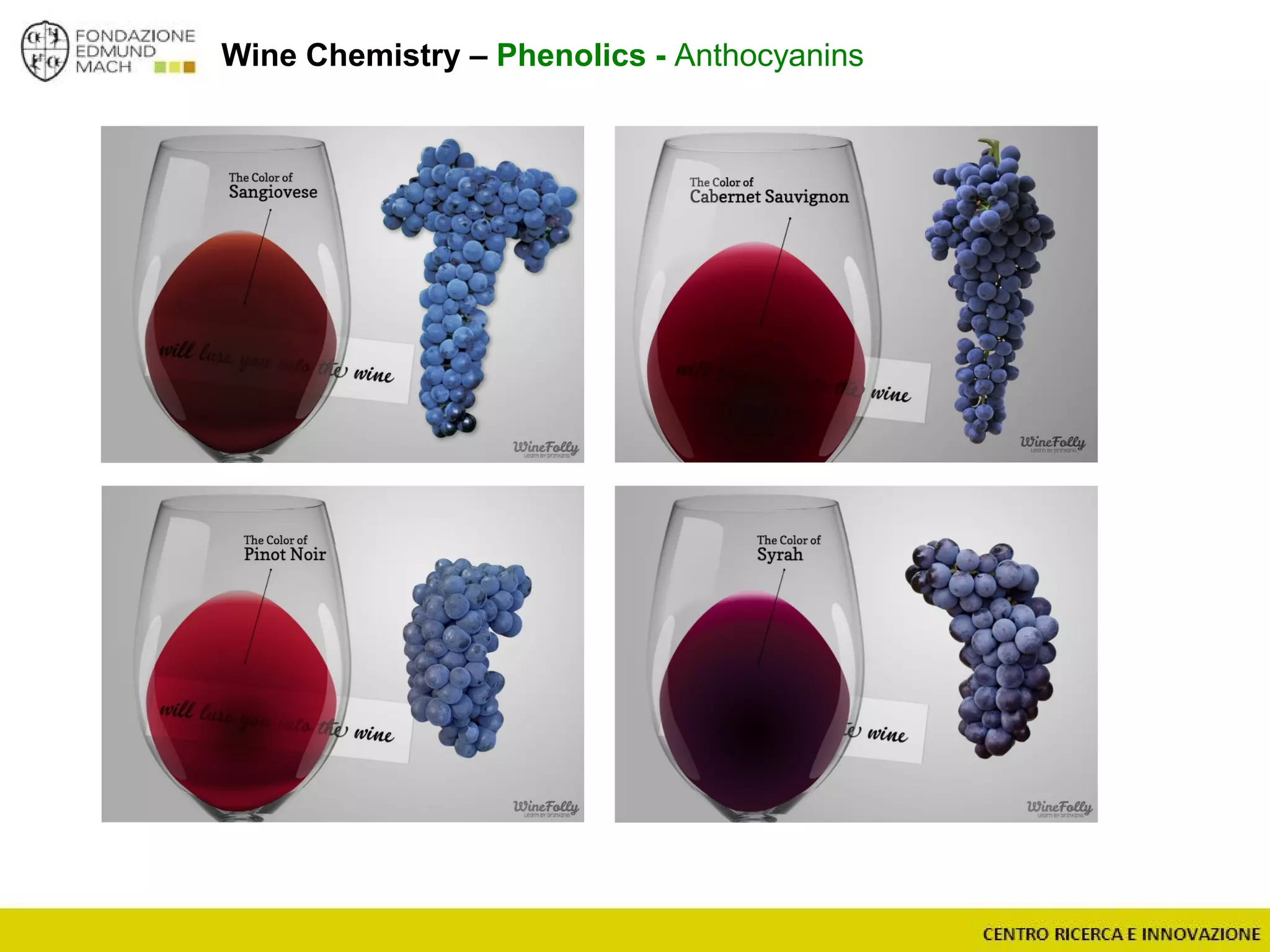
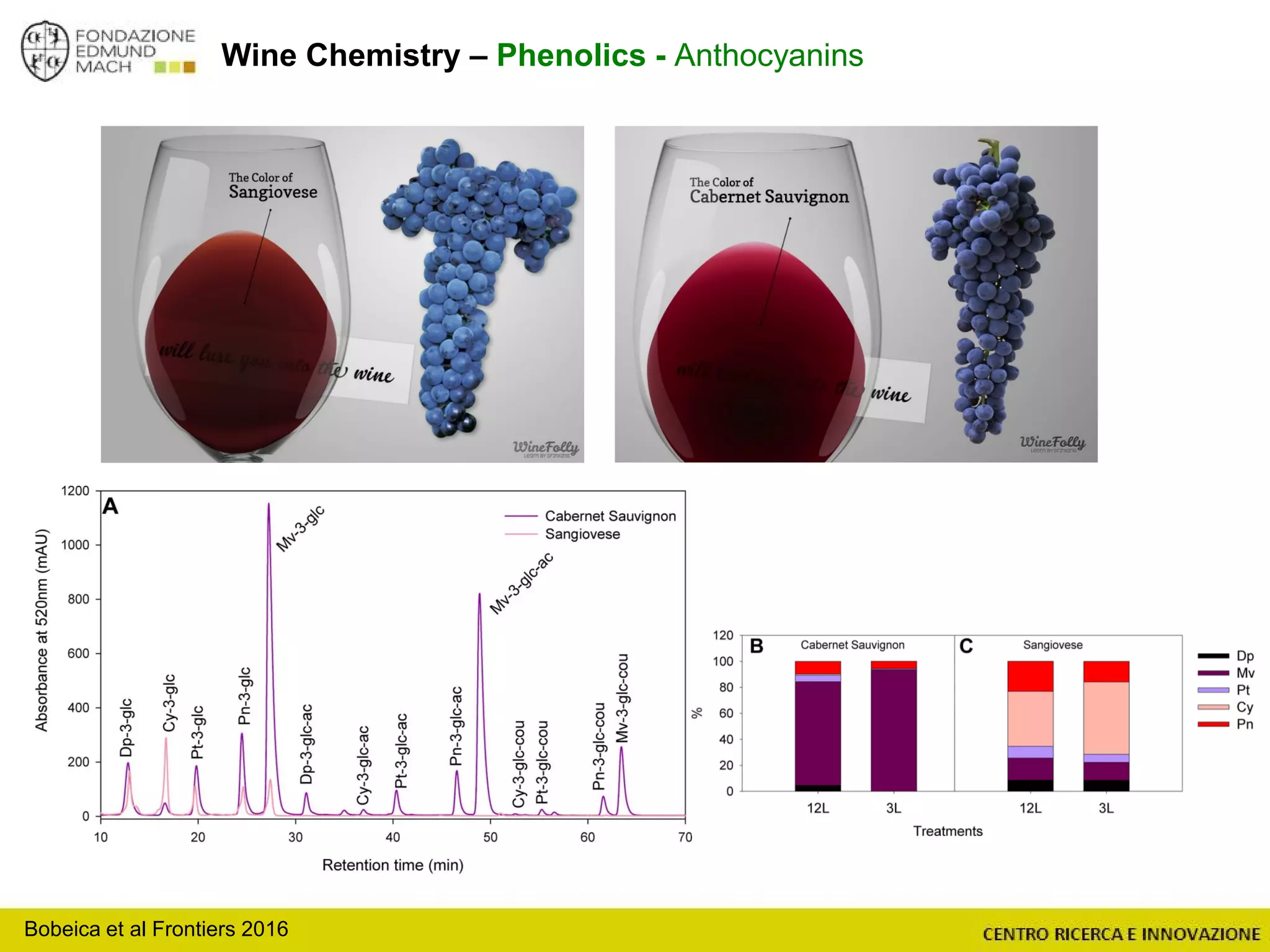
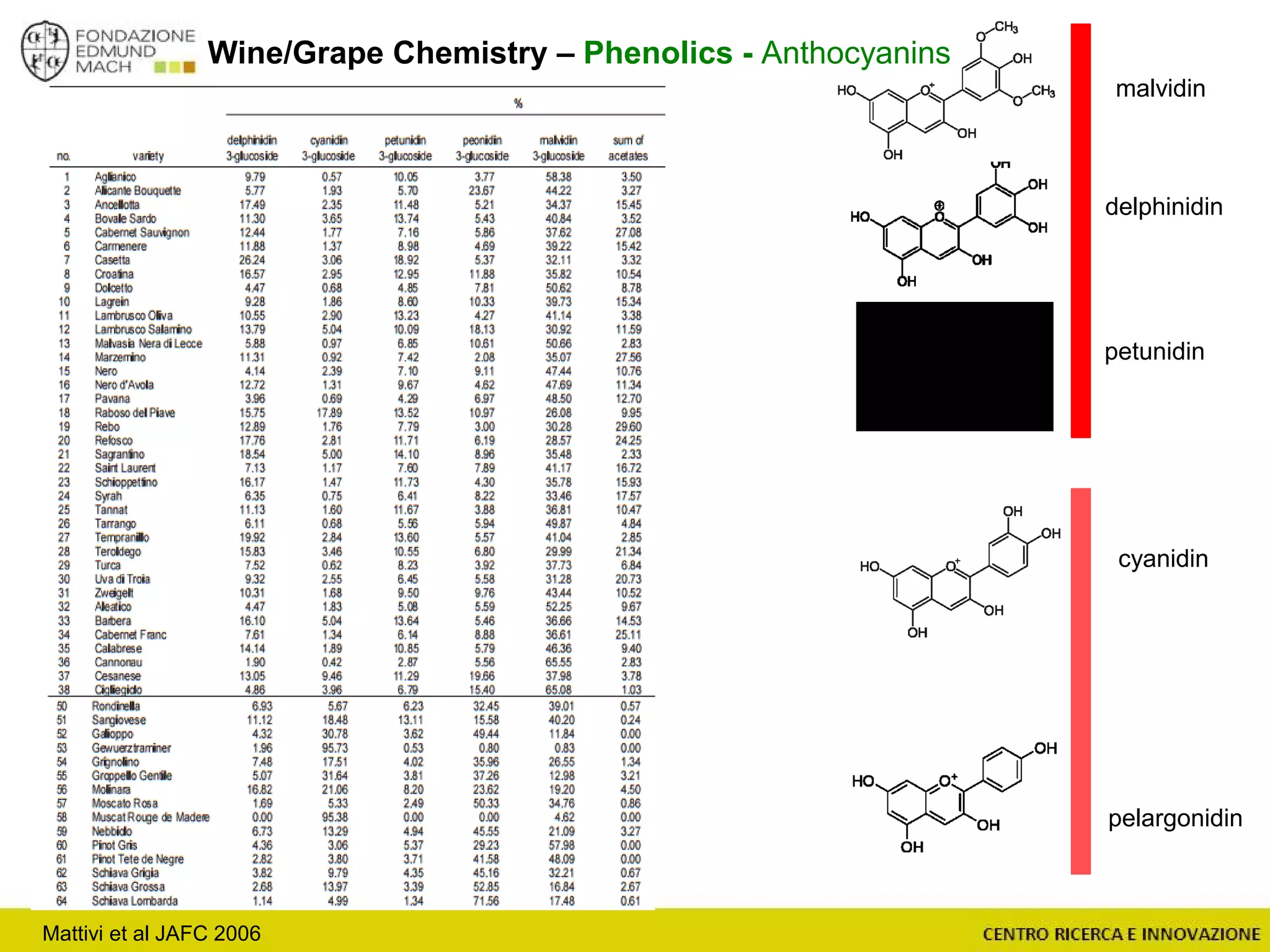
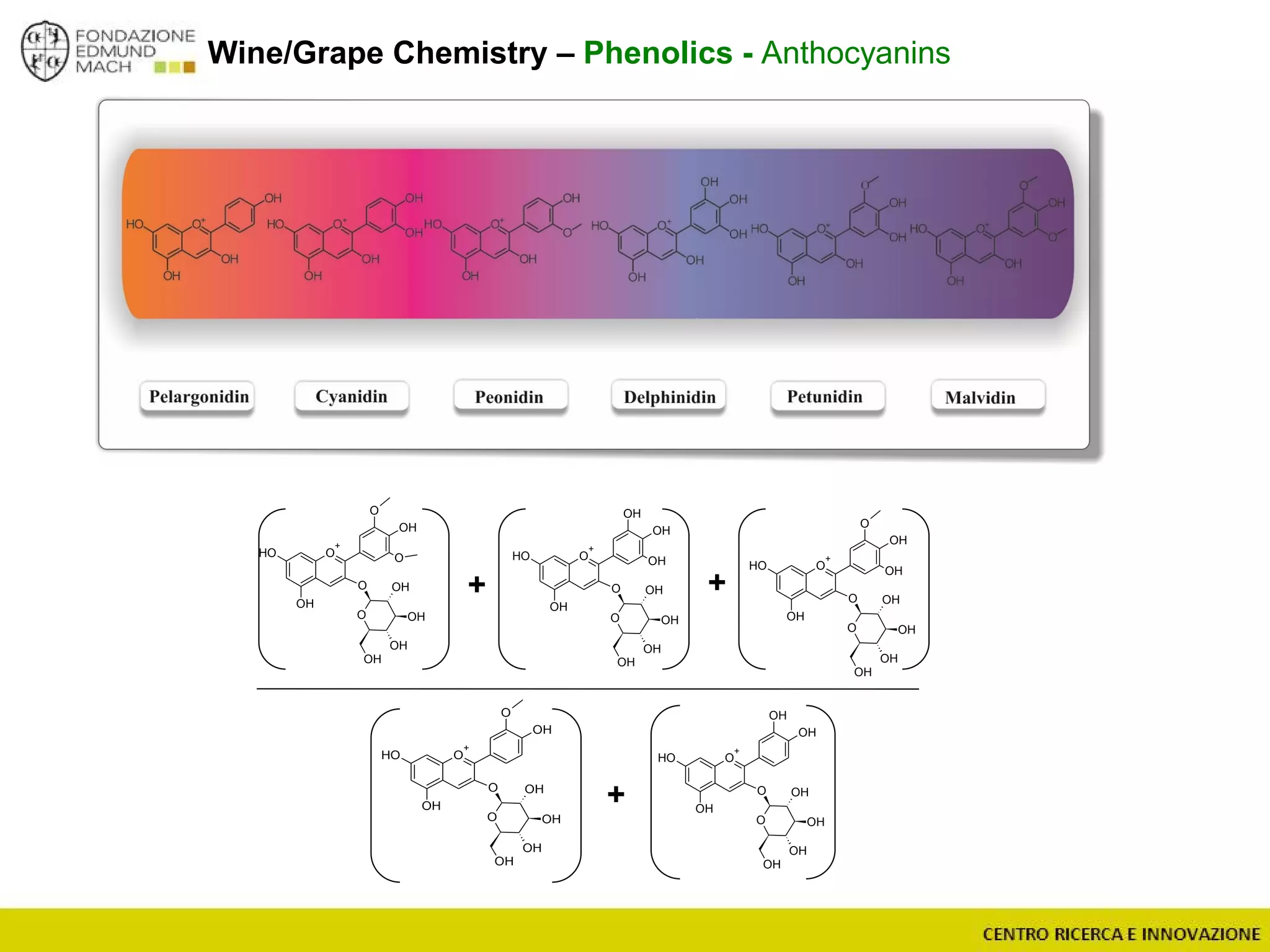
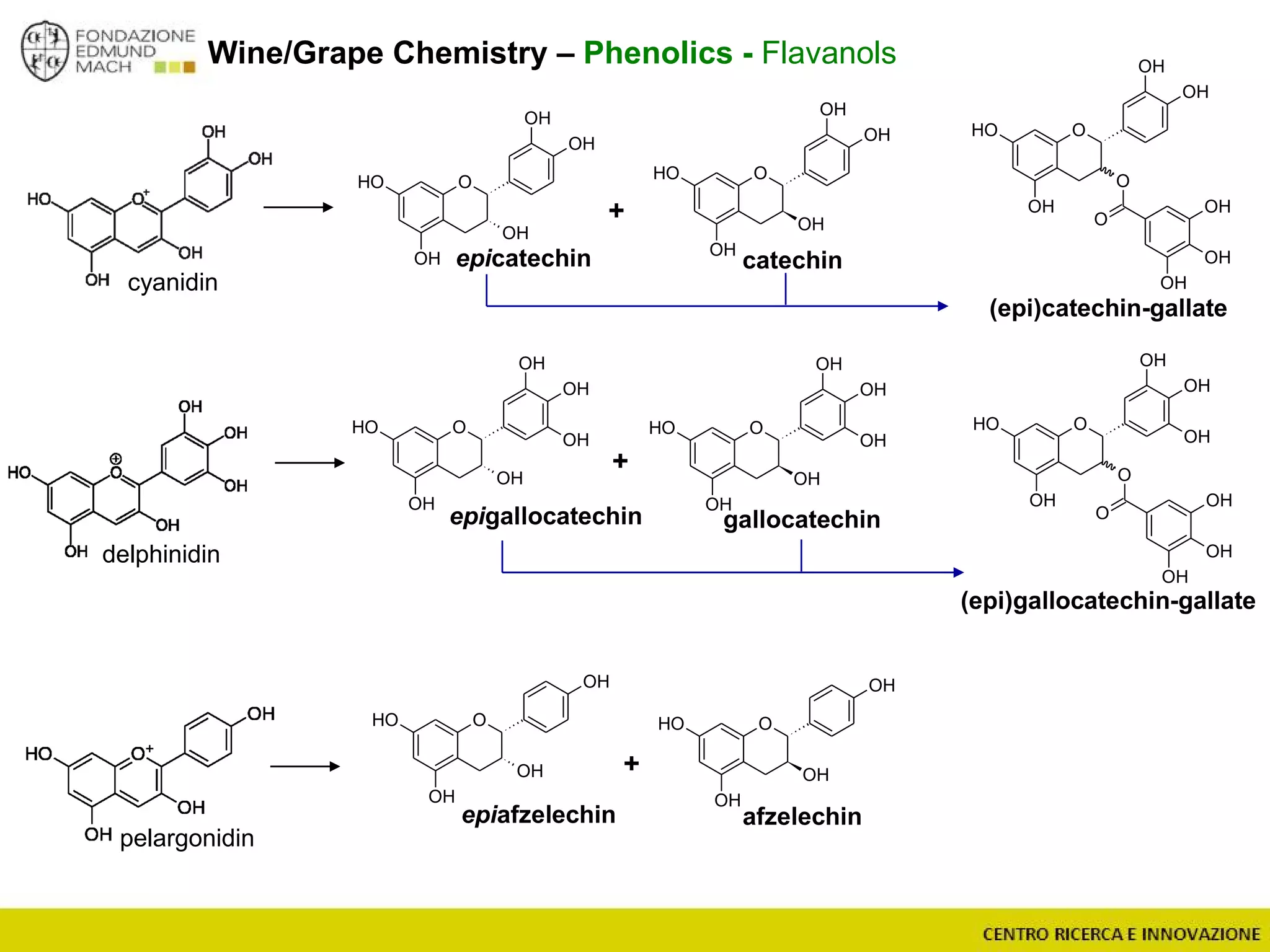
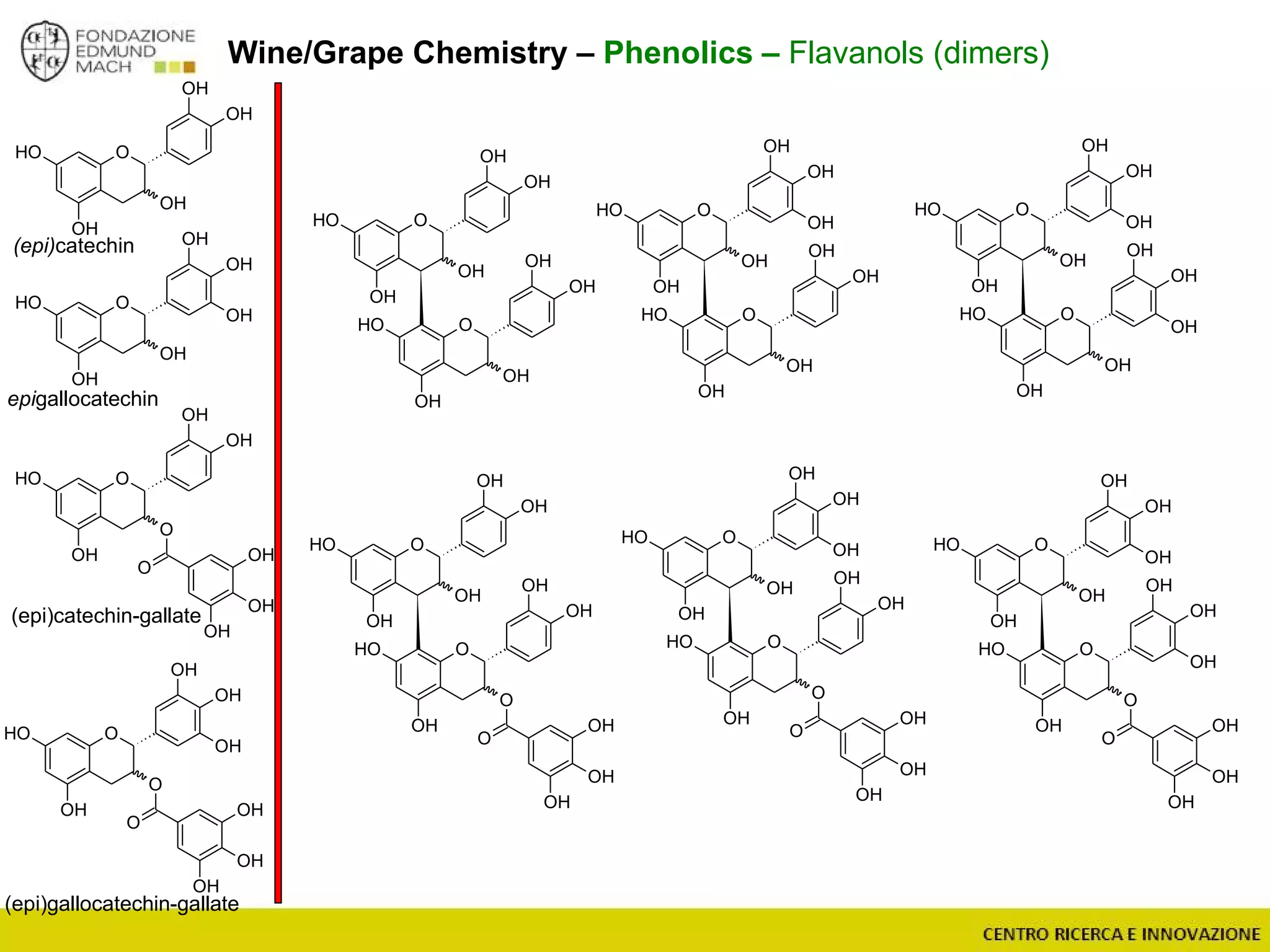
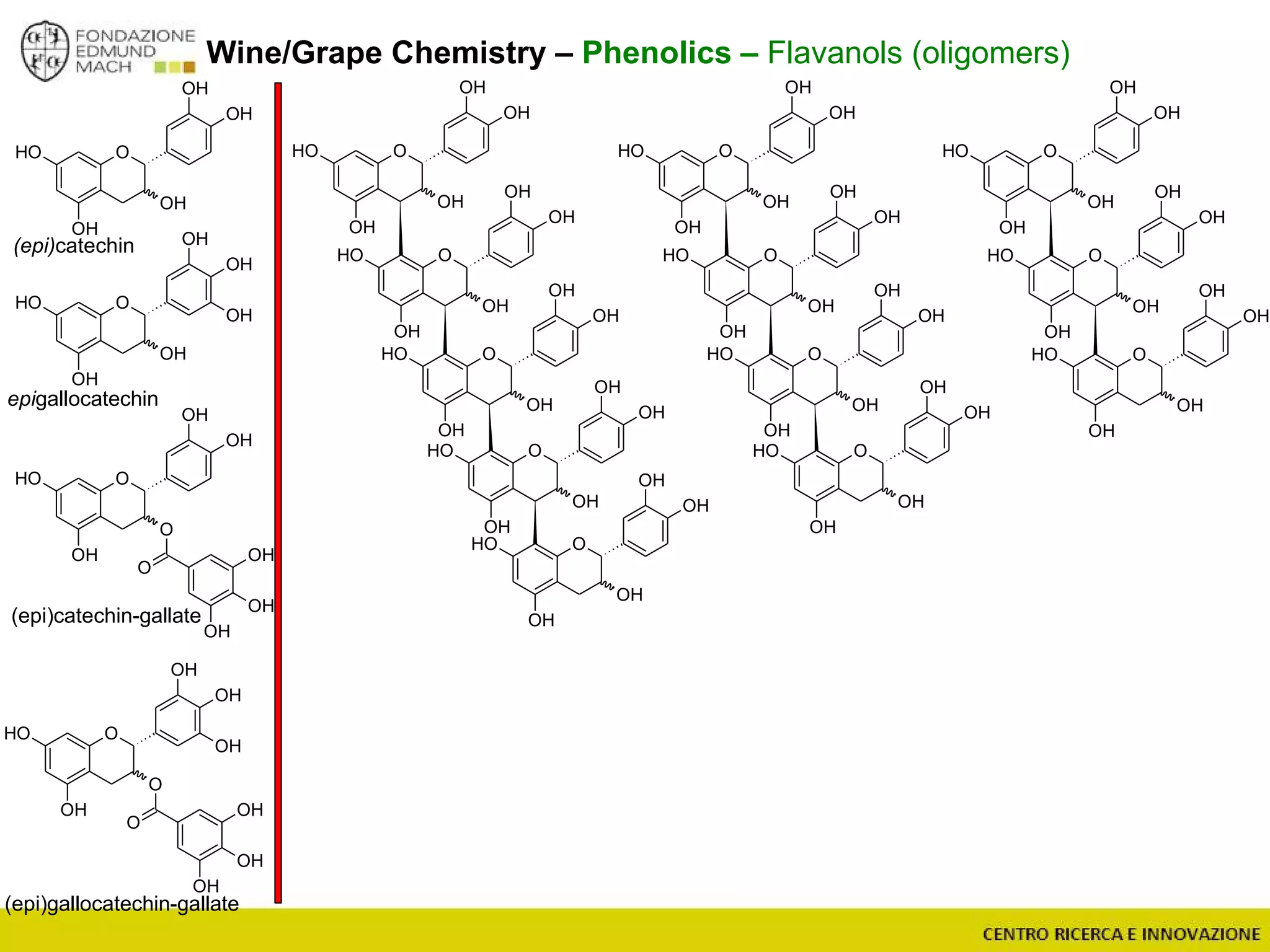
