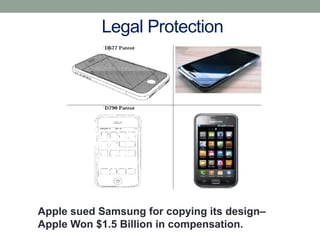
This document discusses why brands matter to both consumers and manufacturers. For consumers, brands help identify products they like or dislike, evaluate quality, reduce purchase time and risk. Brands may also provide psychological rewards. For manufacturers, brands identify their products, make repeat purchases easier, allow introduction of new products carrying existing brands, provide legal protection, allow premium pricing, help differentiate from competitors, and enable cooperation with other well-known brands. The document provides examples like Coke's global sales, Apple's success with the iPhone, Starbucks premium pricing, and Tata Motors' acquisition of Jaguar and Land Rover.