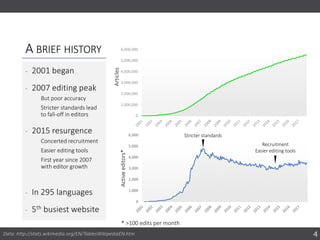
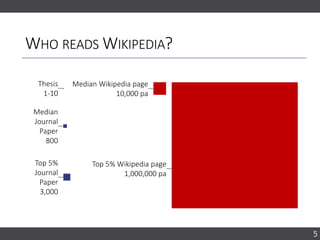
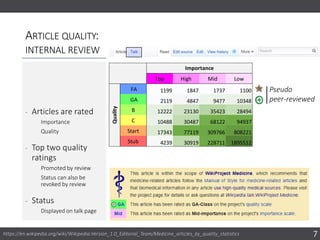
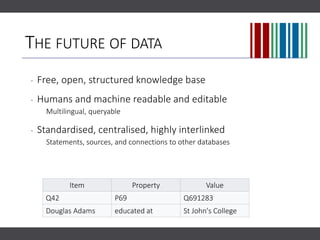
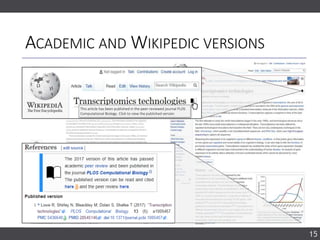
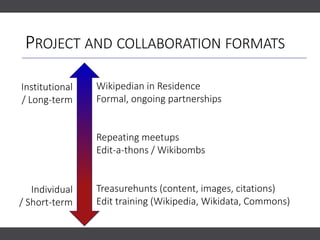
The document discusses the importance of collaborating with Wikipedia, focusing on the evolution of its content and engagement of academics. It highlights different project formats, the quality of articles, and the potential impact of contributions to increase accurate information dissemination. The future aims to encourage more diverse participation and improve editing tools while recognizing the value of contributions.