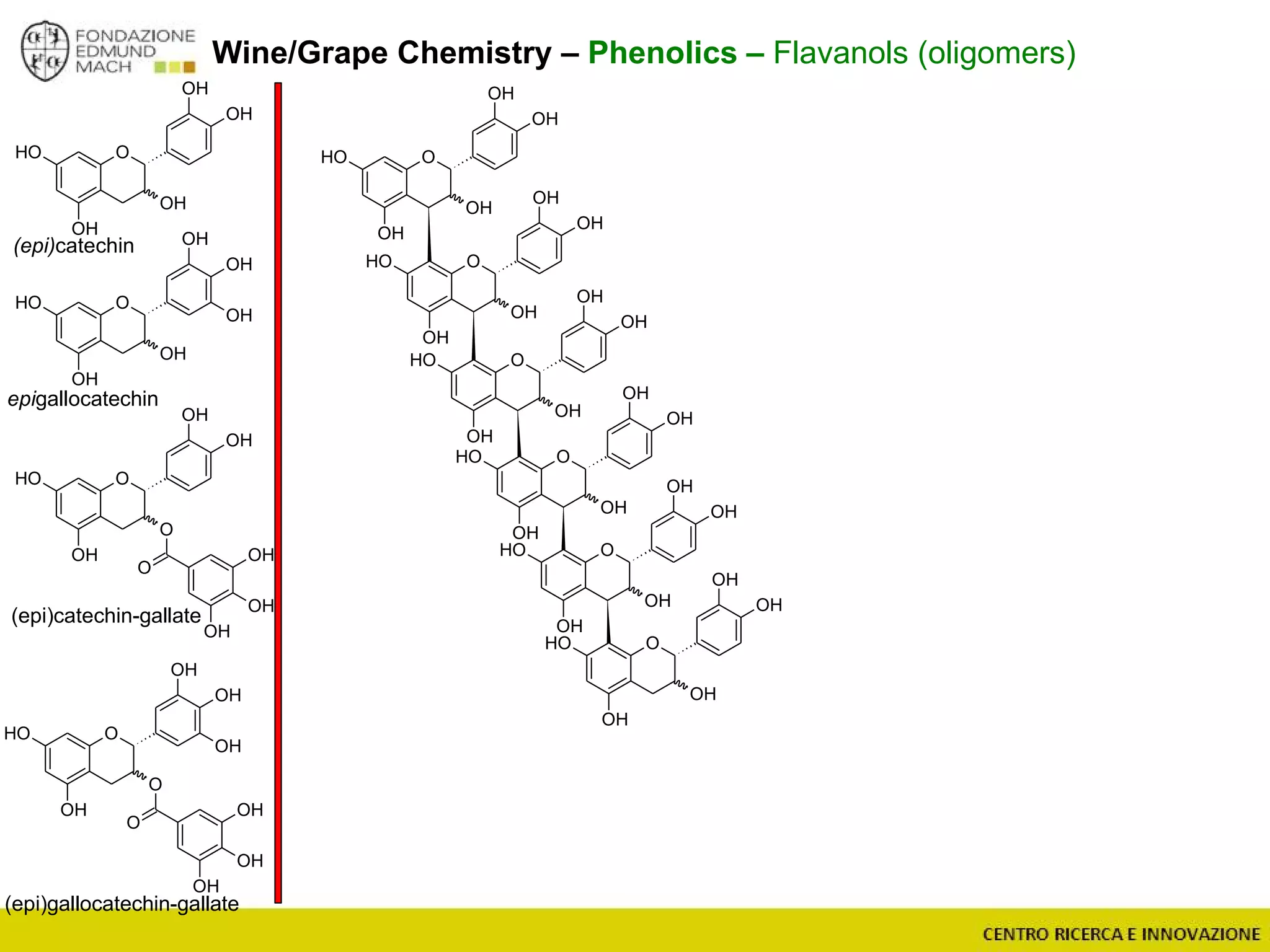
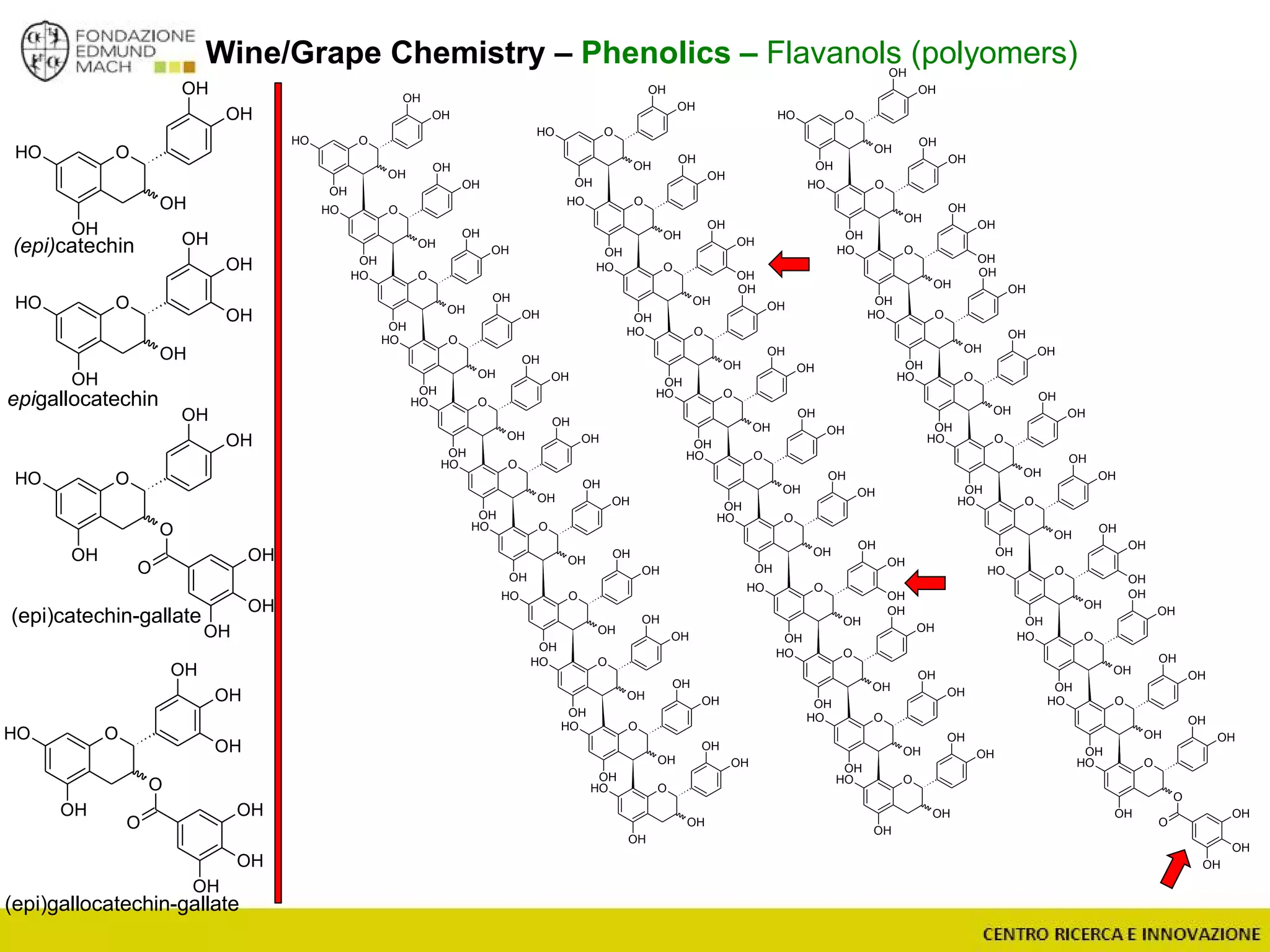
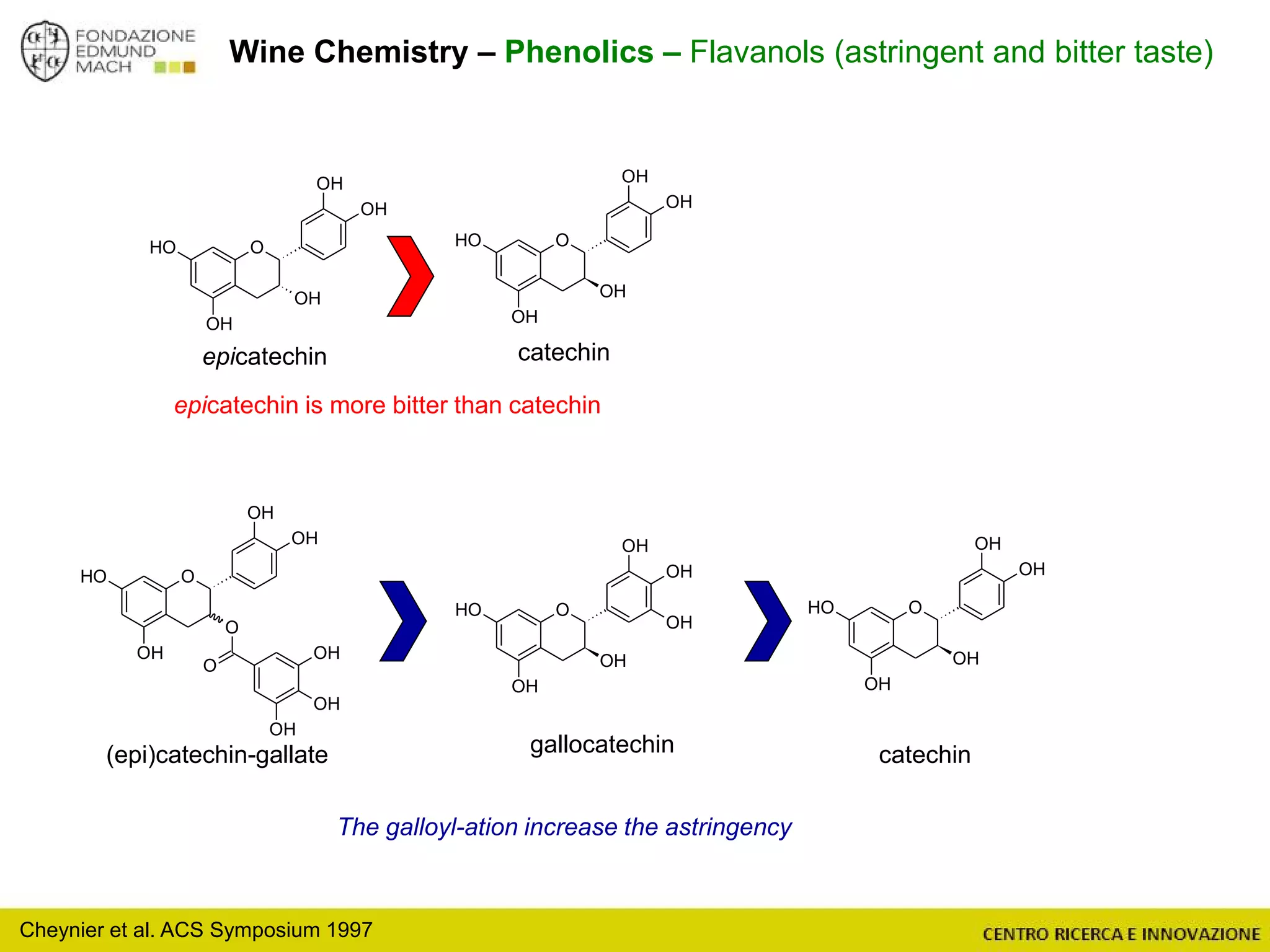
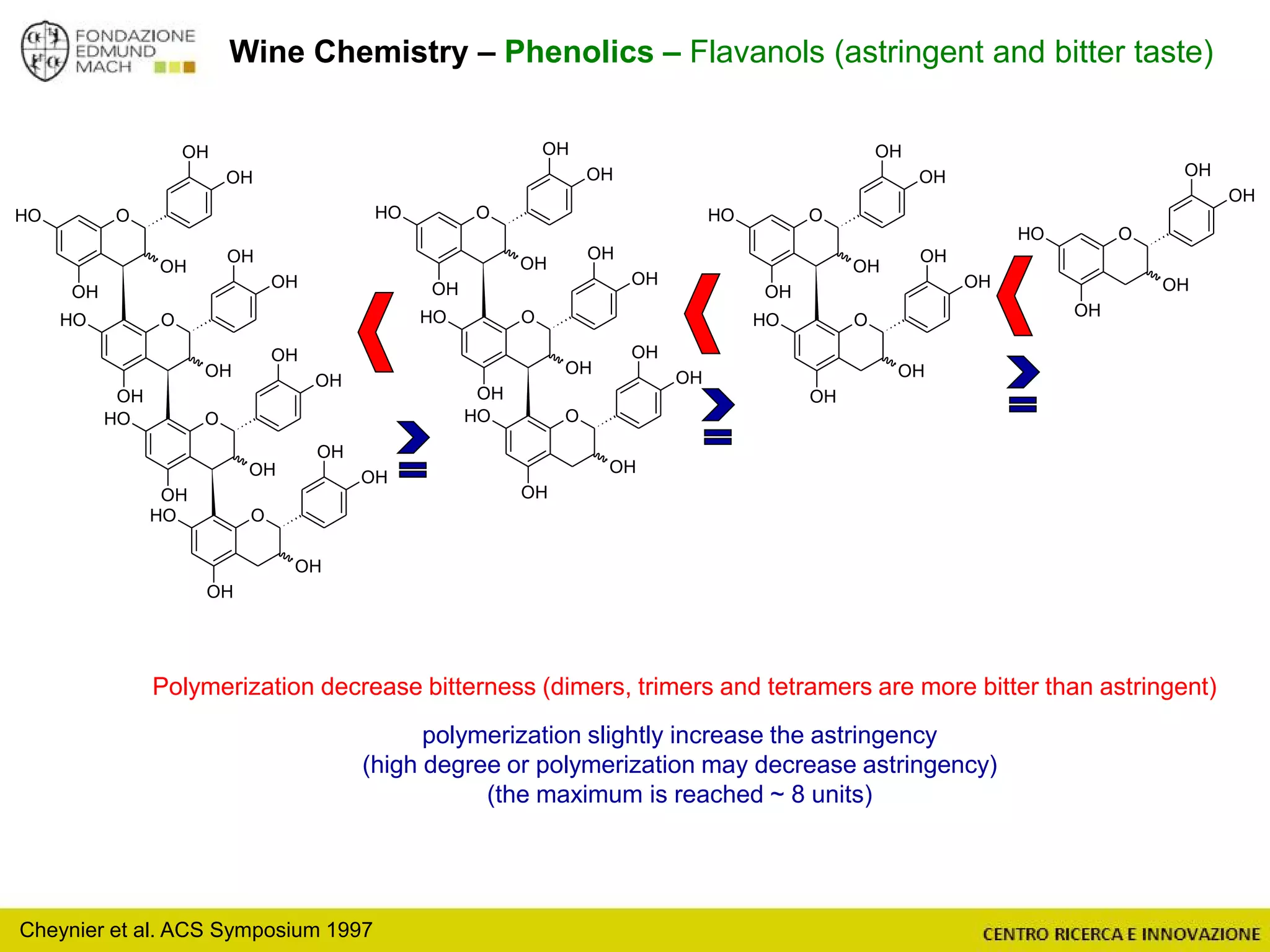
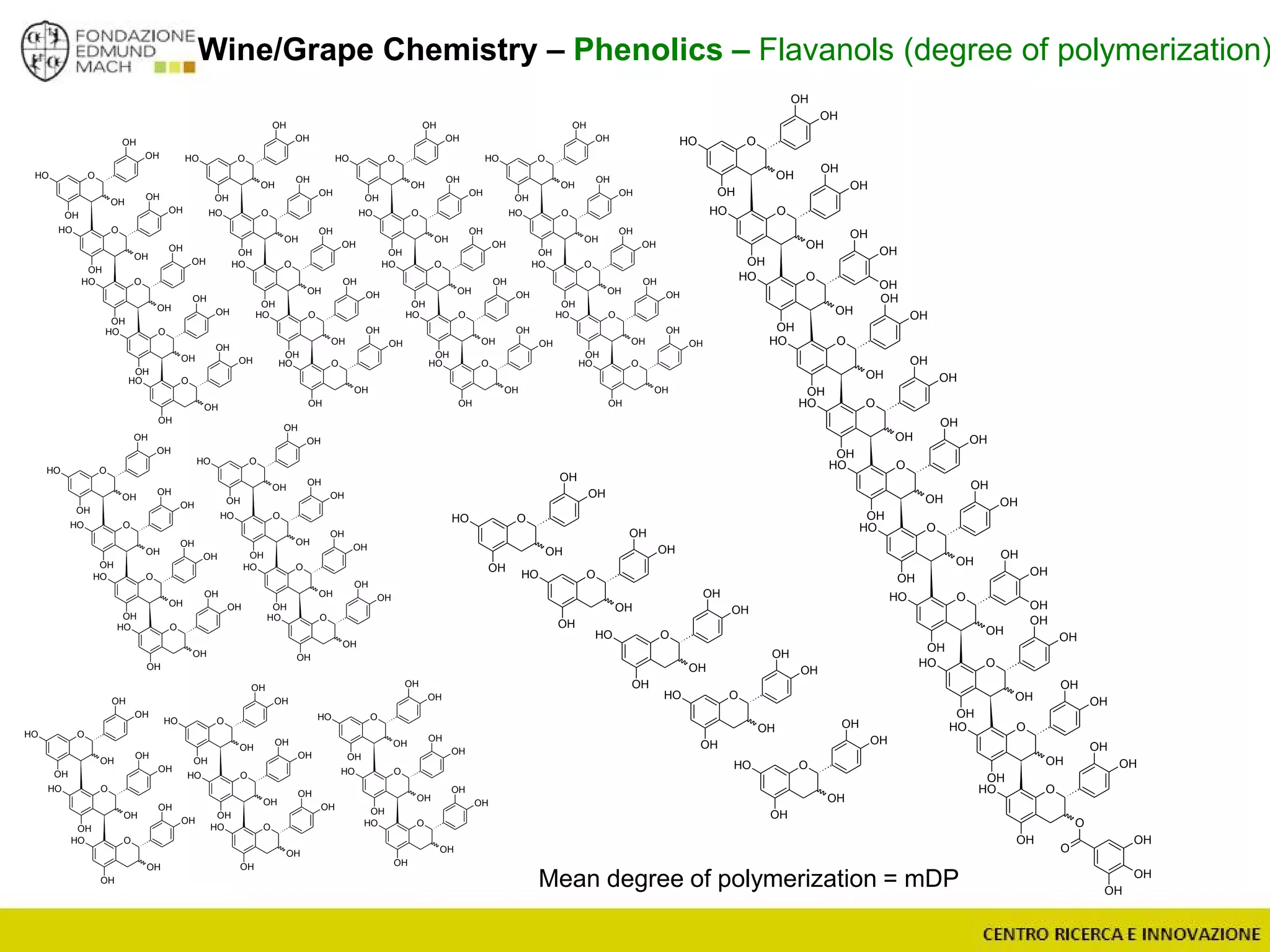
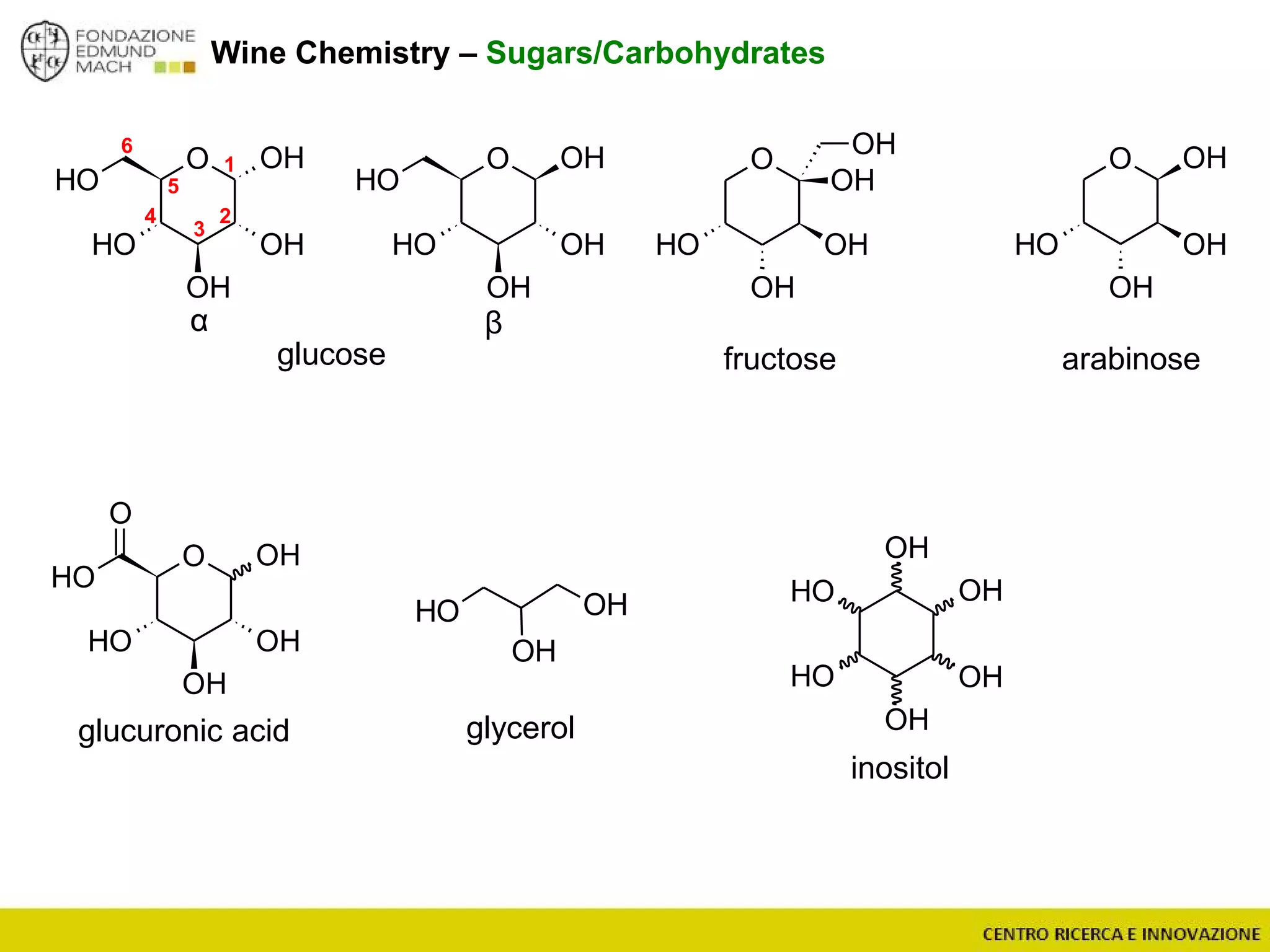
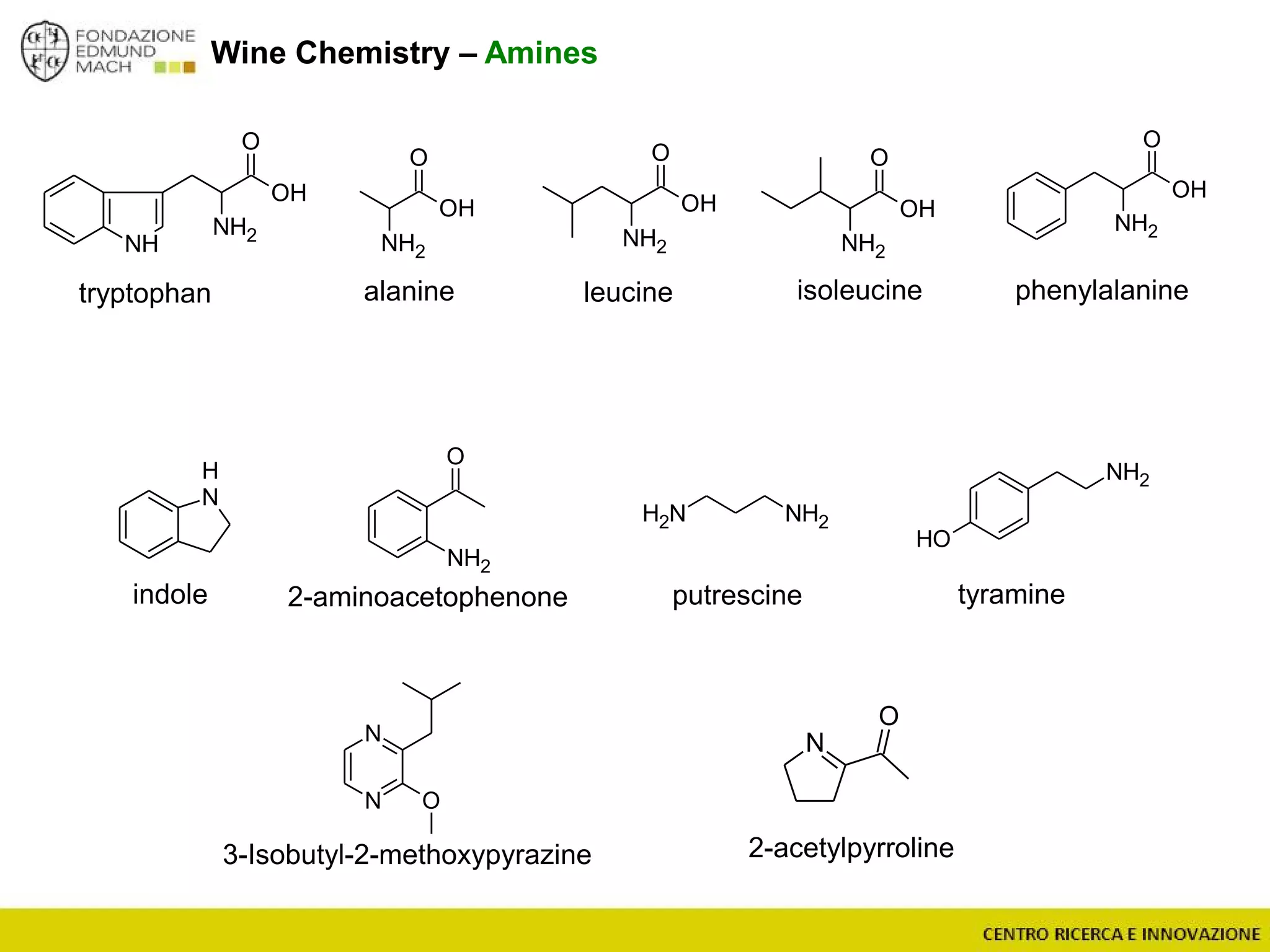
