This document defines and explains different tree data structures:
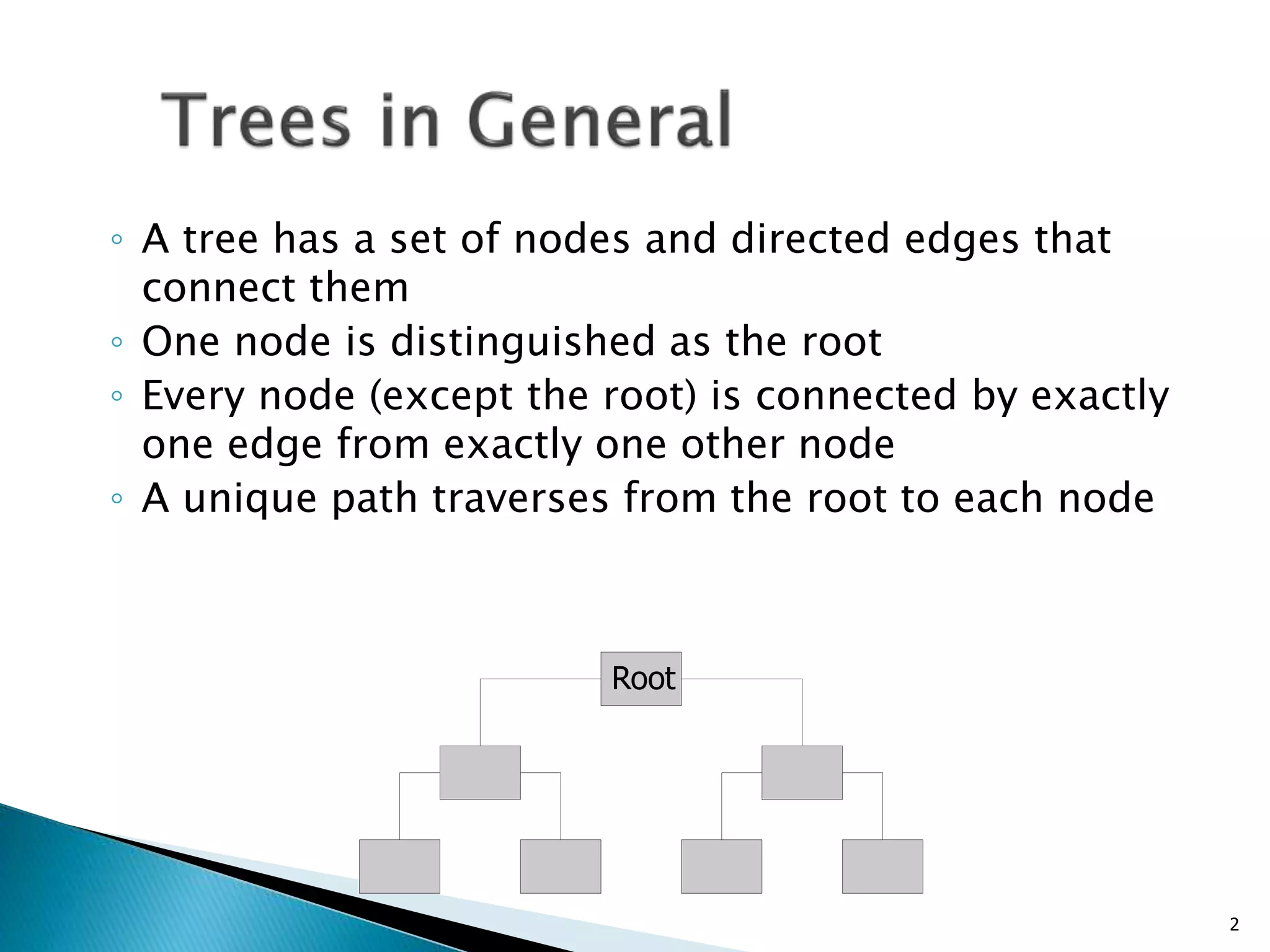
