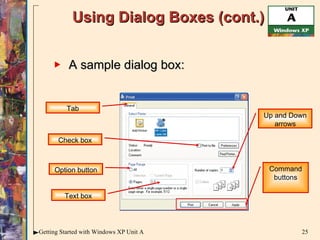
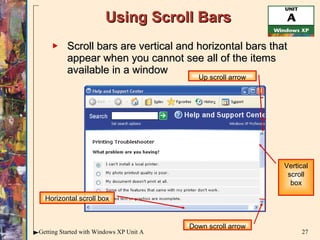
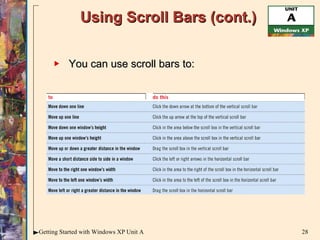
This document provides an overview of how to use the basic features of Microsoft Windows, including starting Windows, using the desktop, starting programs, customizing menus and toolbars, working with windows, dialog boxes, help features, and shutting down. It describes the mouse, icons, taskbar, desktop, programs, files, menus, shortcuts, scroll bars, dialog boxes, and how to open programs, move and resize windows, get help, and properly close programs and shut down Windows.






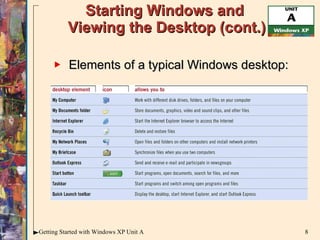
![Starting Windows and Viewing the Desktop (cont.) Turn on your computer and monitor Windows automatically starts and displays the desktop, or a logon screen where you must enter a password, then press [Enter] Mouse pointer Start button Desktop background Taskbar Icon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowsxpunita-110629102649-phpapp01/85/Windows-xp-unit-a-7-320.jpg)











![Using Menus, Keyboard Shortcuts, and Toolbars (cont.) A keyboard shortcut lets you press a button or combination of buttons to perform a task or navigate through a menu or dialog box For example, press [Ctrl][C] to copy selected text in a document On a menu, keyboard navigation indicators , underlined letters in a command name, can be used instead of the mouse to select items For example, press [Alt][V] to open the View menu, then press [T] to open the Toolbars submenu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowsxpunita-110629102649-phpapp01/85/Windows-xp-unit-a-22-320.jpg)




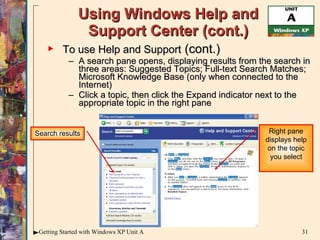
![Using Windows Help and Support Center (cont.) To use Help and Support: Click the Start button on the taskbar, then click Help and Support The Help and Support Center window opens In the Search text box, type the search criteria, then press [Enter] Search text box Links for popular topics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowsxpunita-110629102649-phpapp01/85/Windows-xp-unit-a-30-320.jpg)