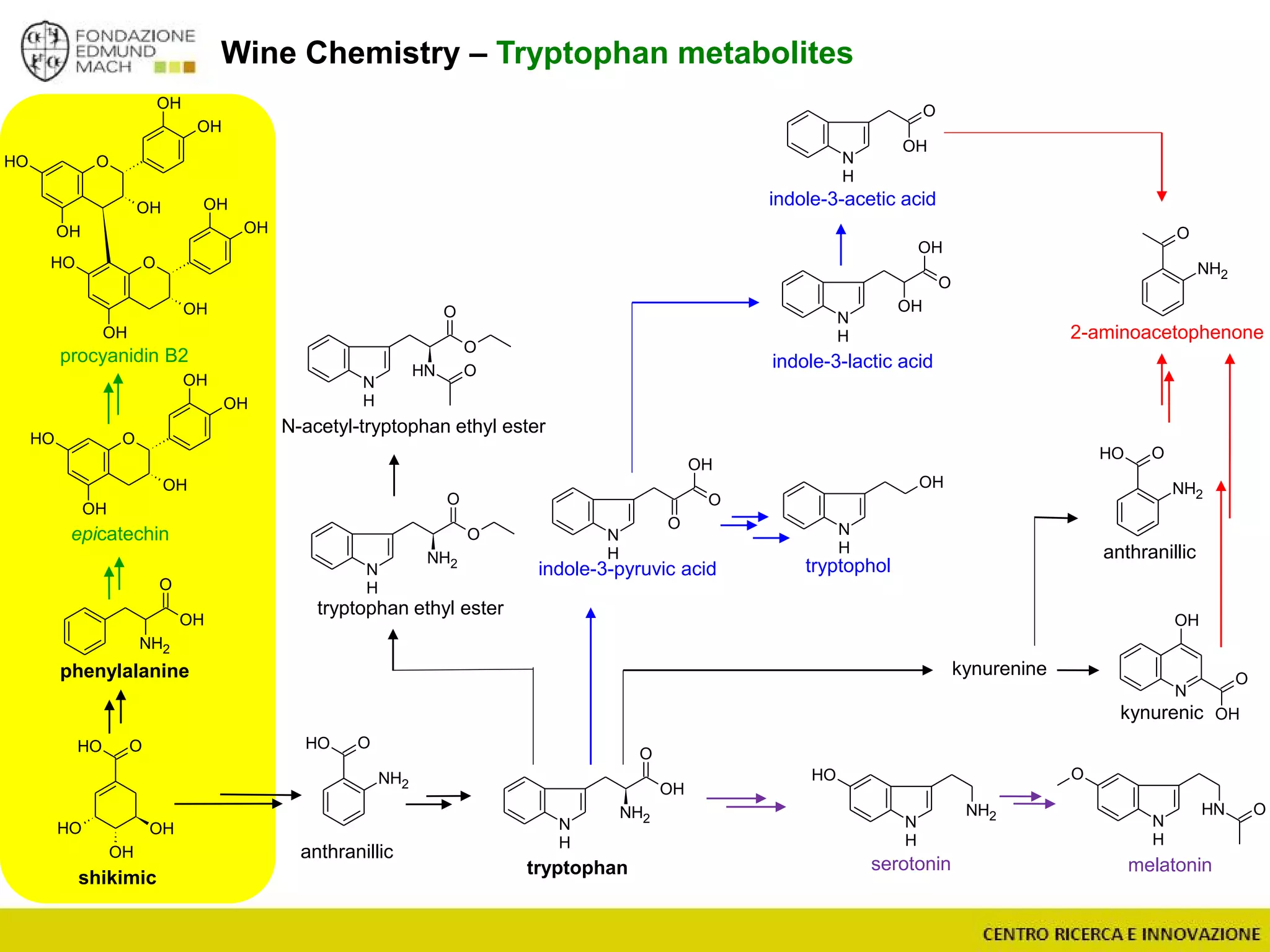
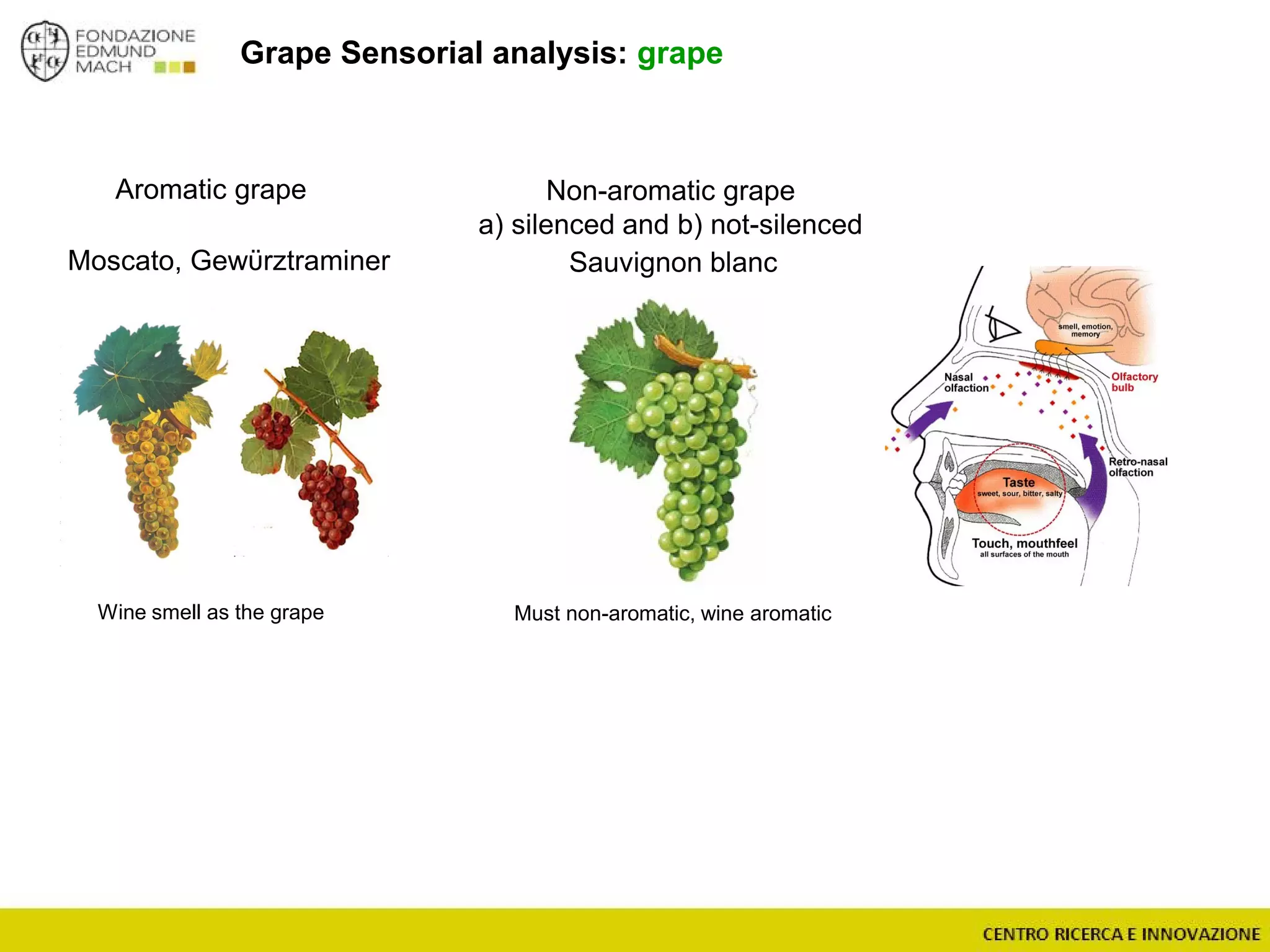
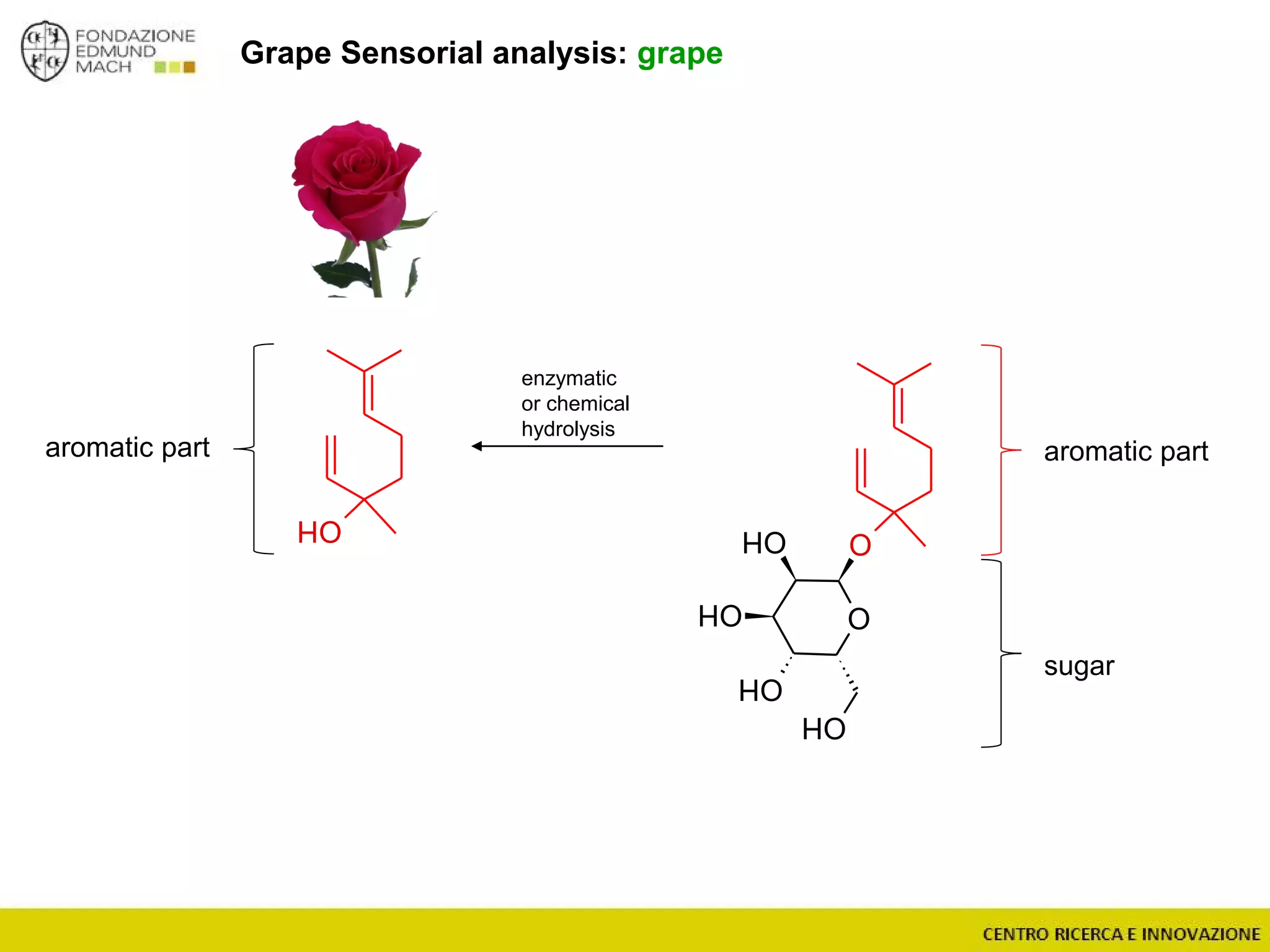
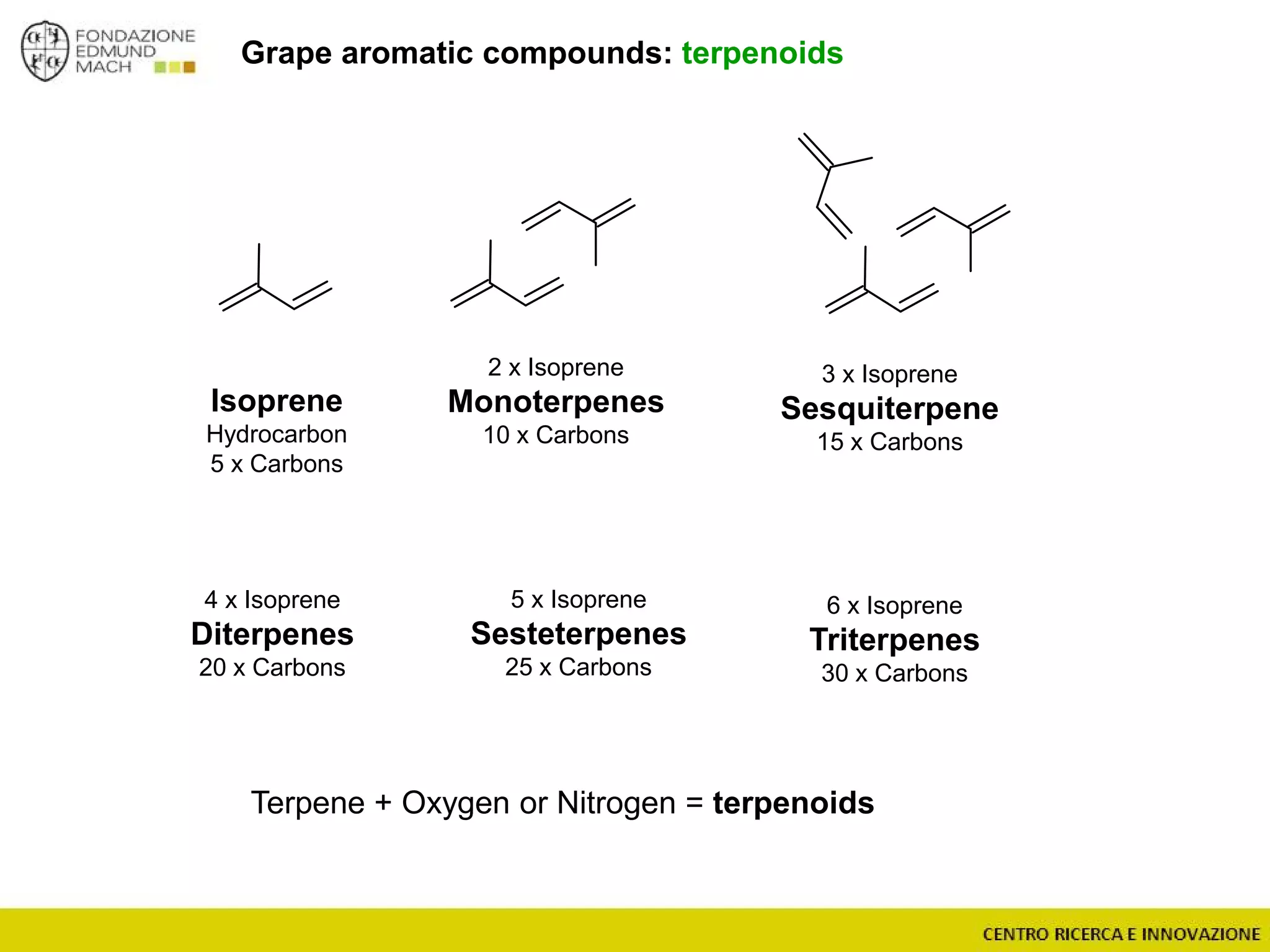
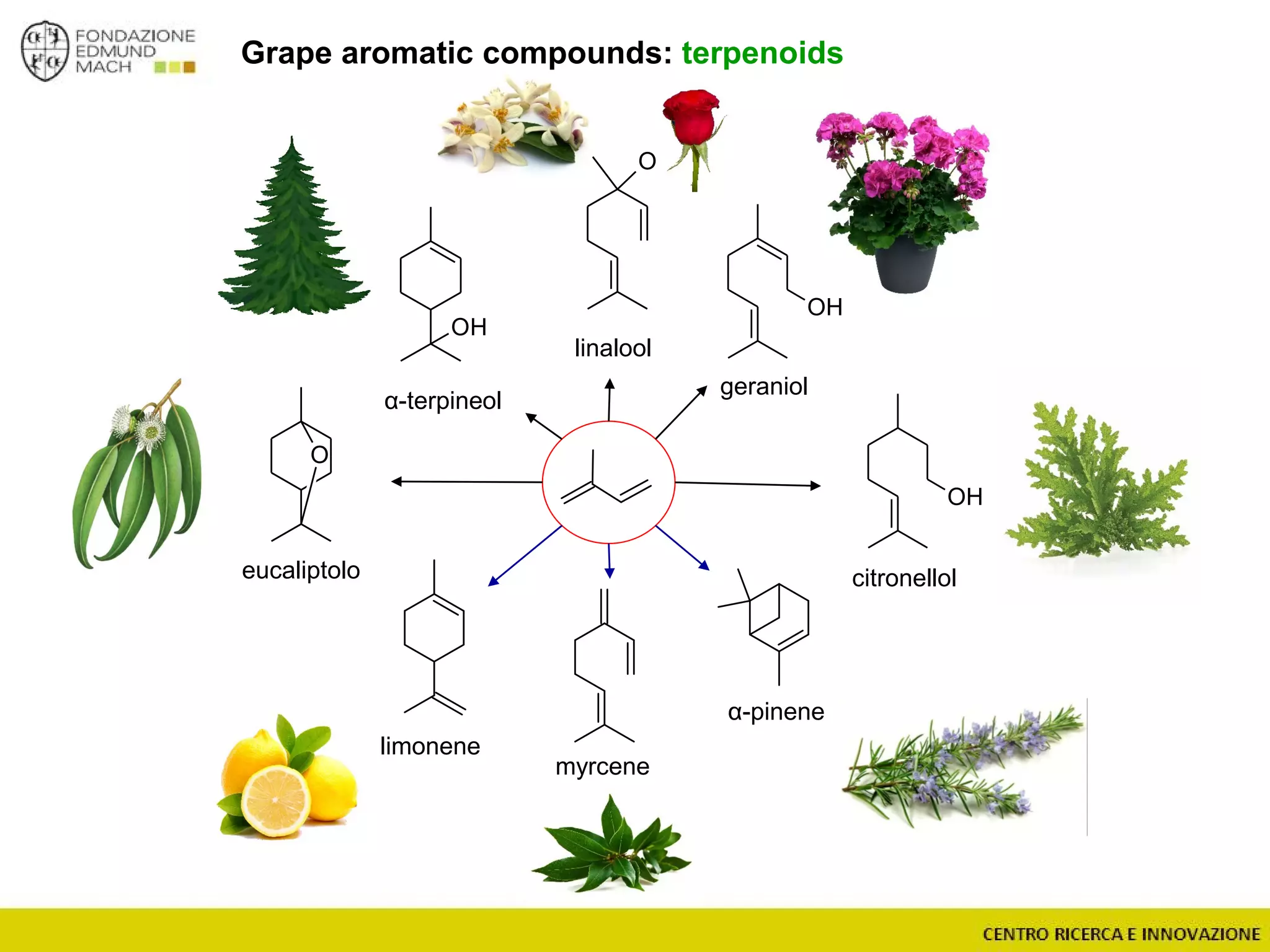
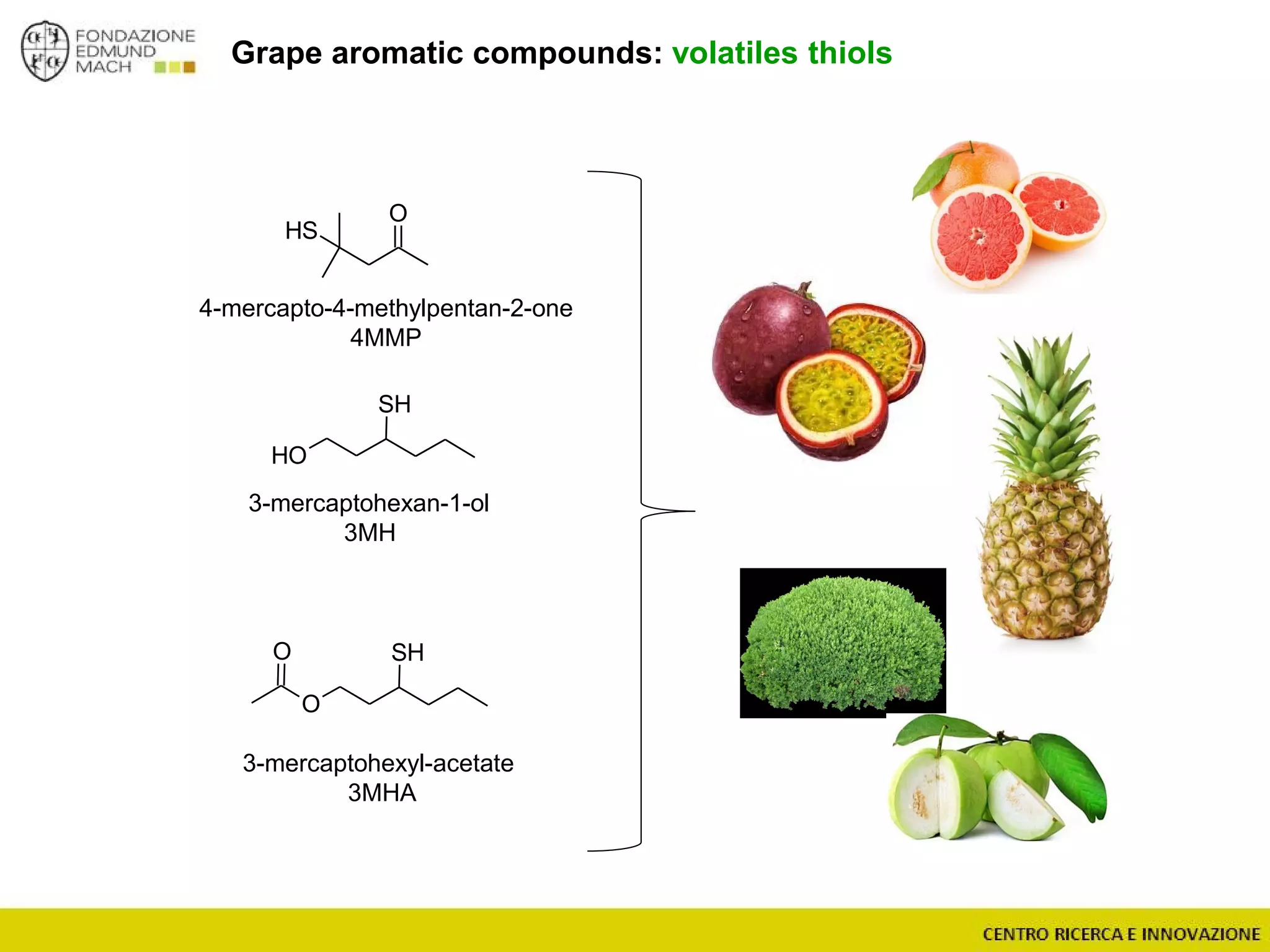
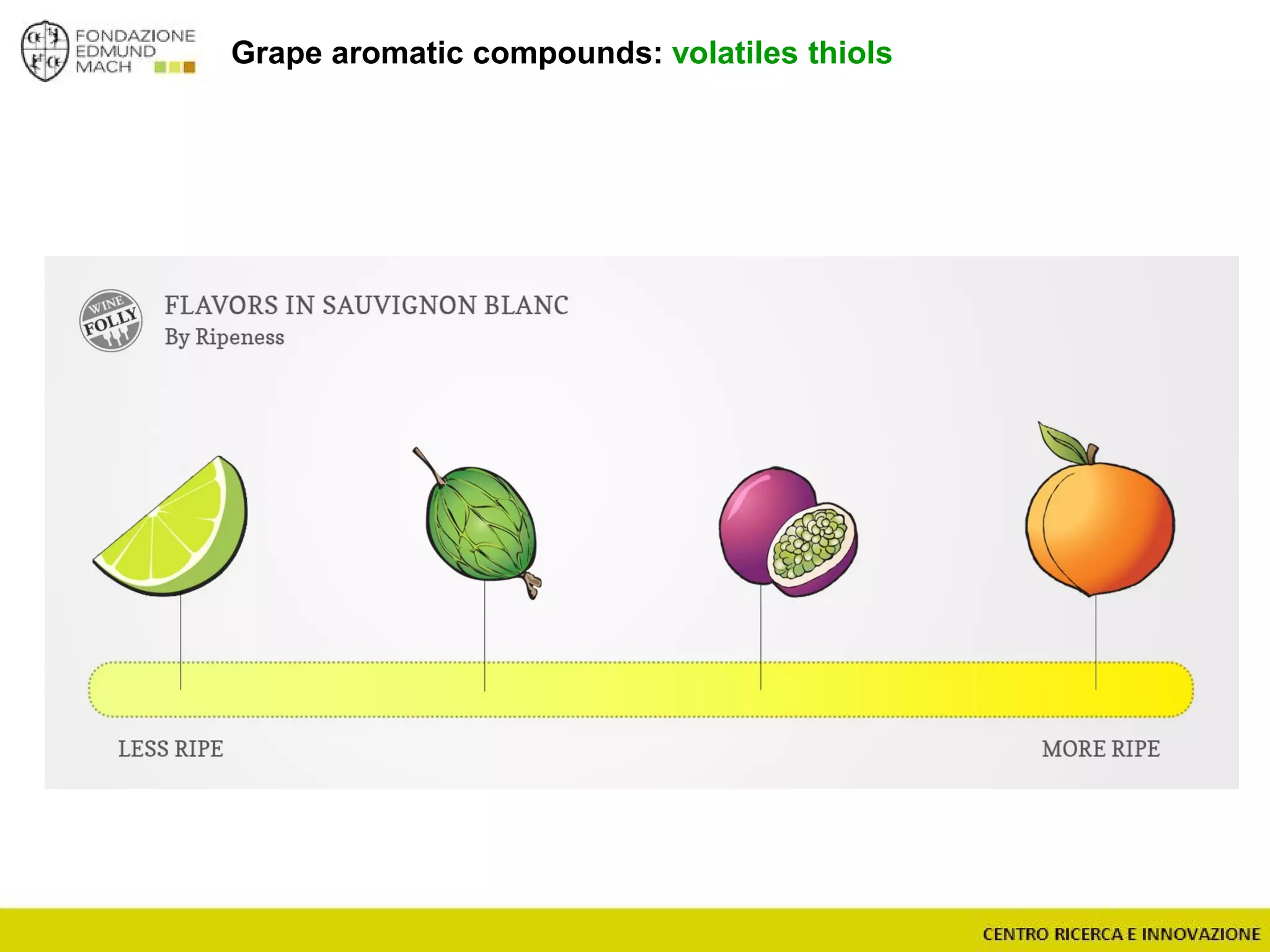