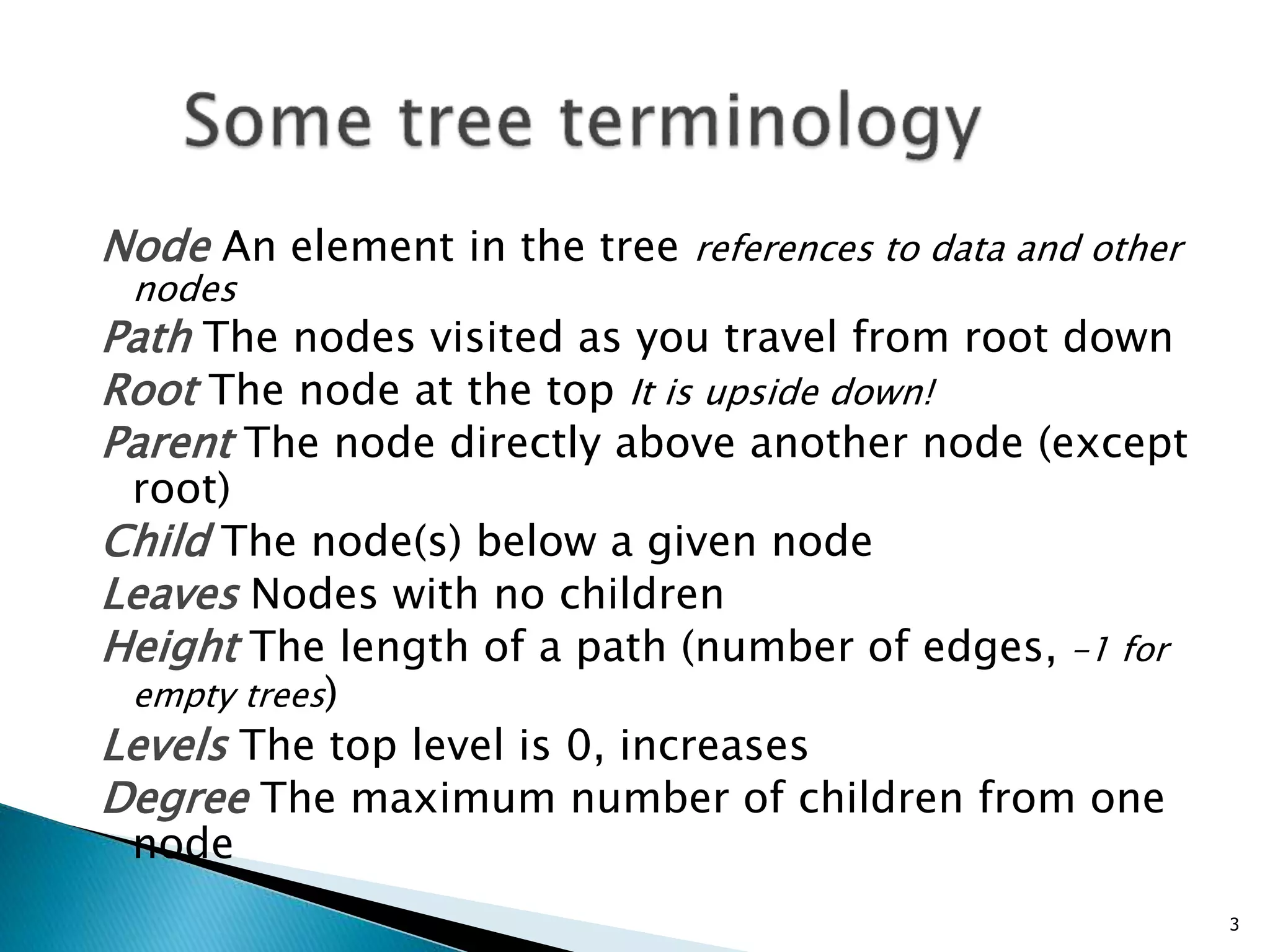
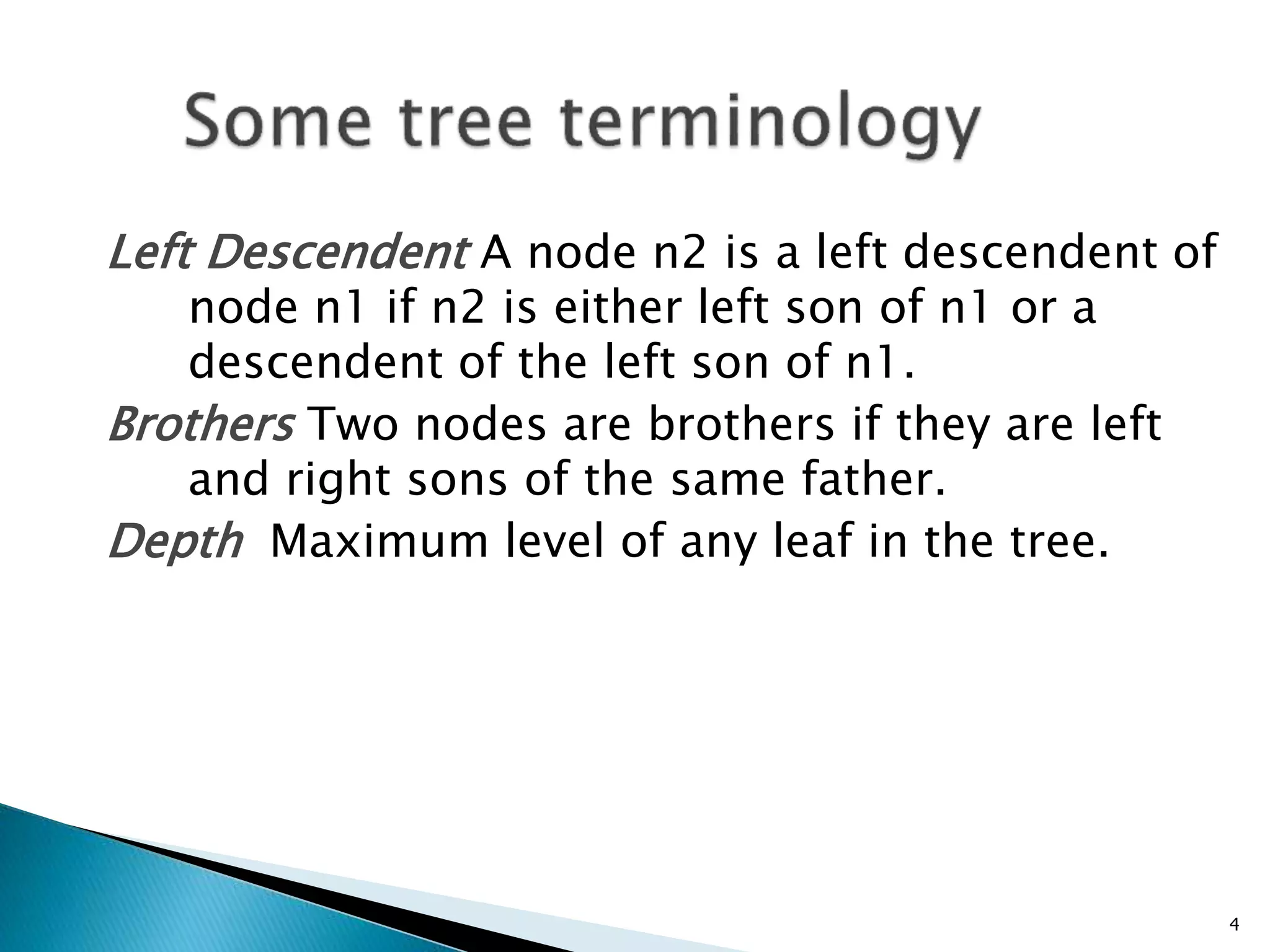
