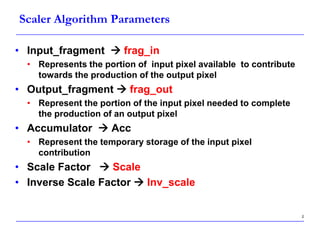
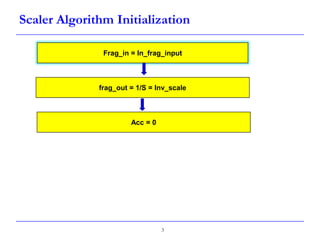
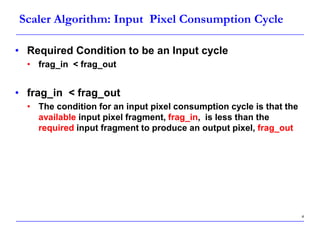
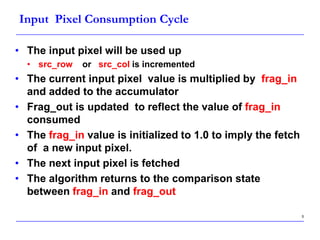
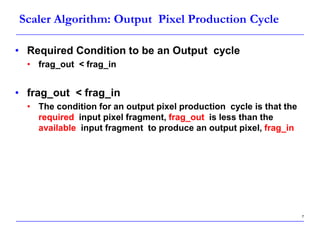
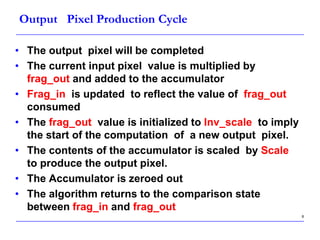
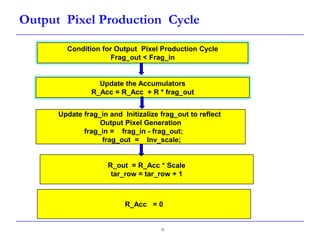
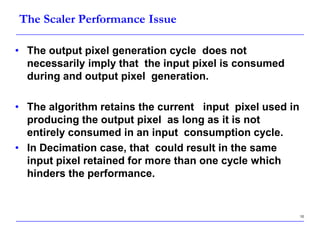
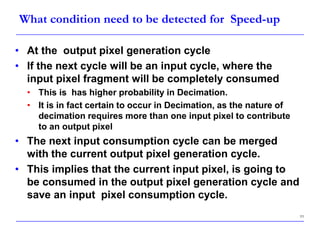
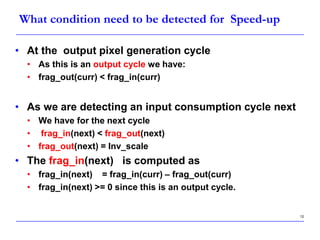
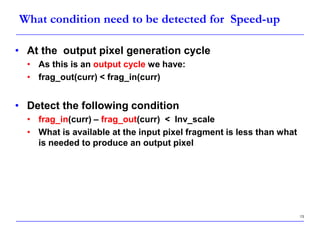
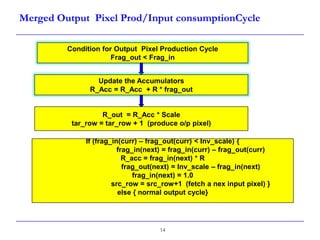
This document describes a speed-up technique for a Windows image scalar algorithm. It involves detecting when an output pixel generation cycle will be immediately followed by an input pixel consumption cycle. In this case, the cycles can be merged to improve performance. Specifically:
- During an output cycle, the algorithm checks if the remaining input fragment after subtracting the output fragment is less than the inverse scale factor.
- If so, the input pixel is fully consumed in this merged cycle. The accumulator is updated, the output pixel is produced, and a new input pixel is fetched.
- This avoids retaining the input pixel for an extra cycle and improves efficiency, especially for decimation cases where an input pixel often contributes to multiple