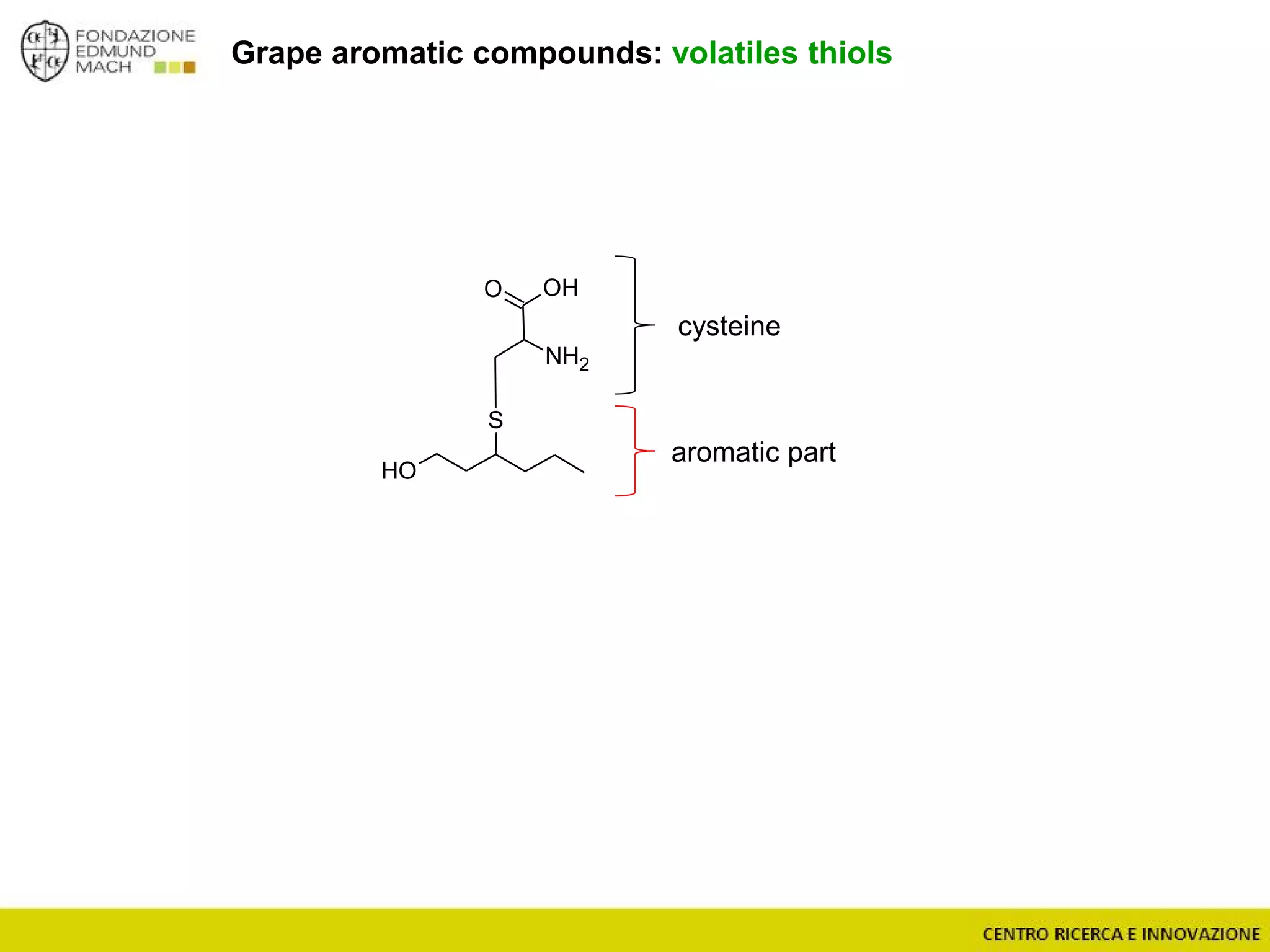
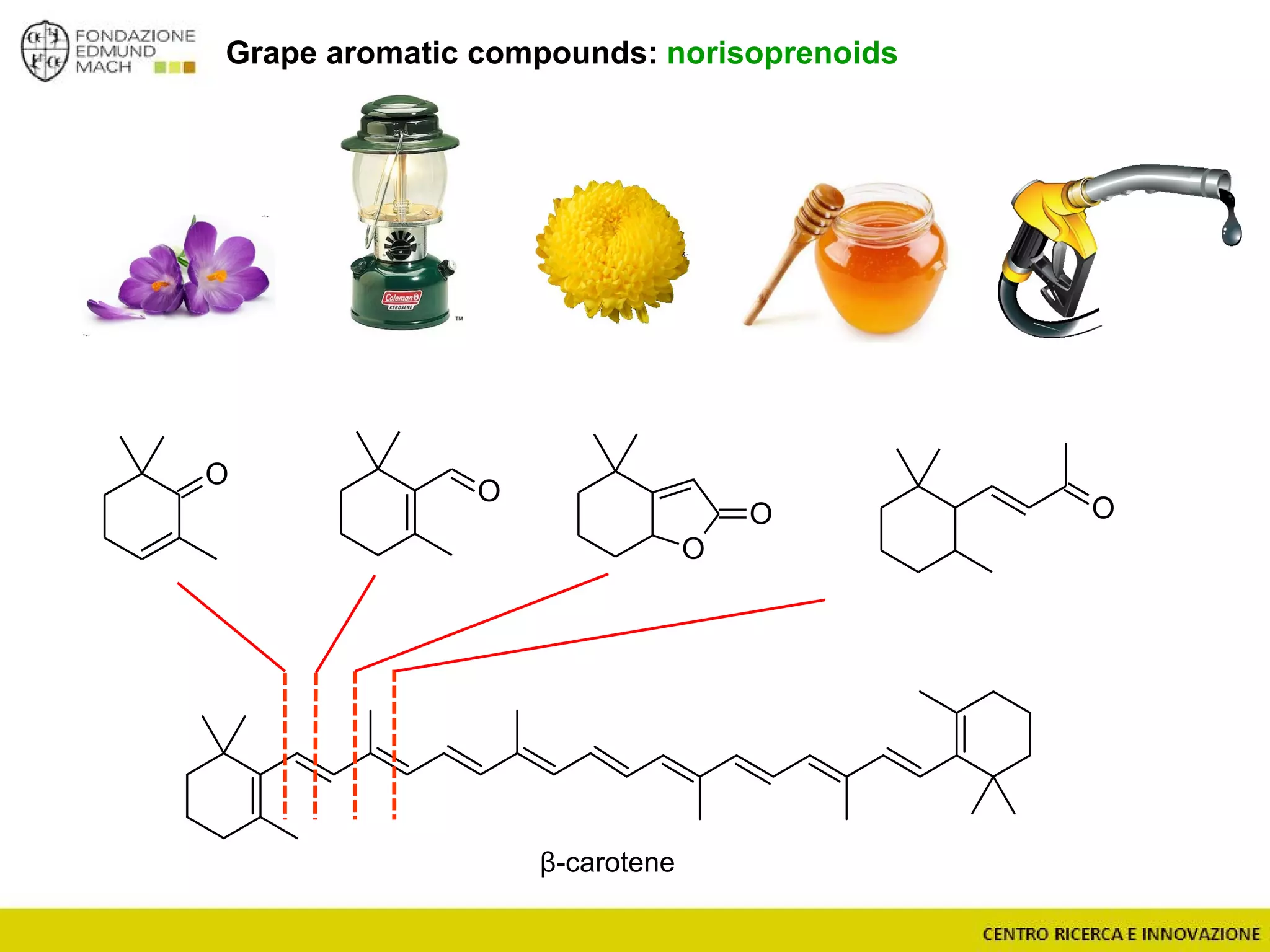
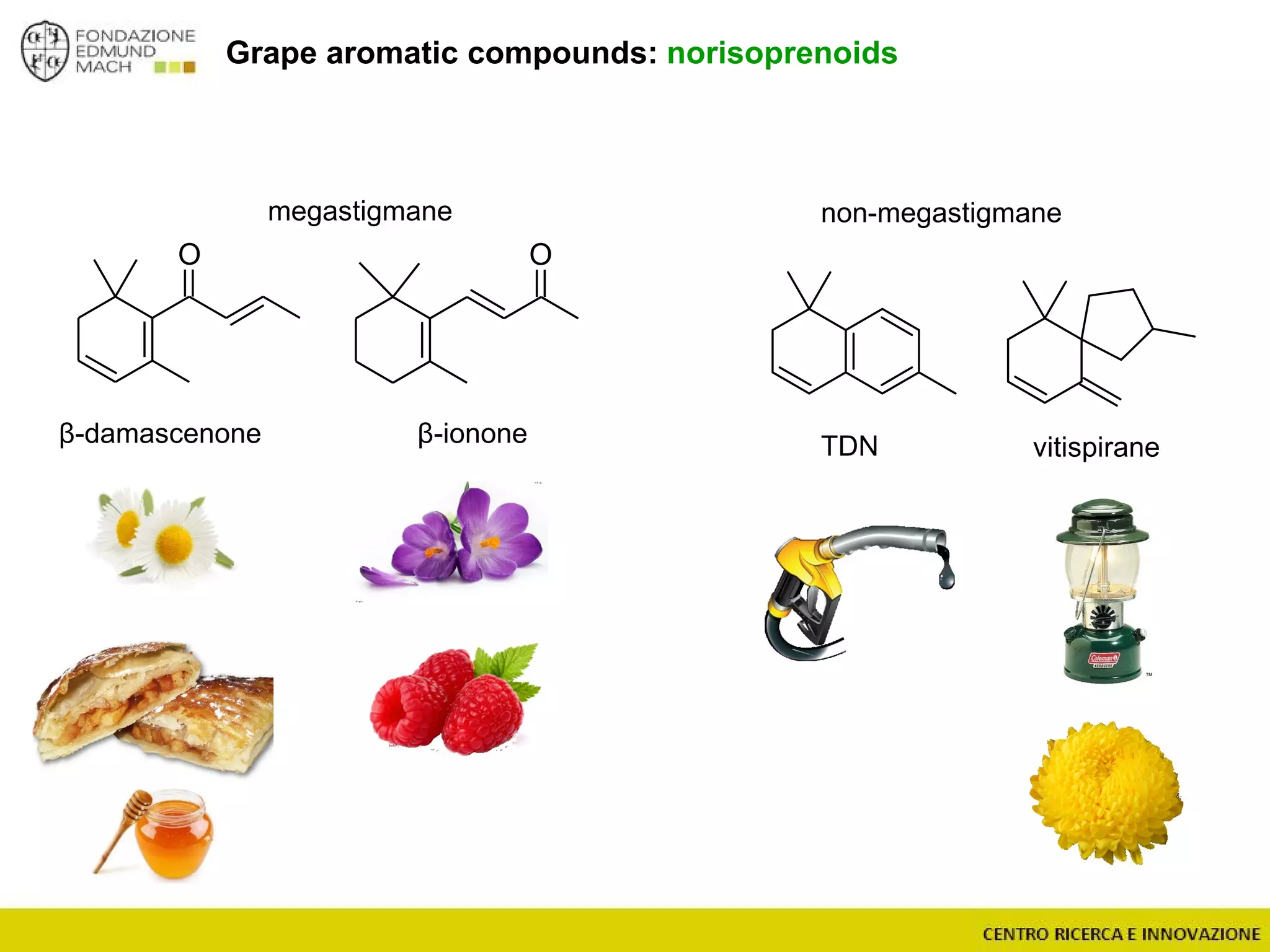
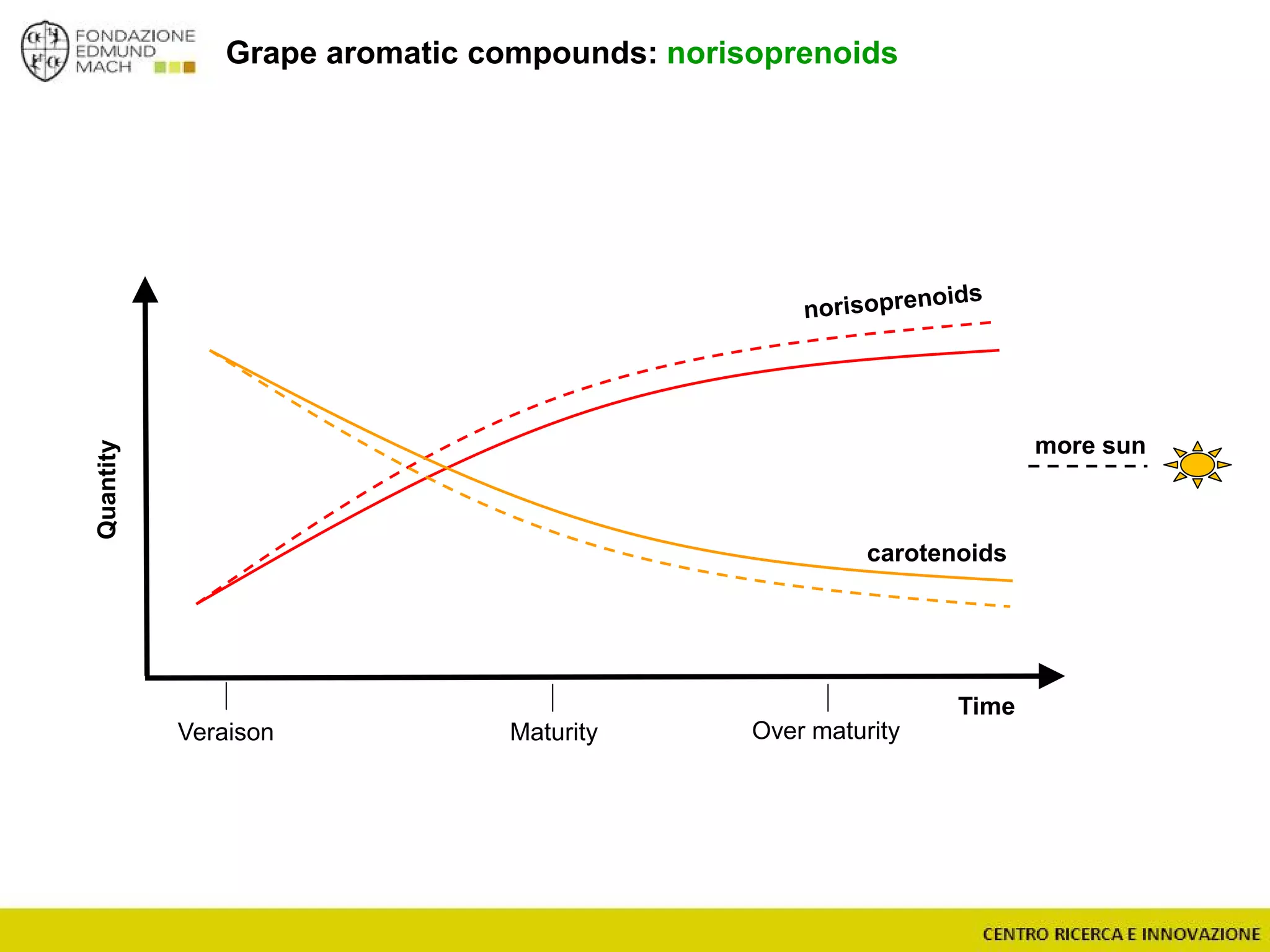
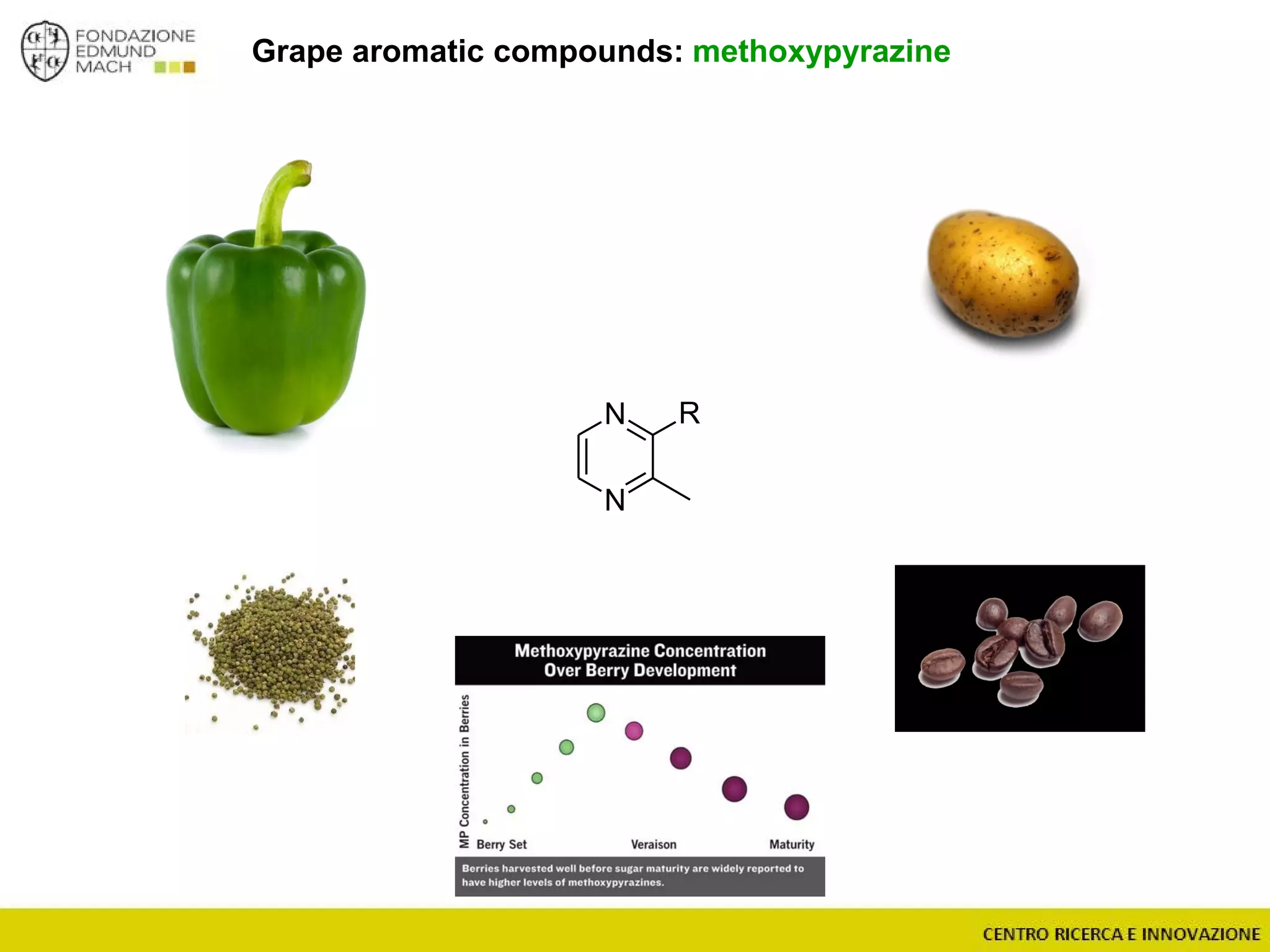
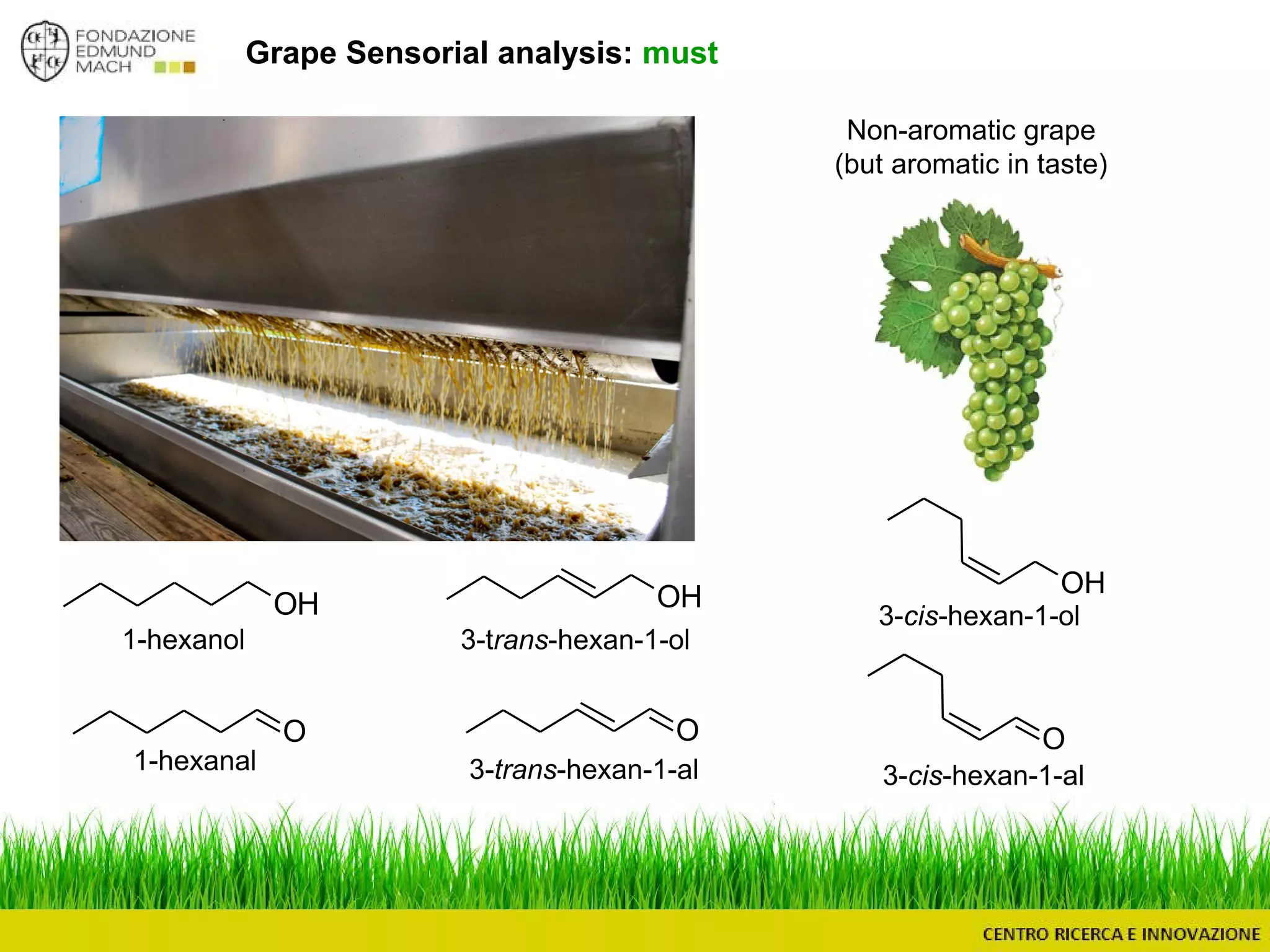
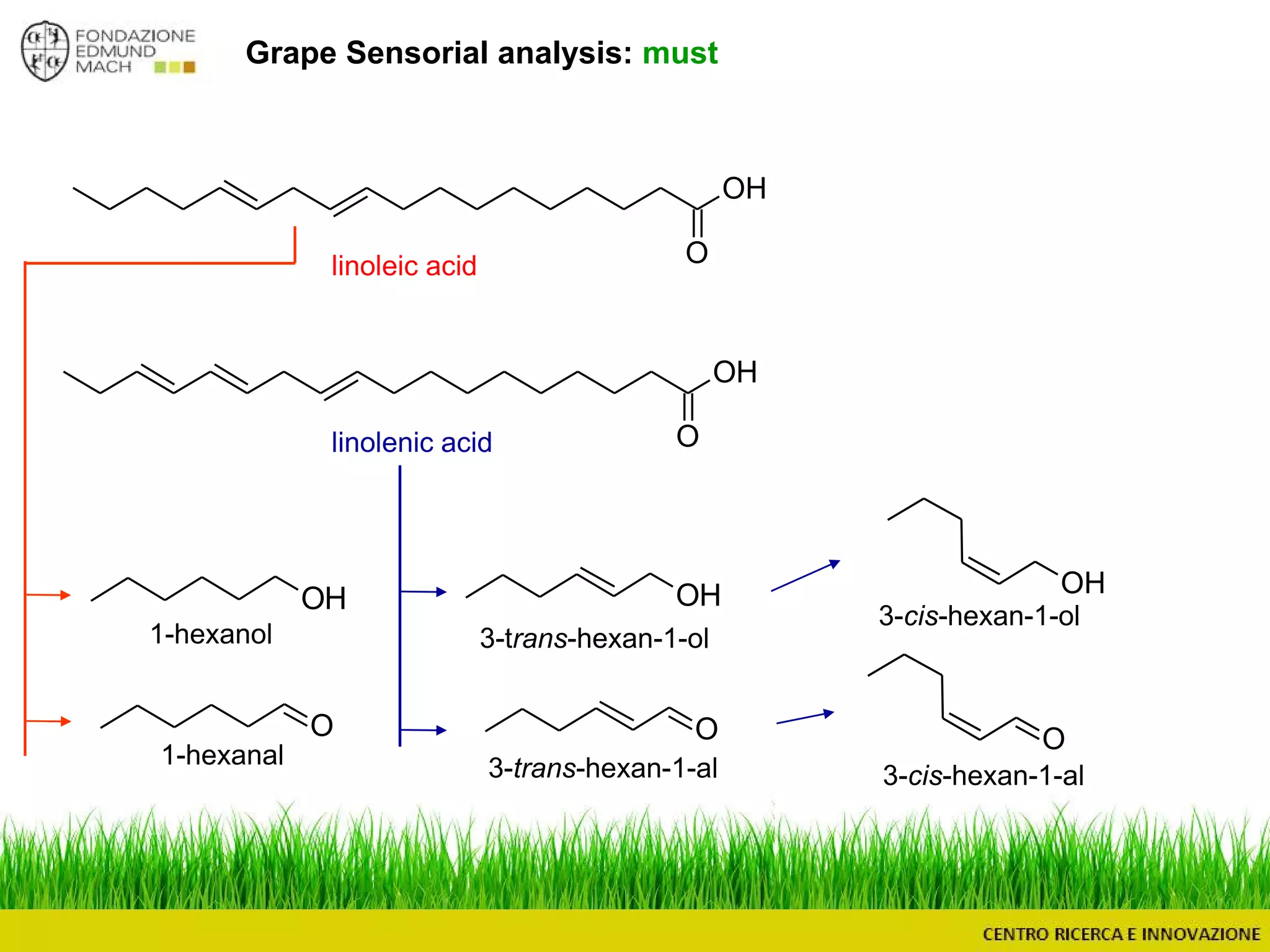
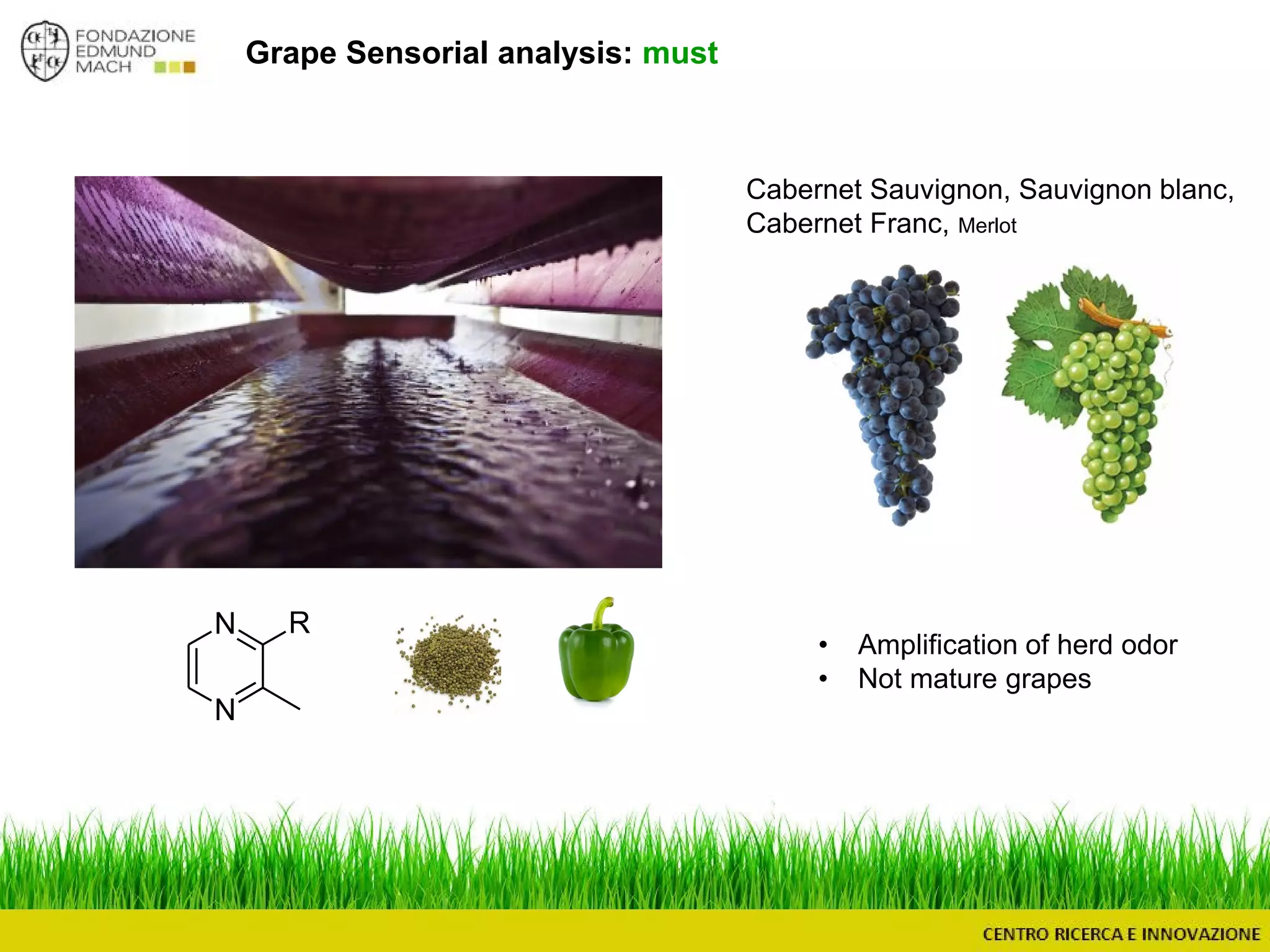