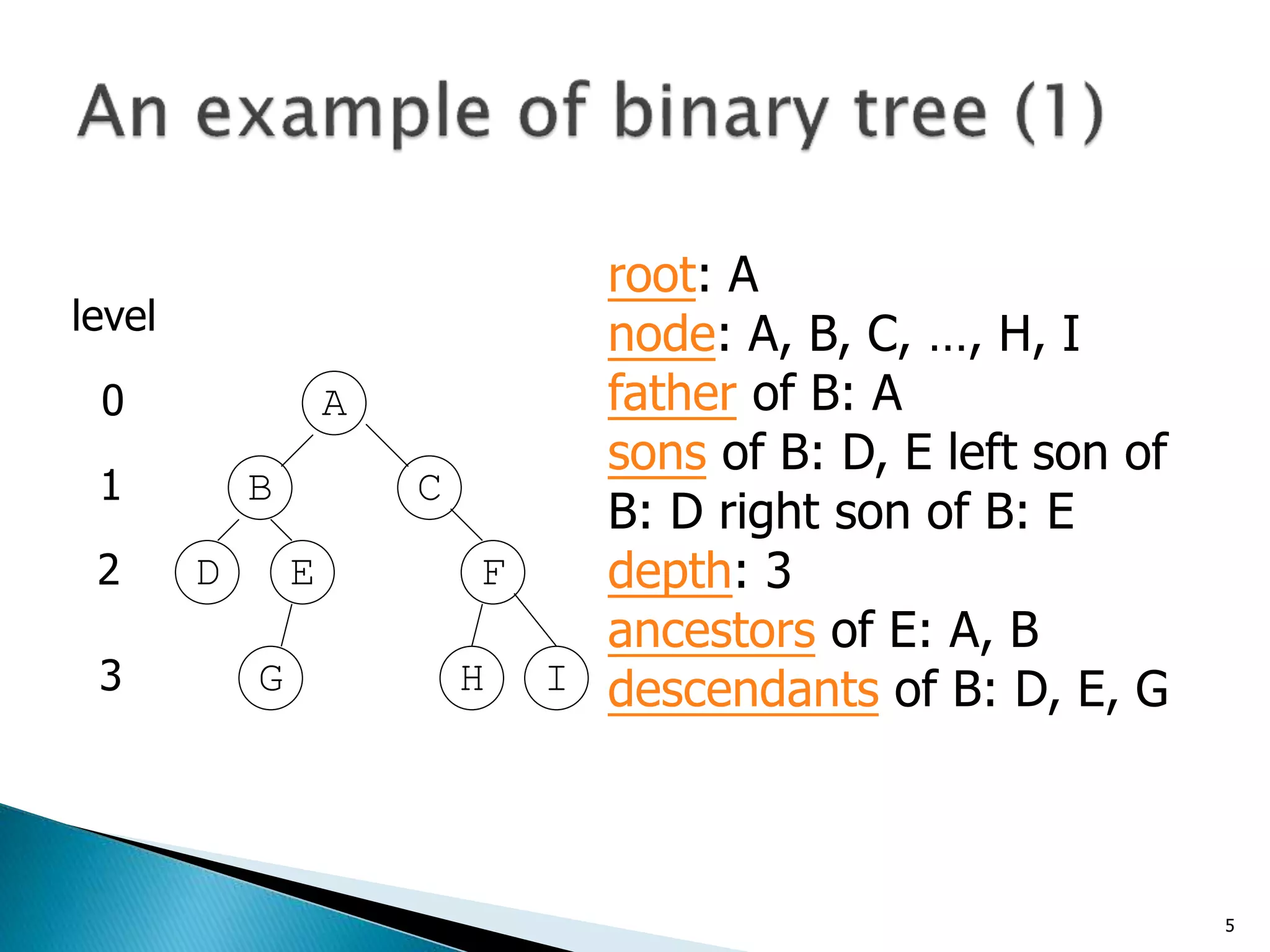
- A tree consists of nodes connected by edges, with one