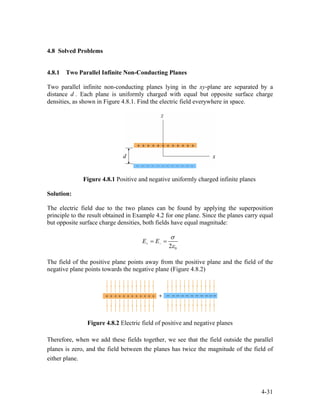
This document describes Gauss's law and how to apply it to calculate electric fields. It includes:
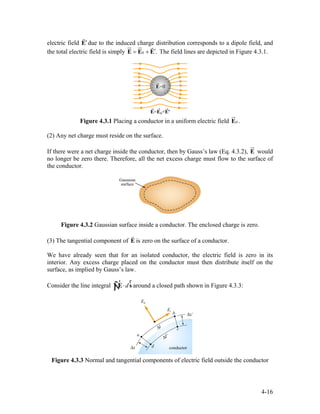
1) An introduction to electric flux and Gauss's law, which states that the total electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the net charge enclosed.
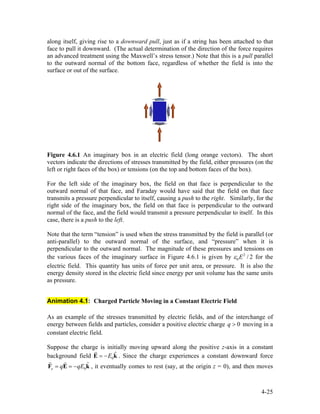
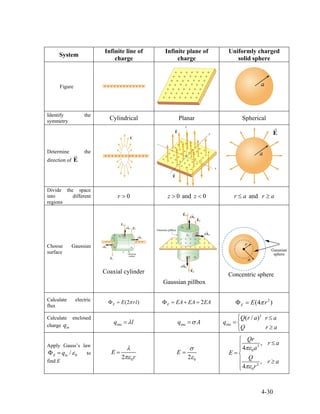
2) Examples of applying Gauss's law to calculate the electric field of an infinitely long rod with uniform charge density, an infinite plane of charge, and a spherical shell.
3) Guidelines for using Gauss's law, such as choosing an appropriate Gaussian surface where the electric field is constant over parts of the surface.








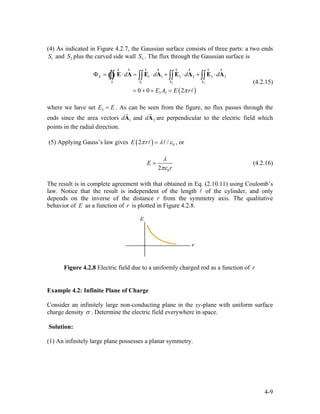
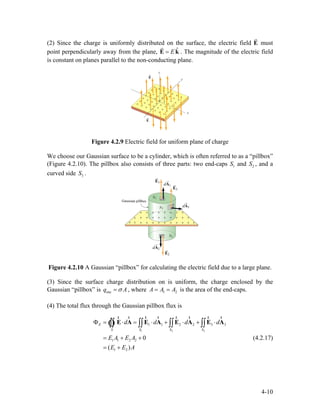




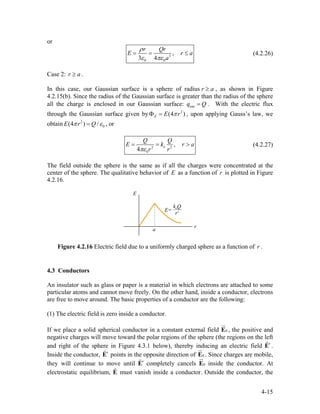











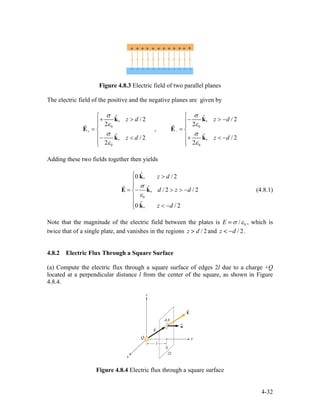




![charge density +ρ0 . The adjacent P-type material lies in the range and has
uniform charge density
−a < z< 0
−ρ0 . Thus:
0
0
0
( , , ) ( ) 0
0 | |
z a
x y z z a z
z a
ρ
ρ ρ ρ
+ <⎧
⎪
<
= = − − < <⎨
⎪
>⎩
(a) Find the electric field everywhere.
(b) Find the potential difference between the points and . The point is located on a
plane parallel to the slab a distance from the center of the slab. The point is
located on plane parallel to the slab a distance
P1 P2. P1.
z1 > a P2.
z2 < −a from the center of the slab.
4.10.3 Sphere with Non-Uniform Charge Distribution
A sphere made of insulating material of radius R has a charge density arρ = where a
is a constant. Let be the distance from the center of the sphere.r
(a) Find the electric field everywhere, both inside and outside the sphere.
(b) Find the electric potential everywhere, both inside and outside the sphere. Be sure to
indicate where you have chosen your zero potential.
(c) How much energy does it take to assemble this configuration of charge?
(d) What is the electric potential difference between the center of the cylinder and a
distance inside the cylinder? Be sure to indicate where you have chosen your zero
potential.
r
4.10.4 Thin Slab
Let some charge be uniformly distributed throughout the volume of a large planar slab of
plastic of thickness d . The charge density is ρ . The mid-plane of the slab is the y-z
plane.
(a) What is the electric field at a distance x from the mid-plane when | | 2x d< ?
(b) What is the electric field at a distance x from the mid-plane when | | 2x d> ?
[Hint: put part of your Gaussian surface where the electric field is zero.]
4-37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyweneedgsingl-160327141054/85/Why-we-need-Gaussian-surface-in-Gauss-s-law-37-320.jpg)