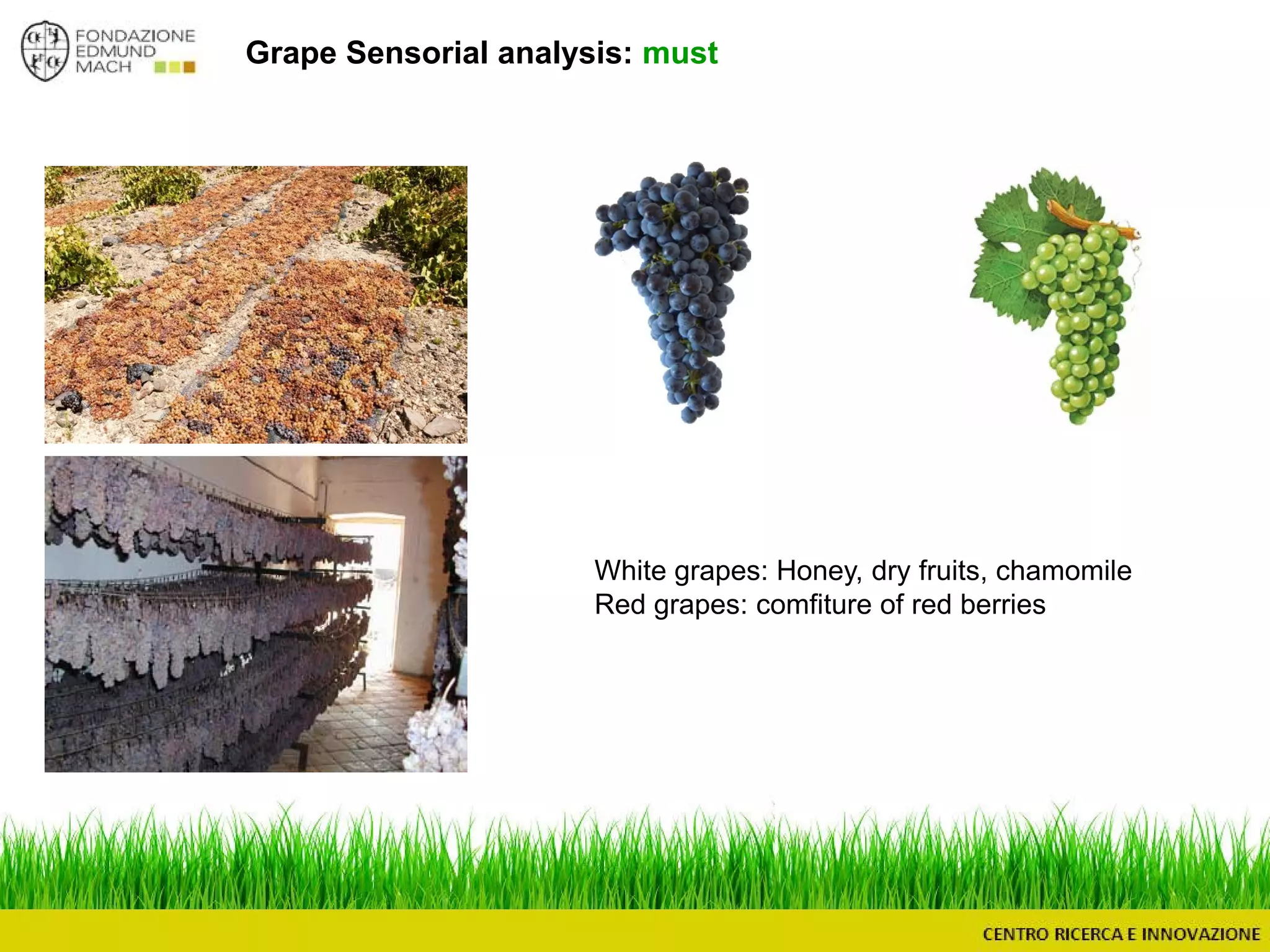
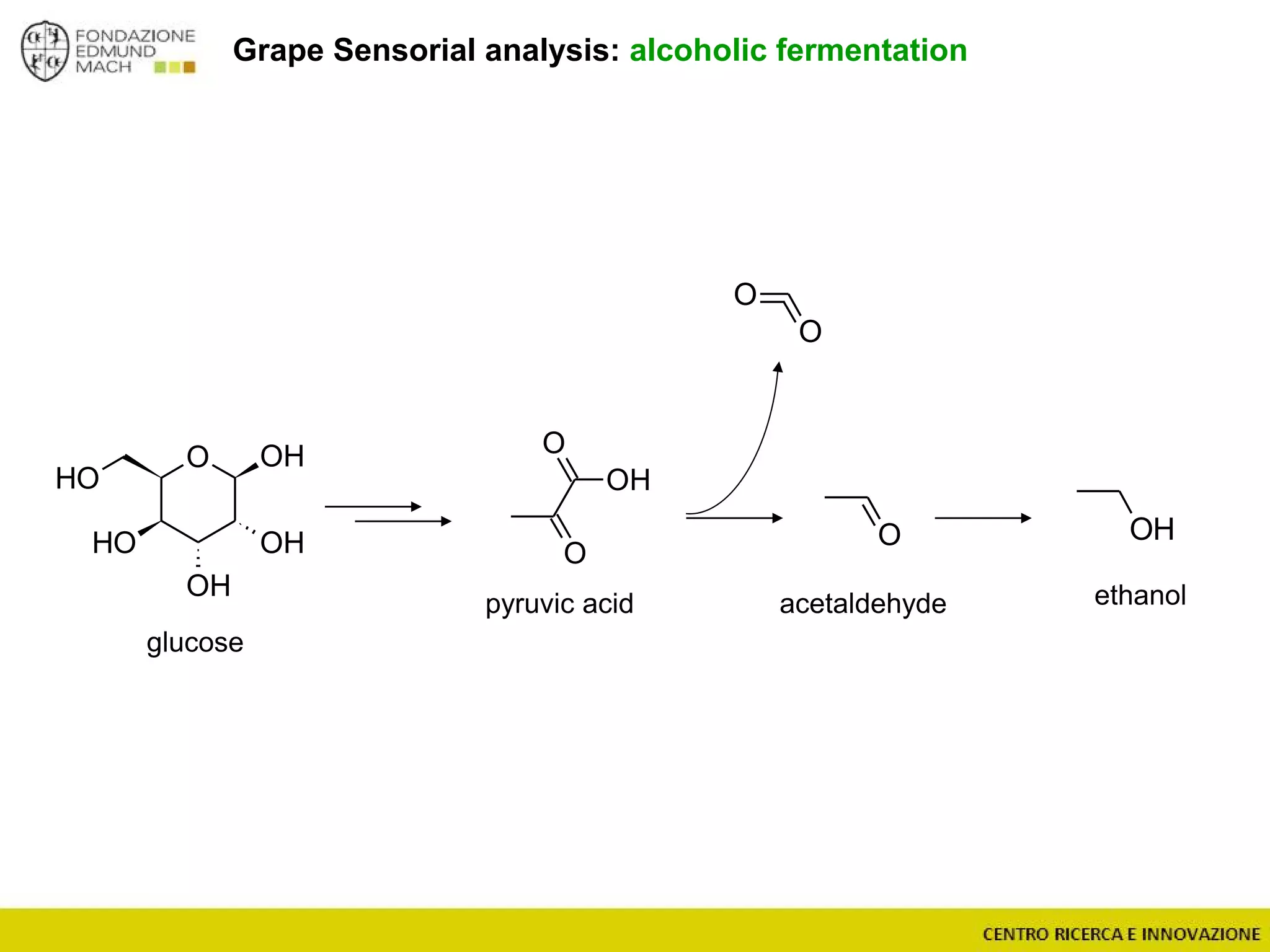
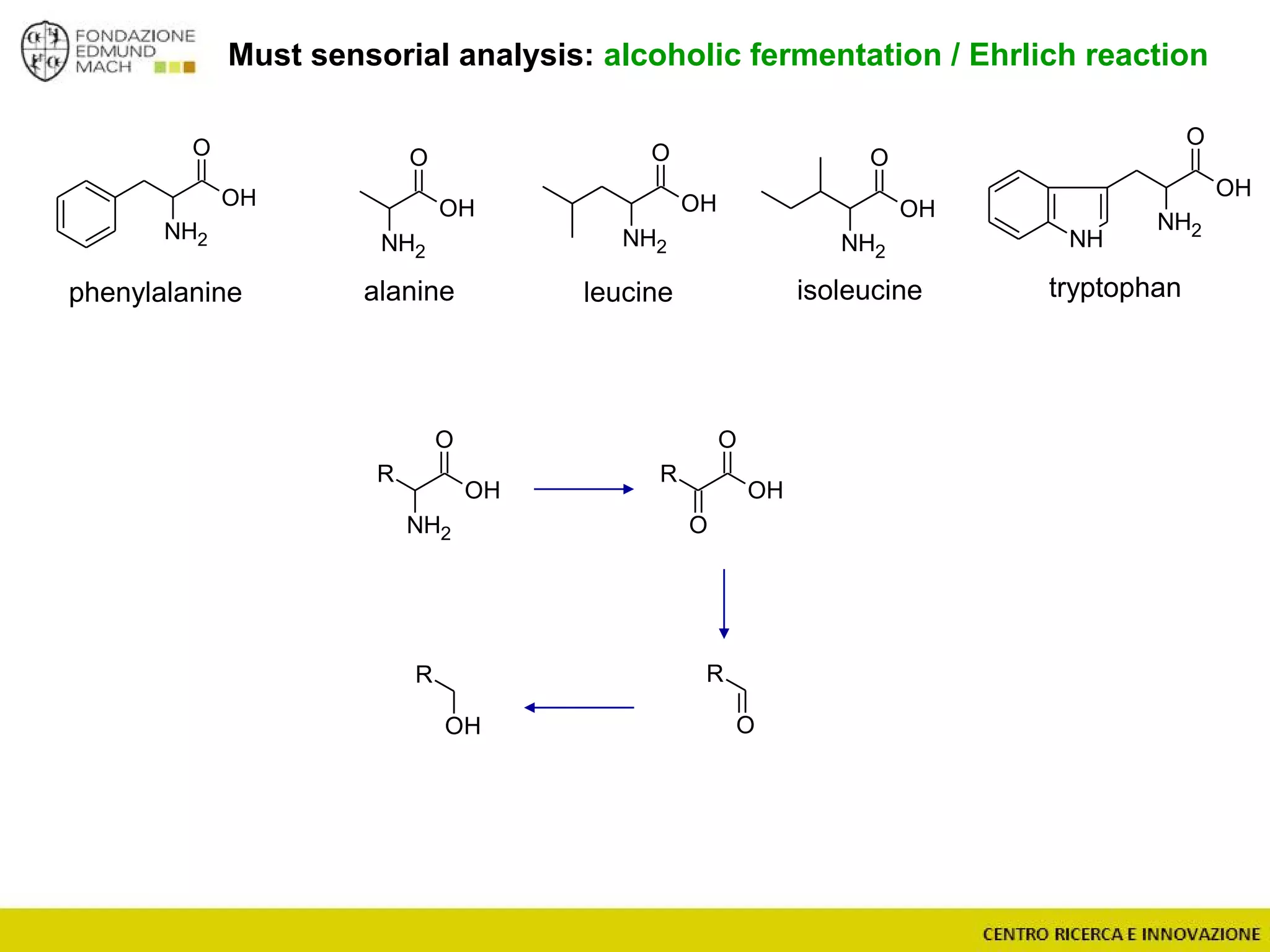
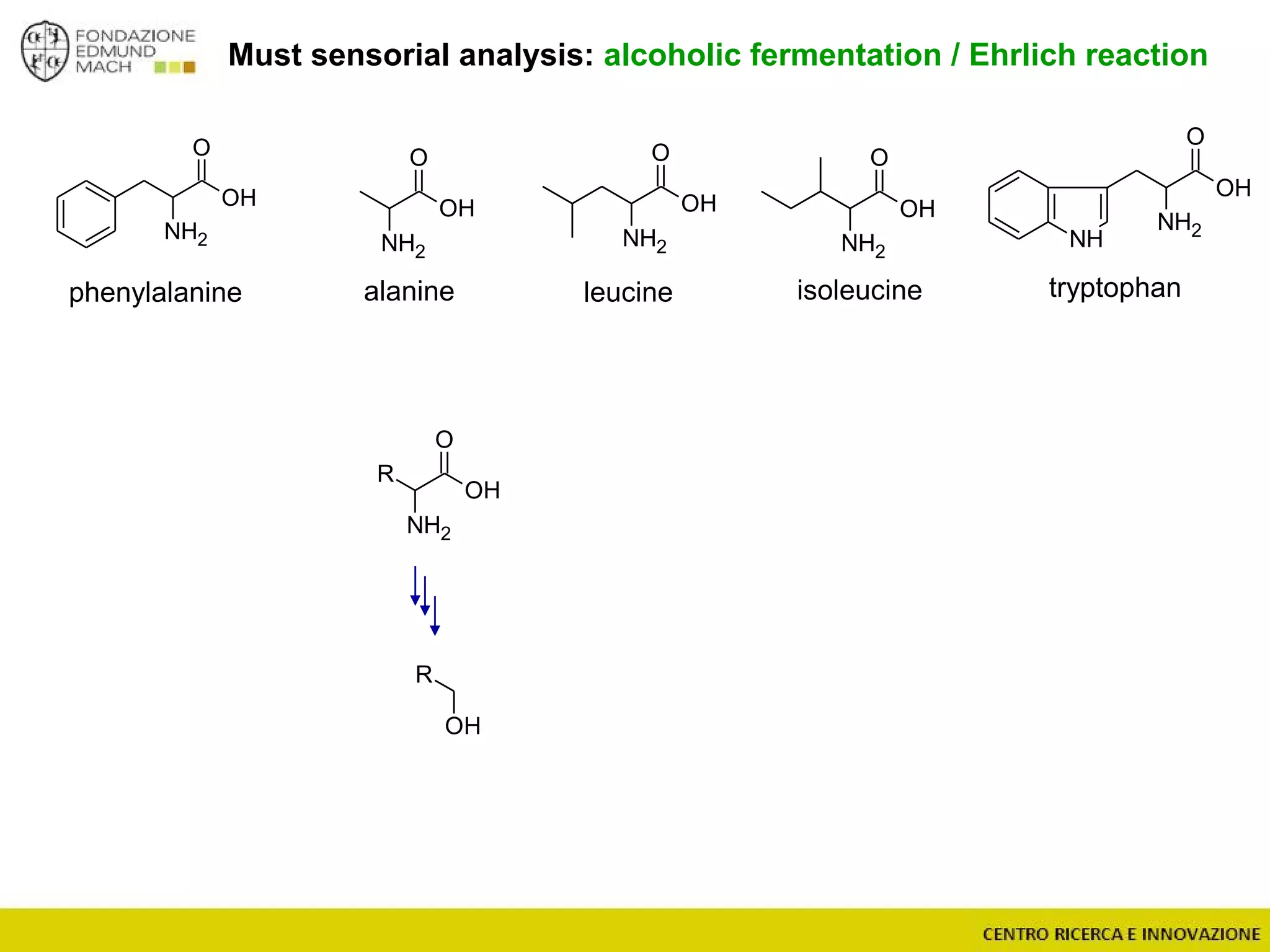
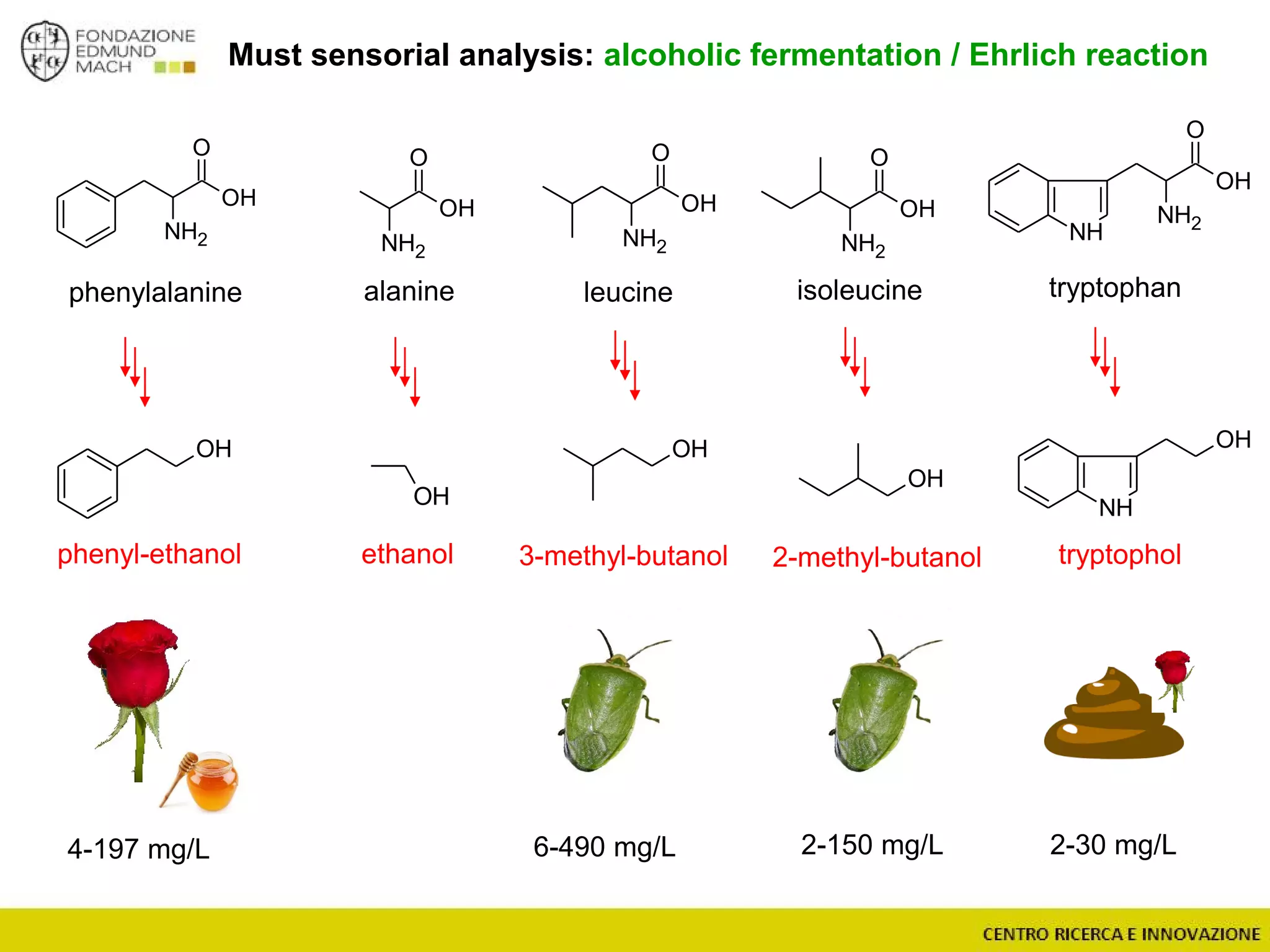
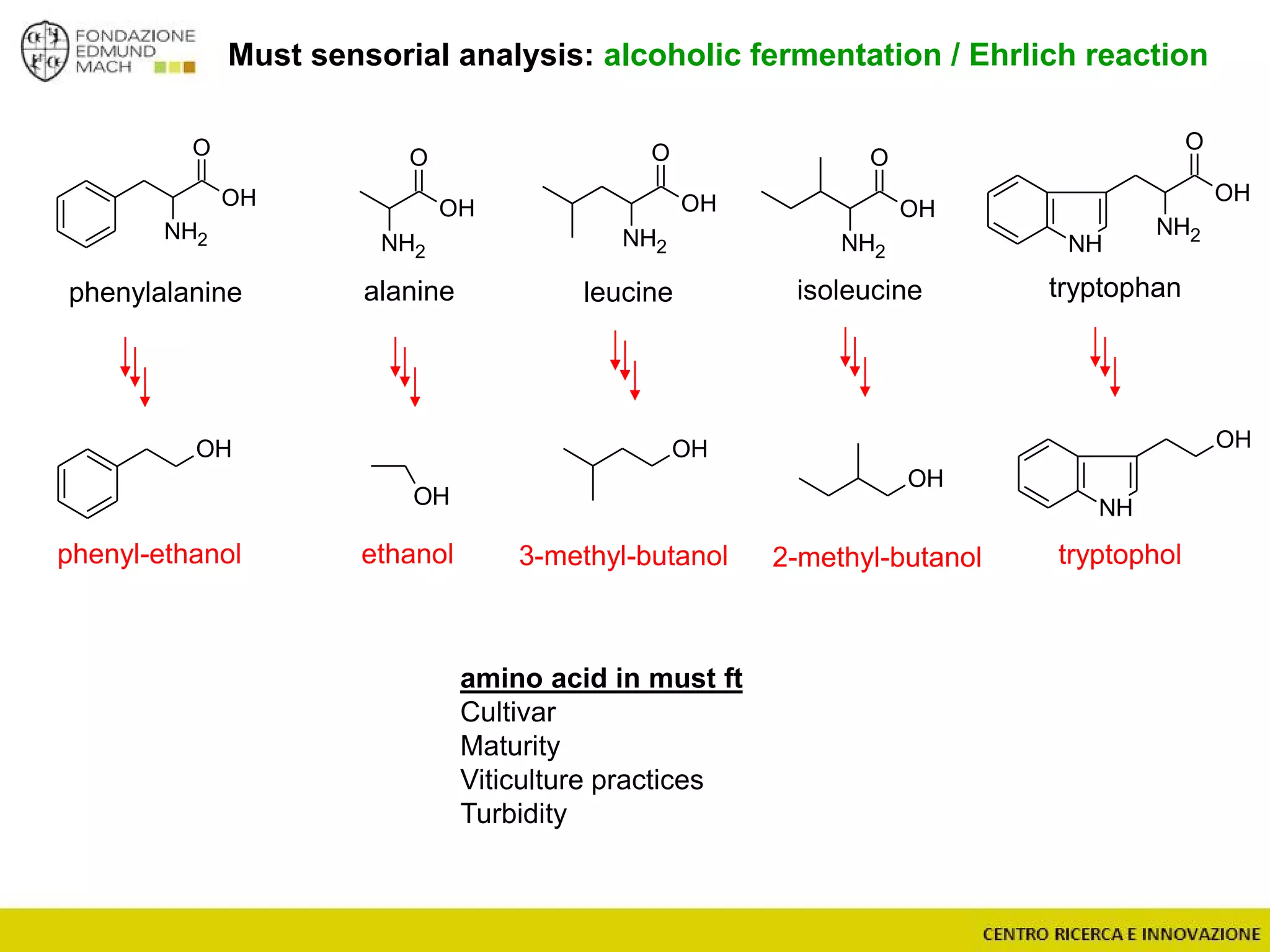
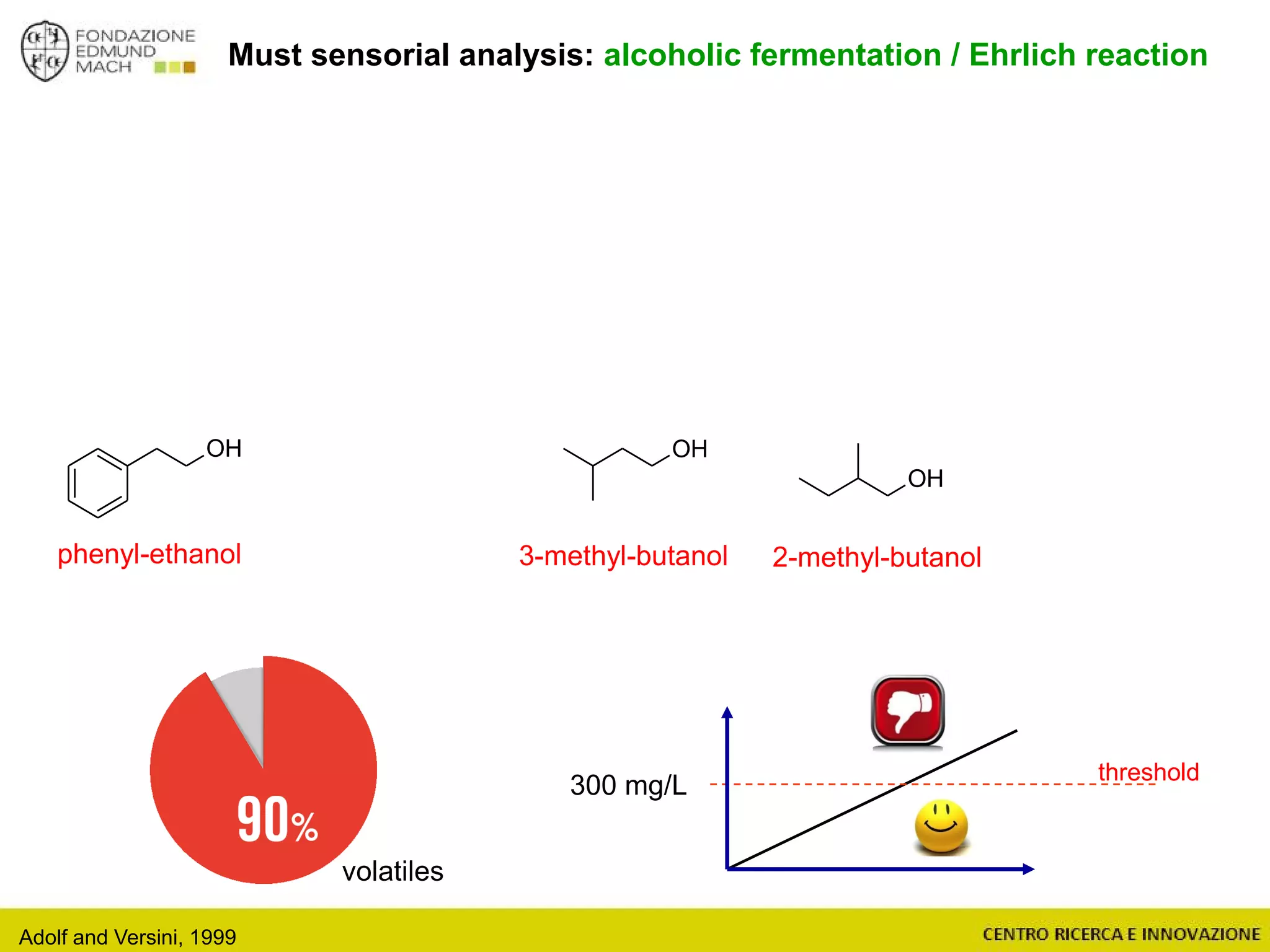