root node and each non-root node connected to exactly one parent node.
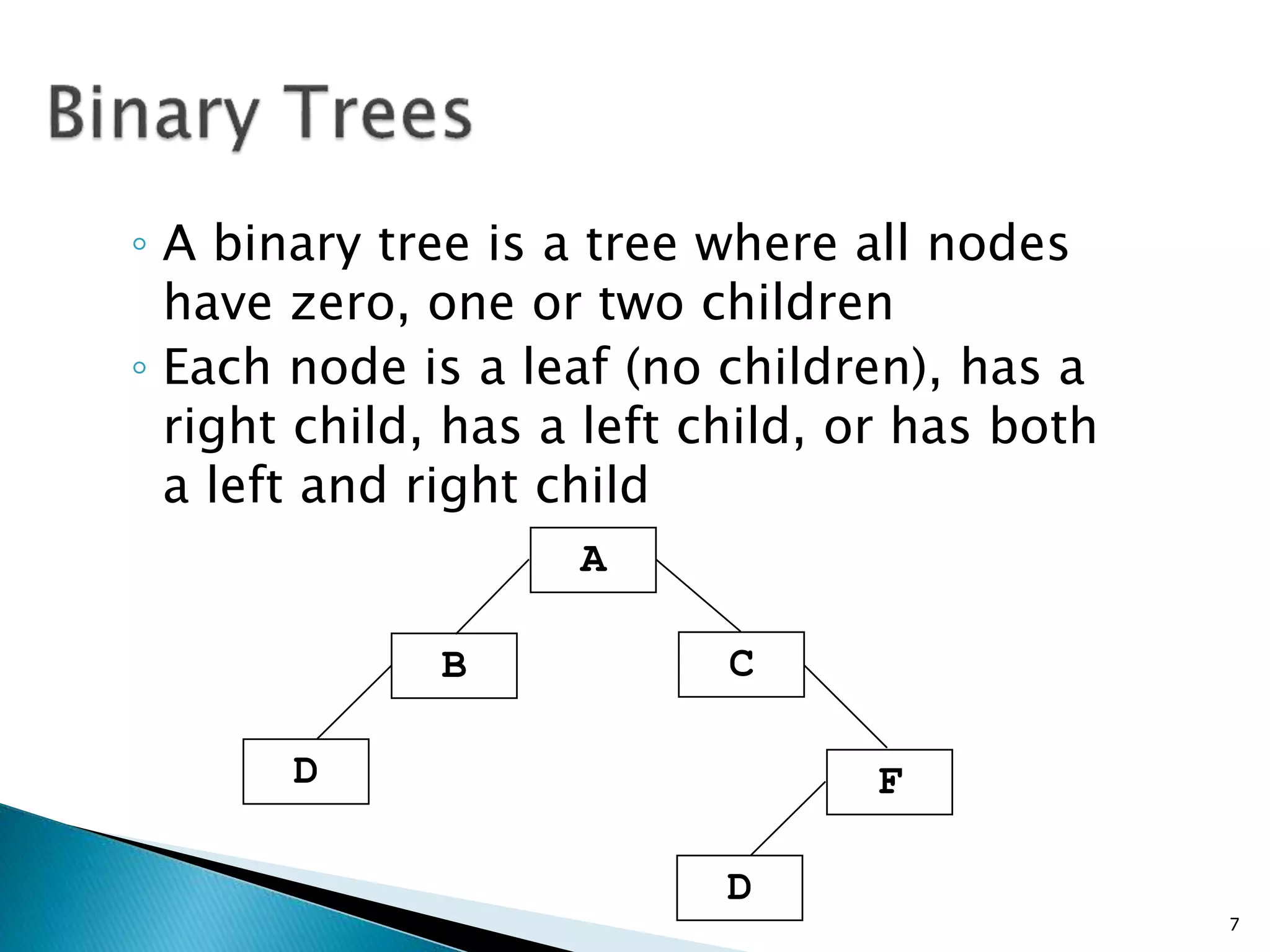
