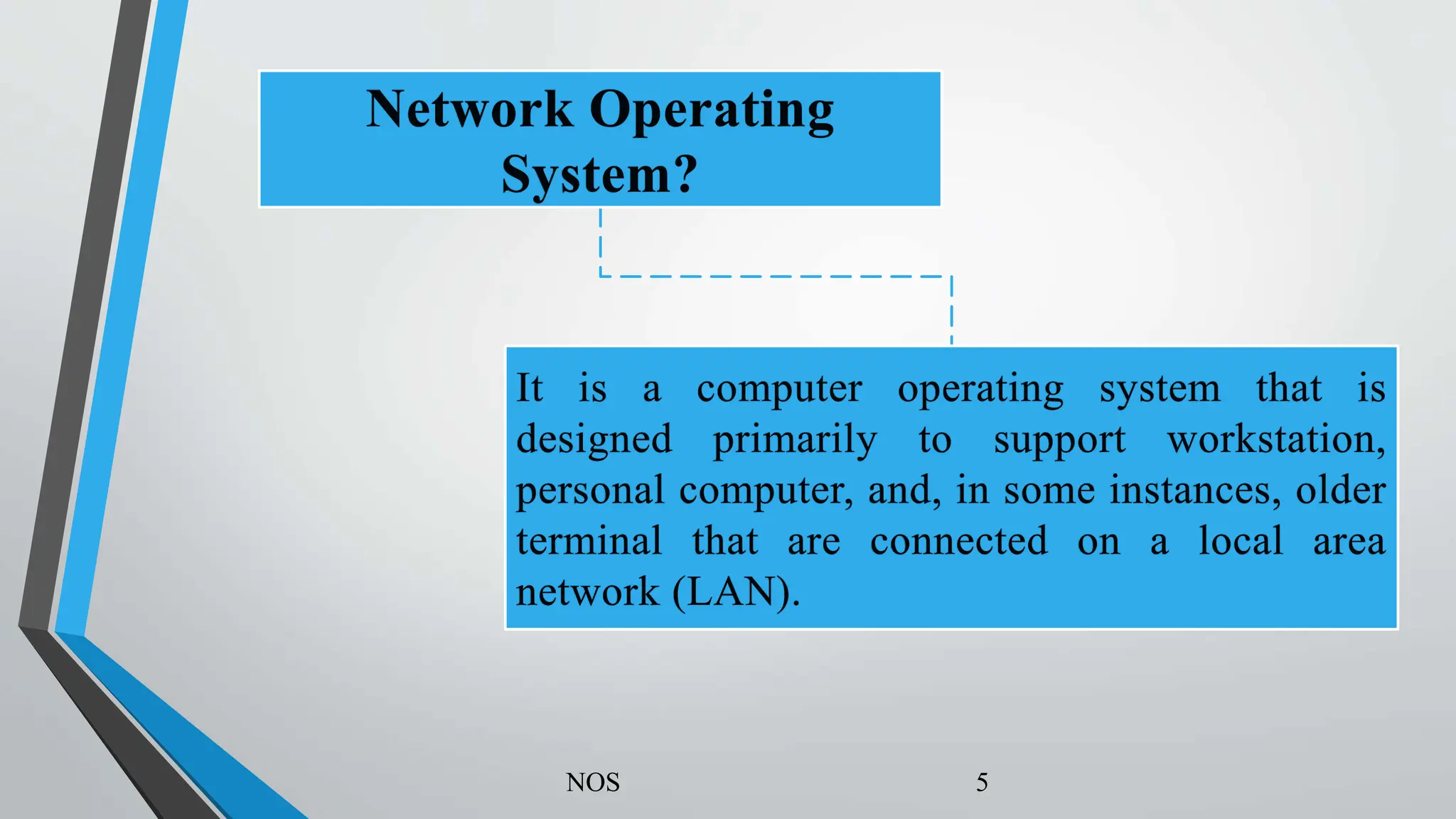
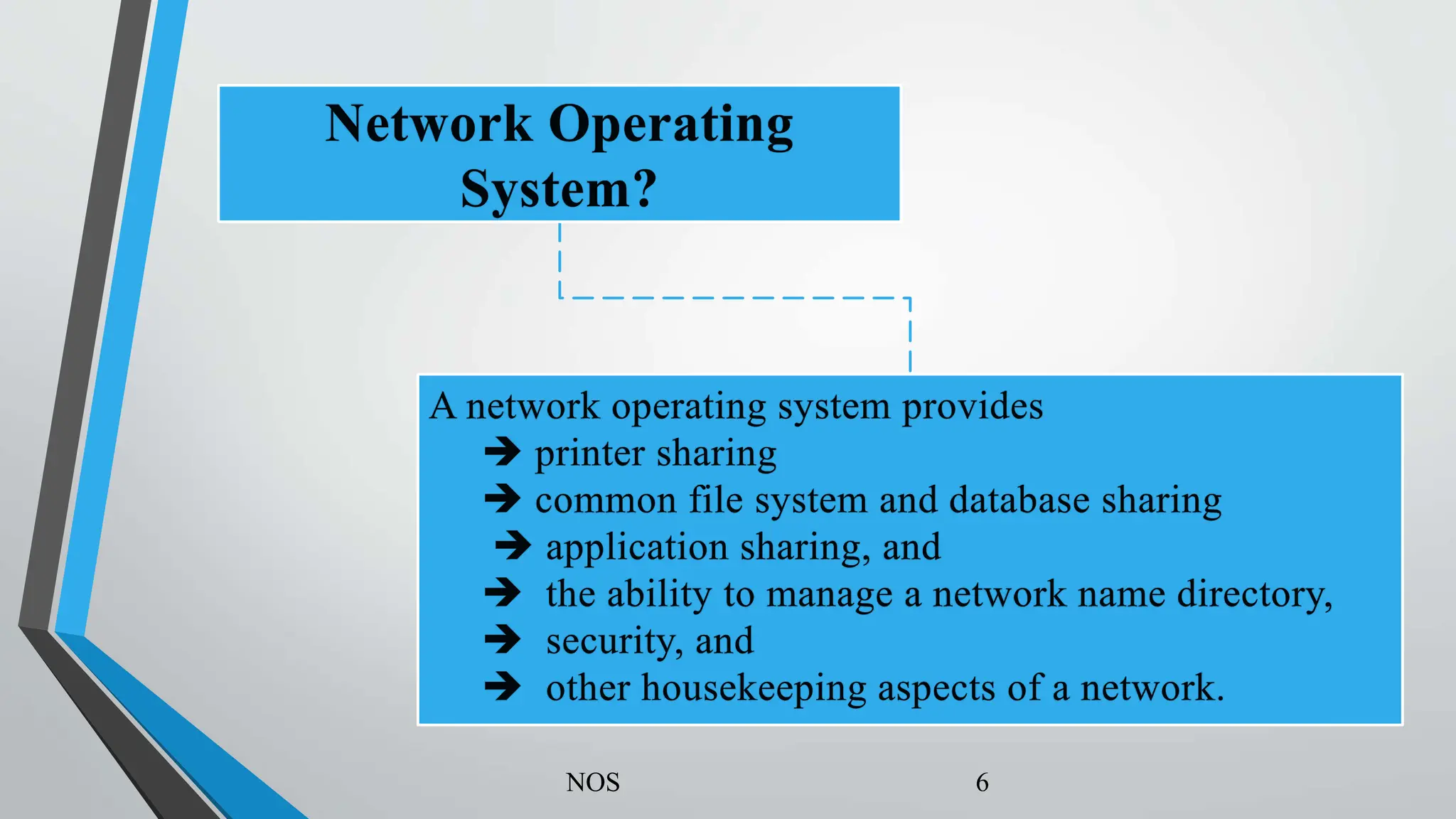
This document provides an overview of network operating systems (NOS) and Windows network concepts. It defines an NOS as a program that manages computer hardware and acts as an intermediary between the user and hardware. The two main types of NOS architecture are peer-to-peer and client/server. The most popular NOS are Windows Server and Linux Server. Windows network concepts include the differences between workgroup and domain networking models, an overview of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and domain controllers.