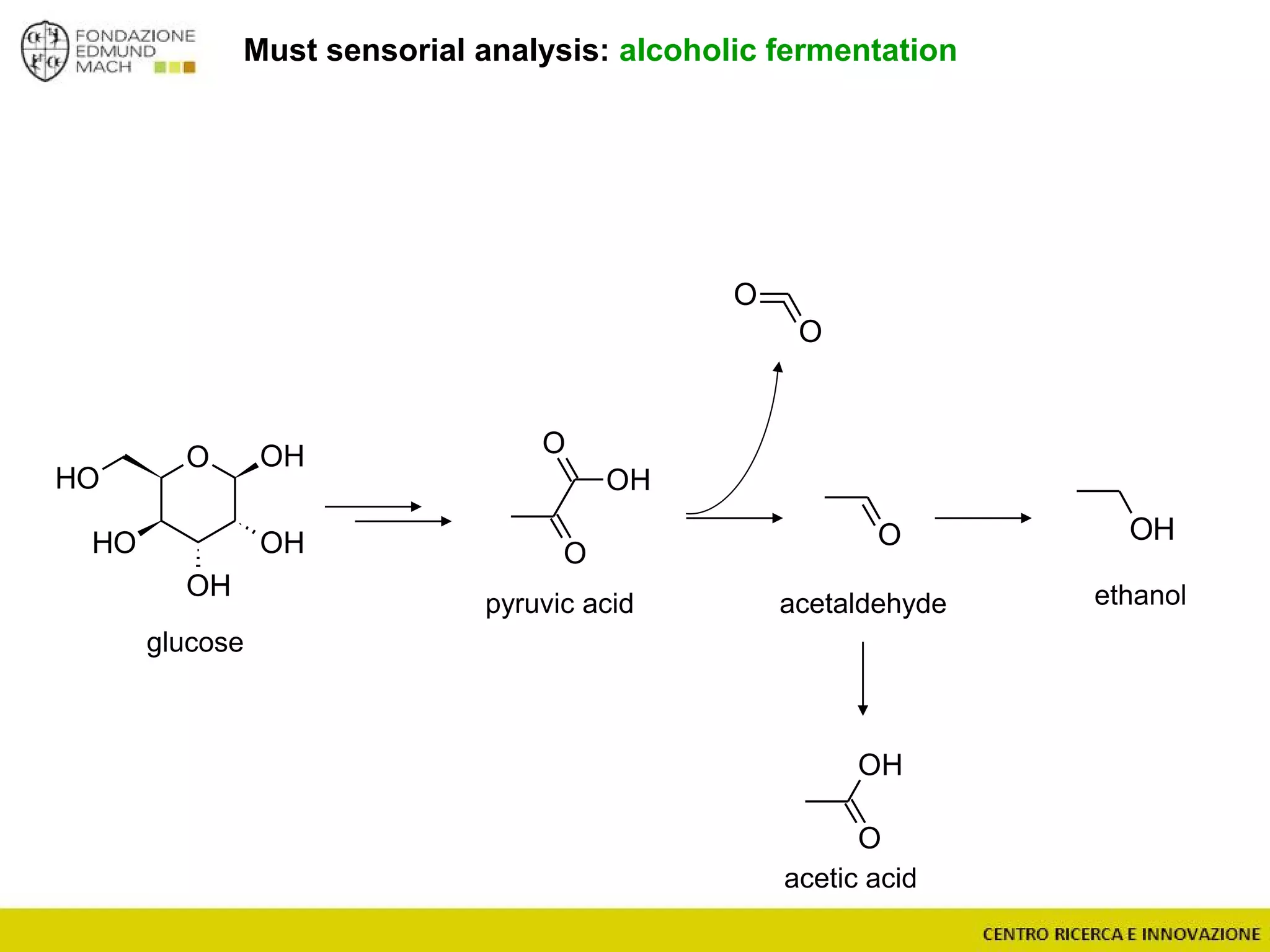
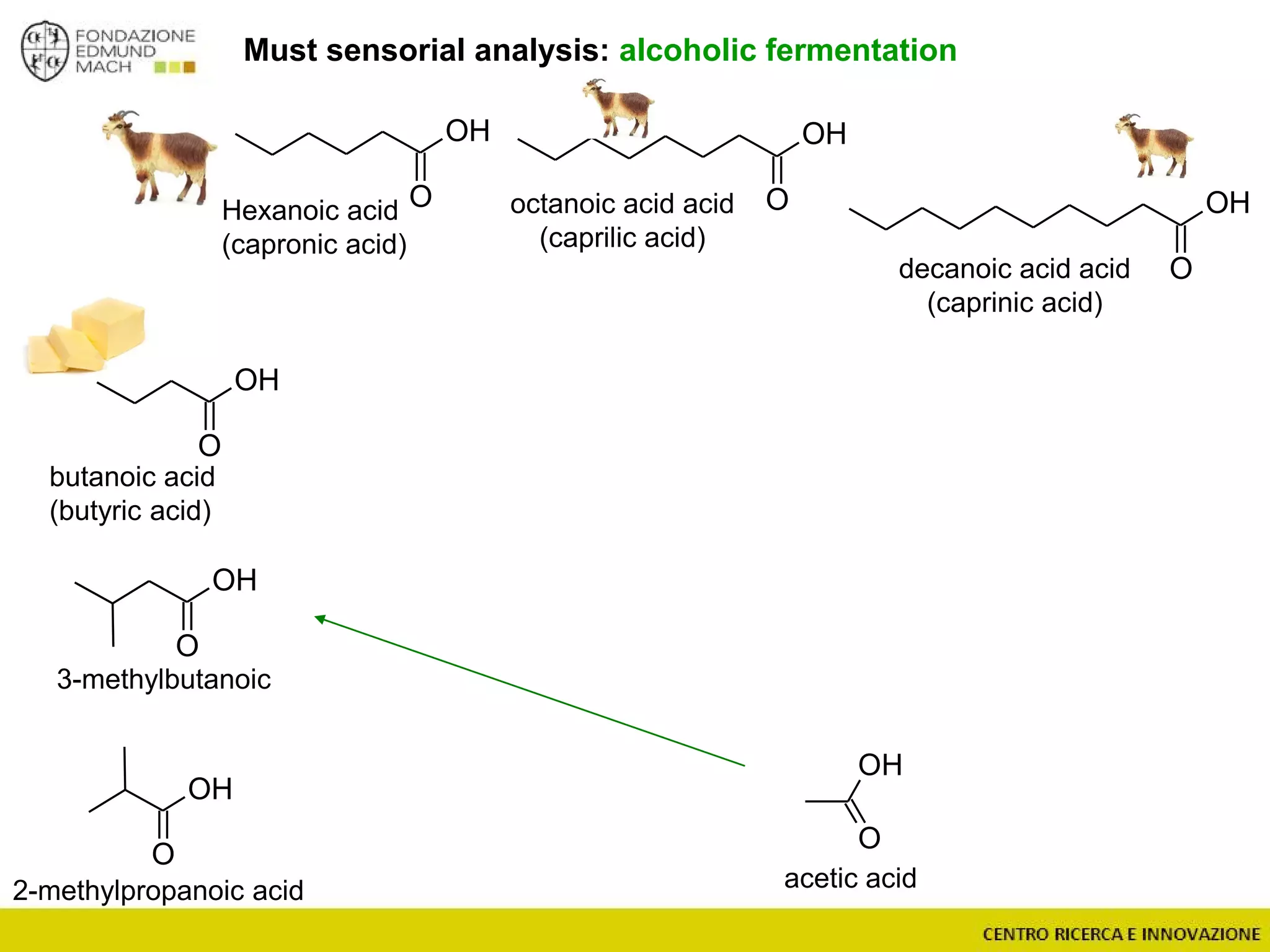
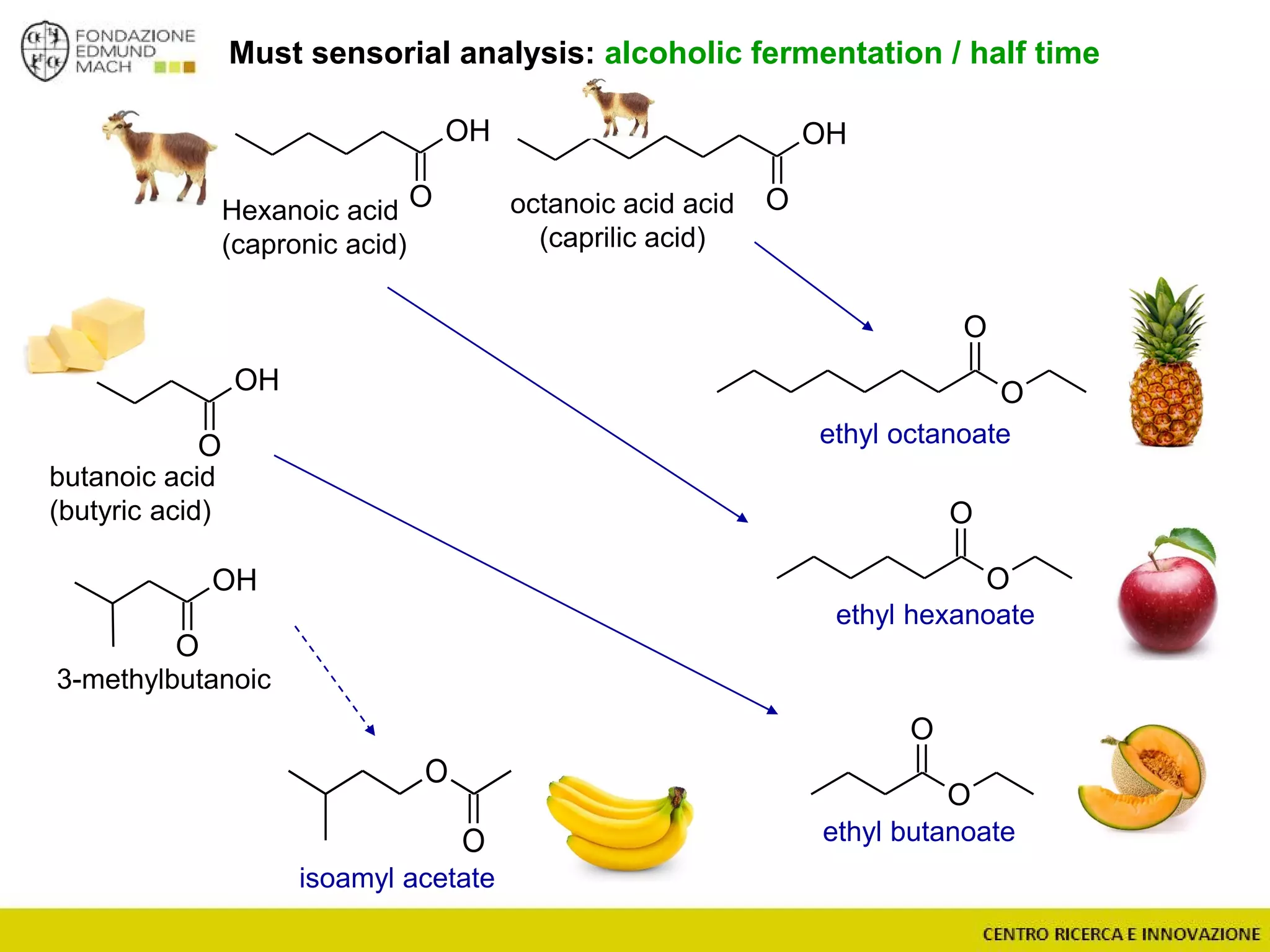
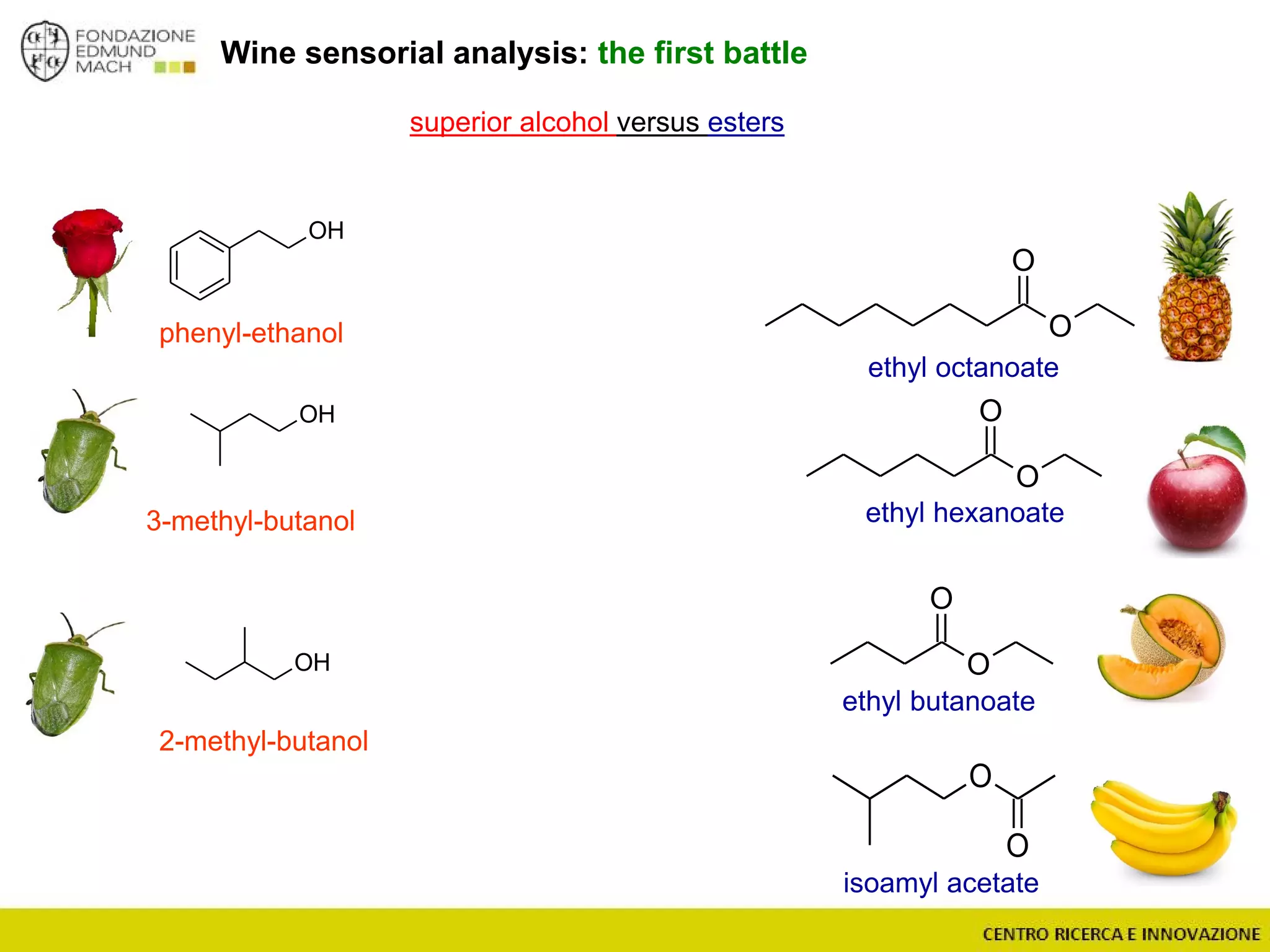
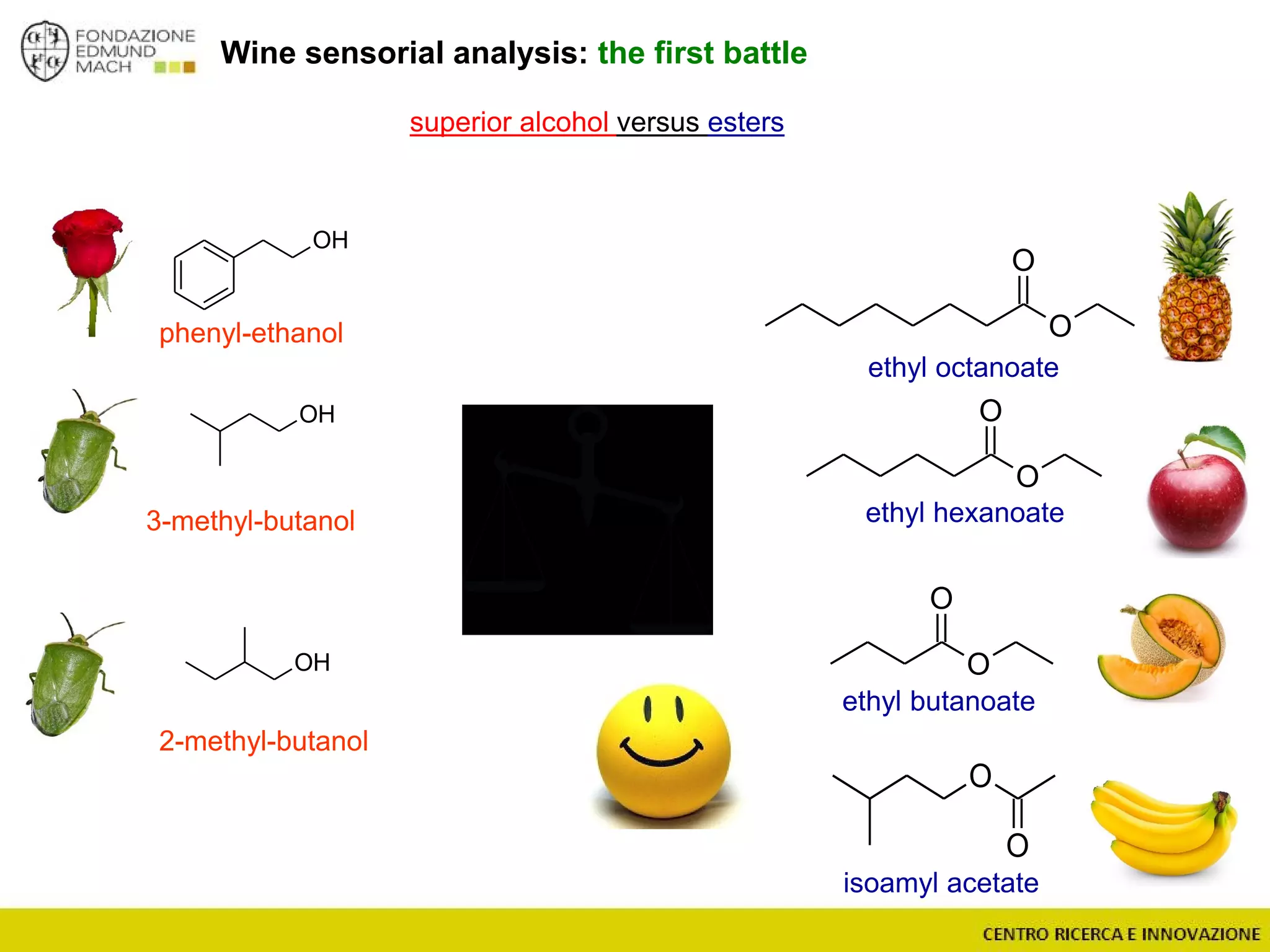
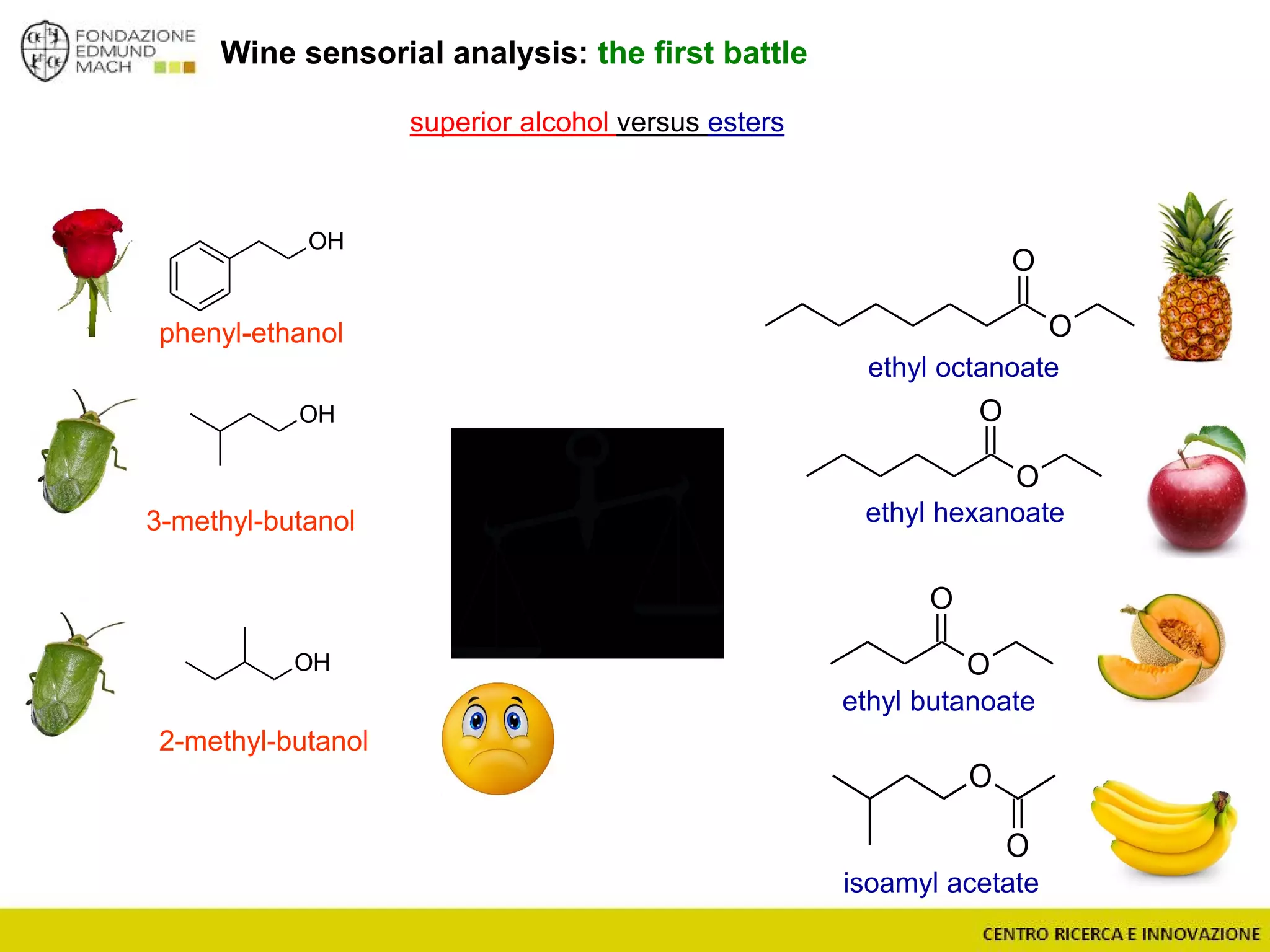
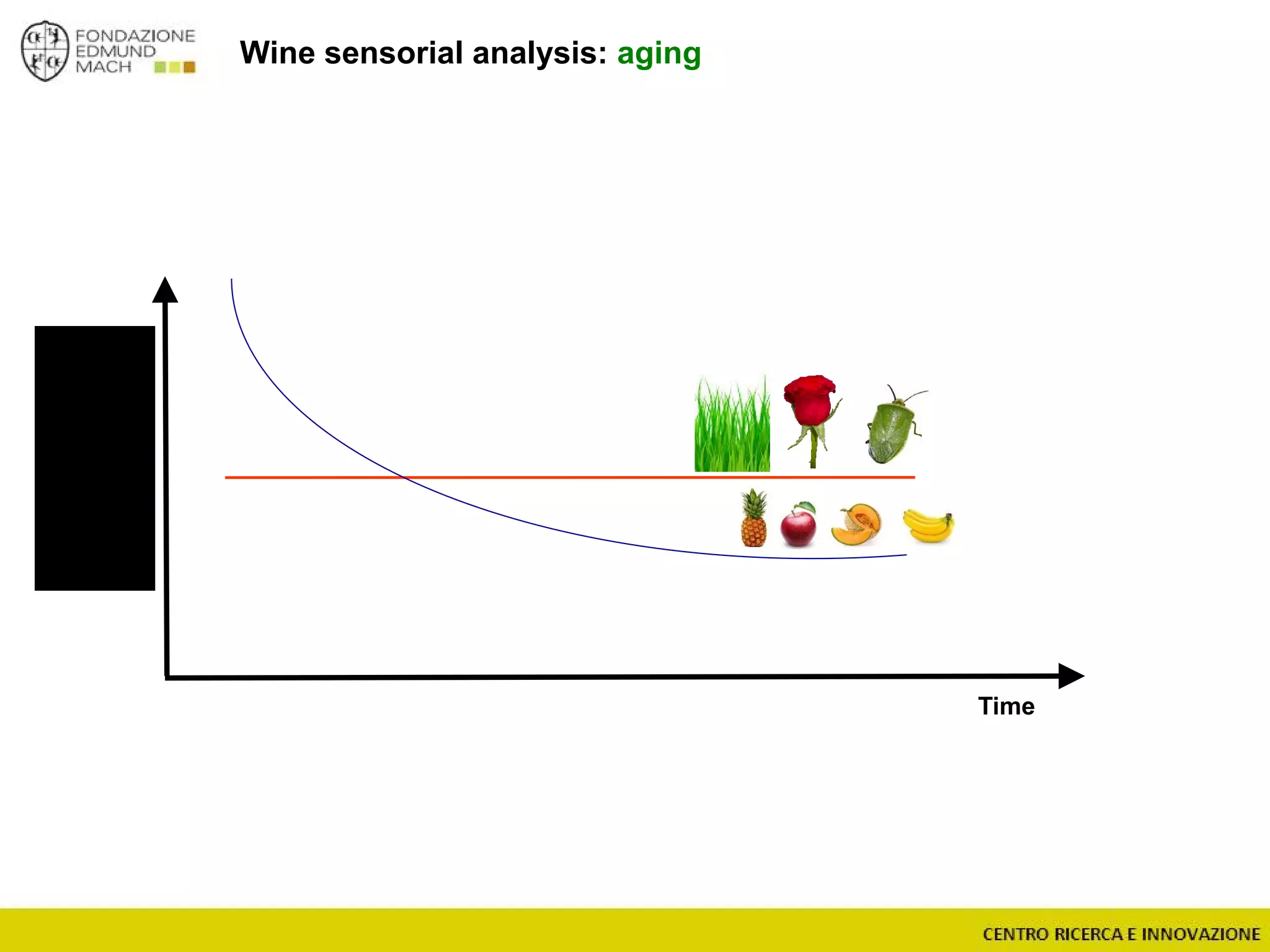