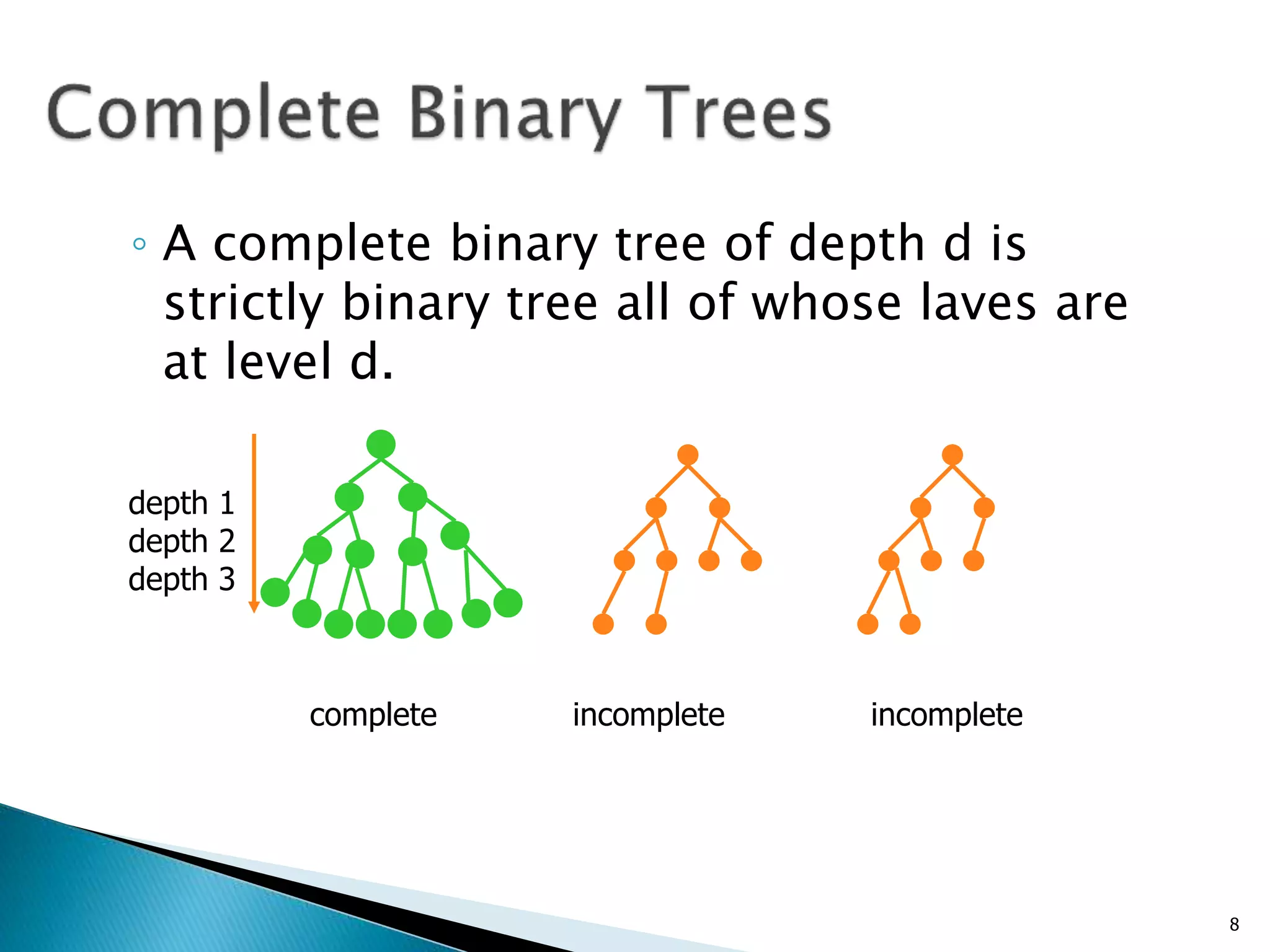
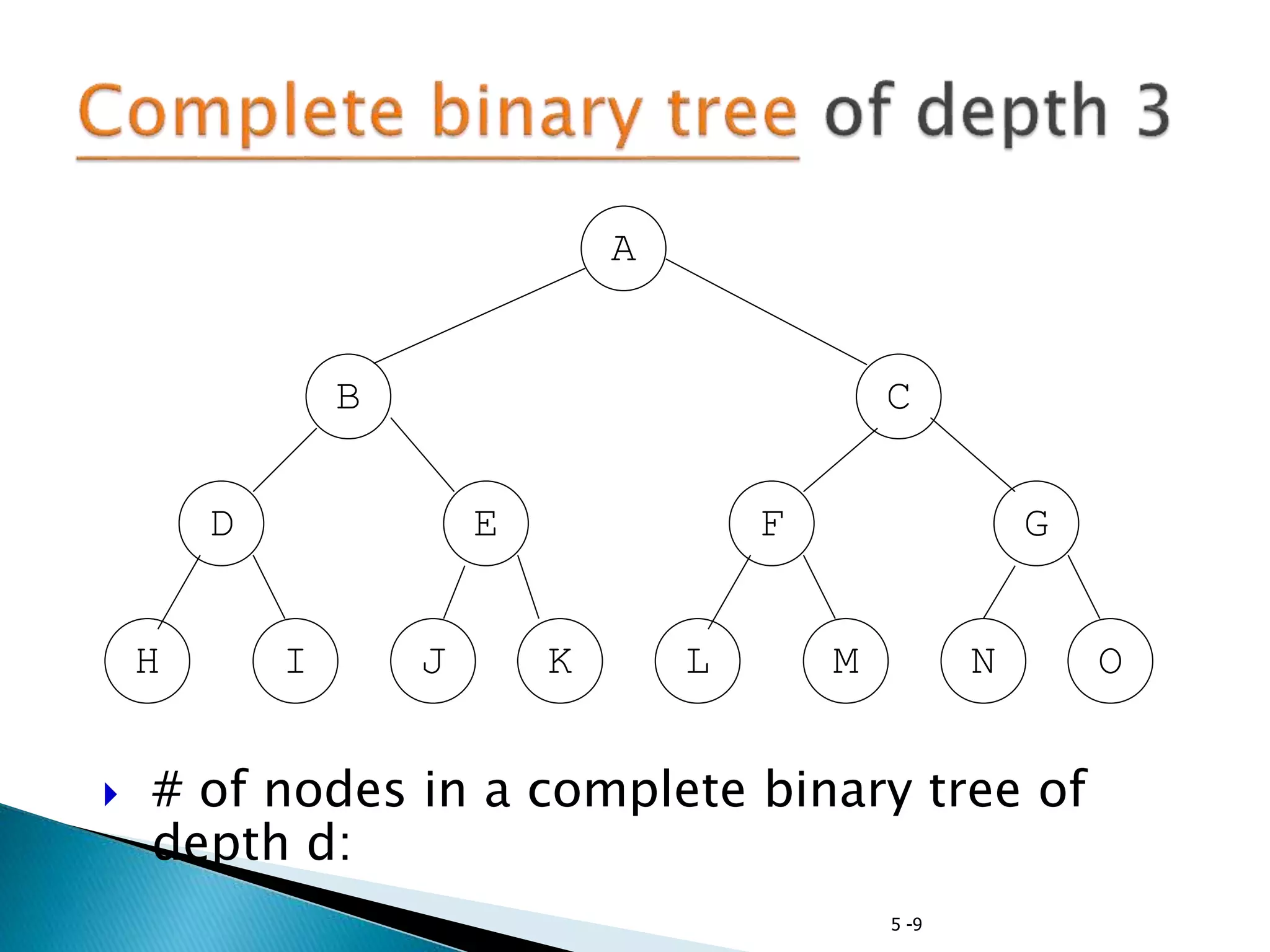
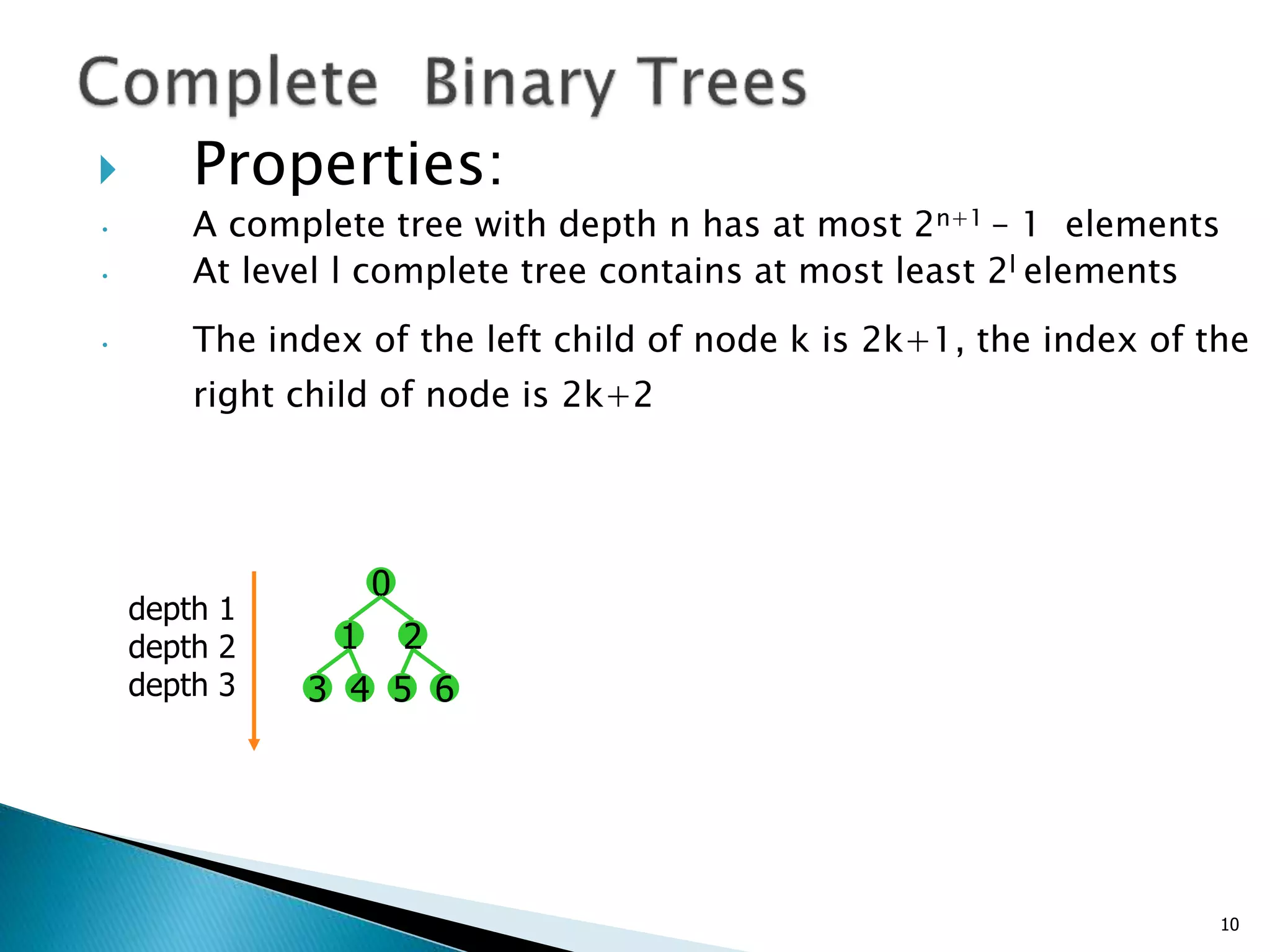
- Binary trees restrict nodes to having at most two children, and complete binary trees ensure all levels are fully filled except possibly the lowest.