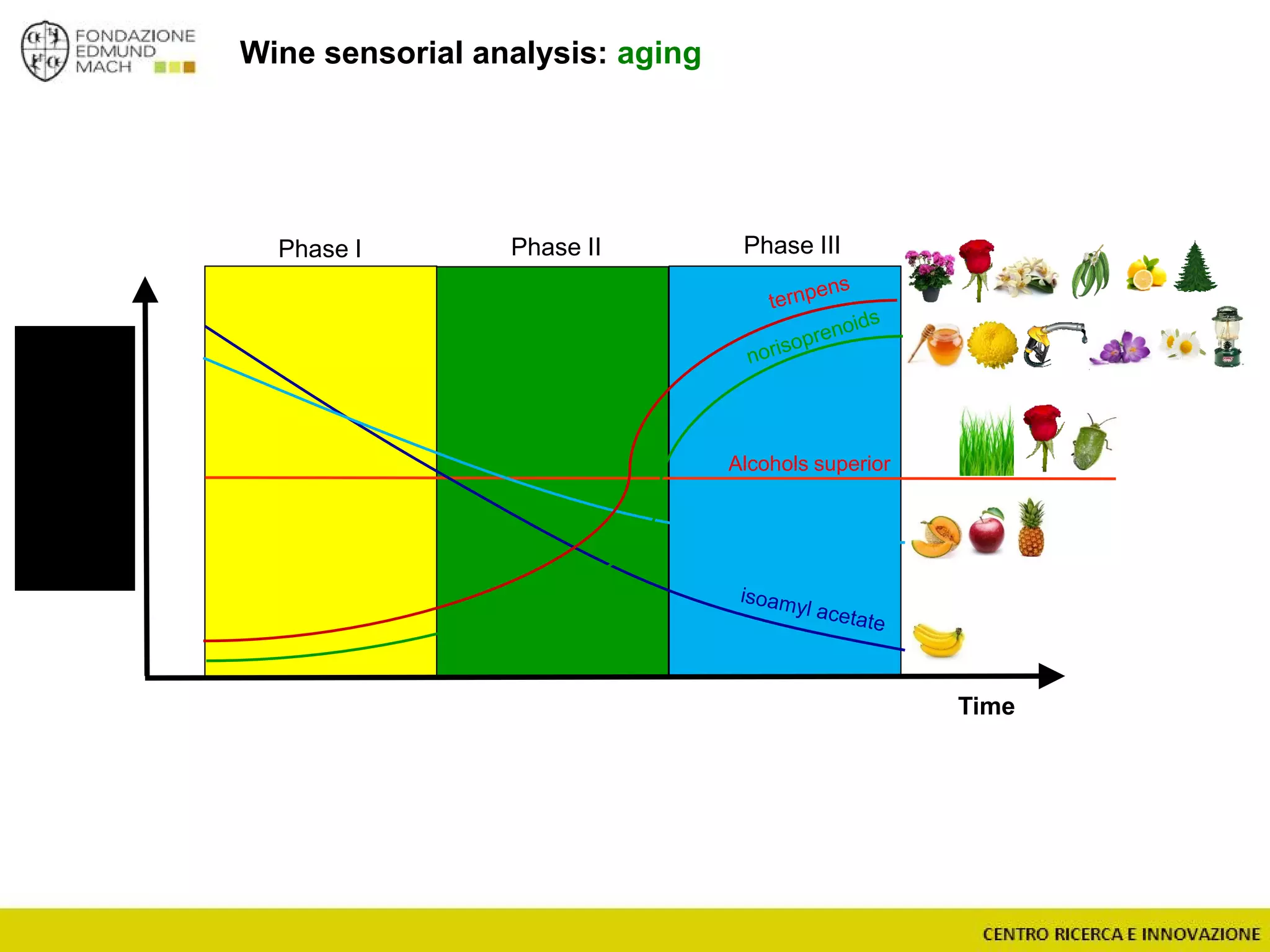
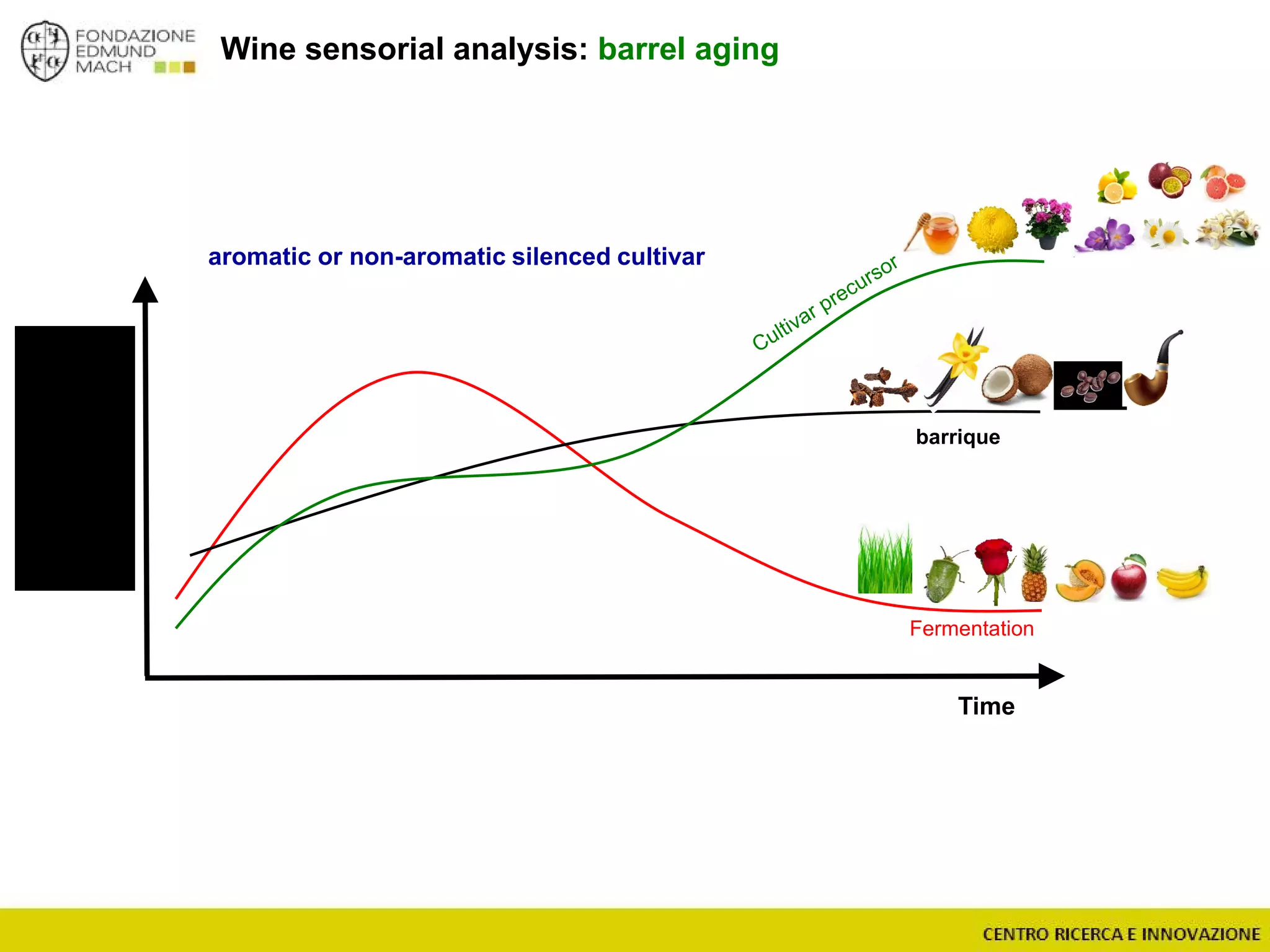
The document outlines a module on untargeted metabolomics in oenology and viticulture, detailing learning outcomes such as understanding wine metabolome terminology and familiarizing students with methods and applications. It consists of 30 hours of lectures, interactive exercises, and group lab work, with prerequisites in chemistry and statistics. The final assessment includes a written test and possibly an oral presentation, focusing on students' knowledge of metabolomics in wine production.