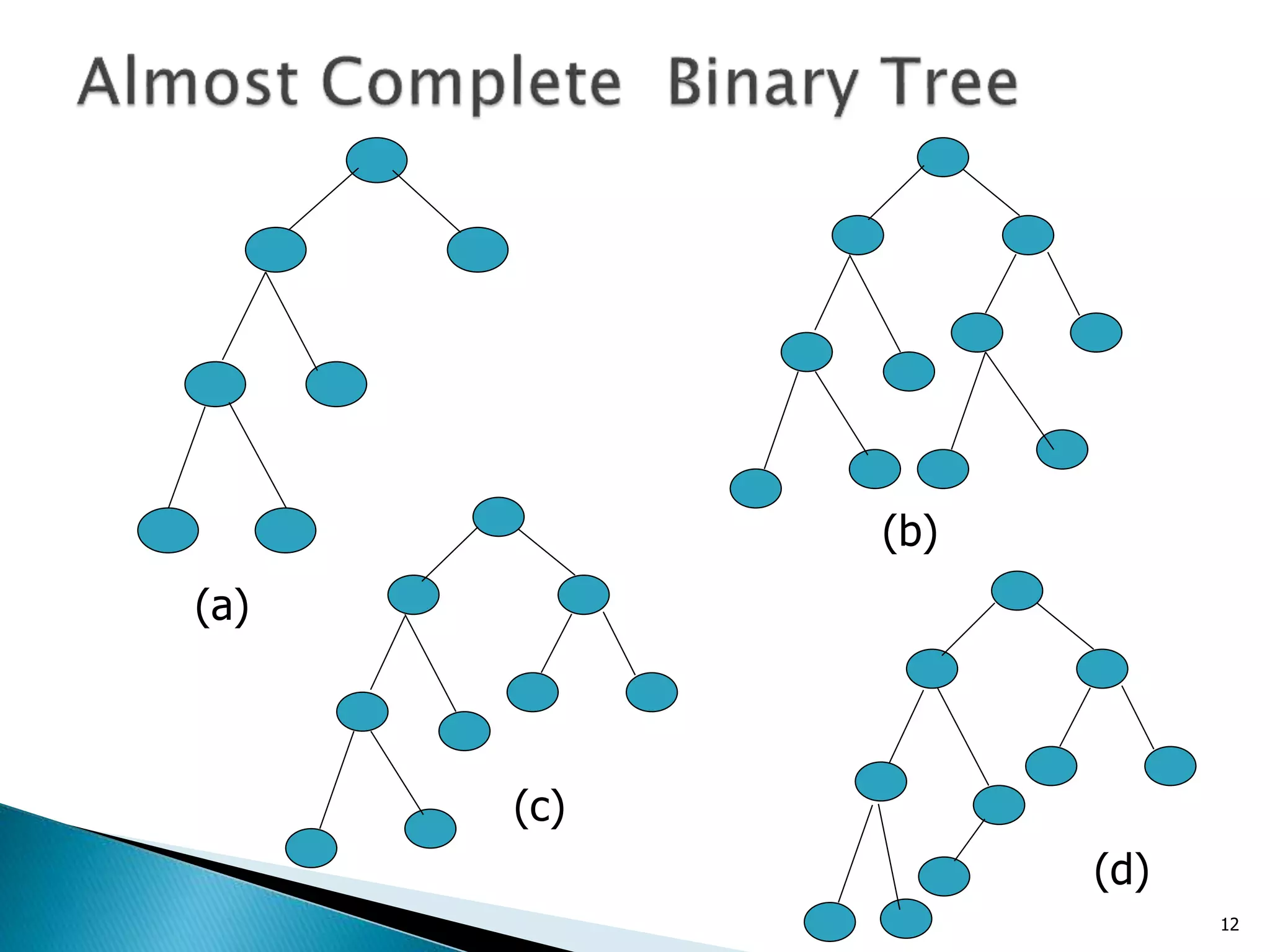
- An almost complete binary tree only allows missing children for nodes whose descendants would be at the lowest level.