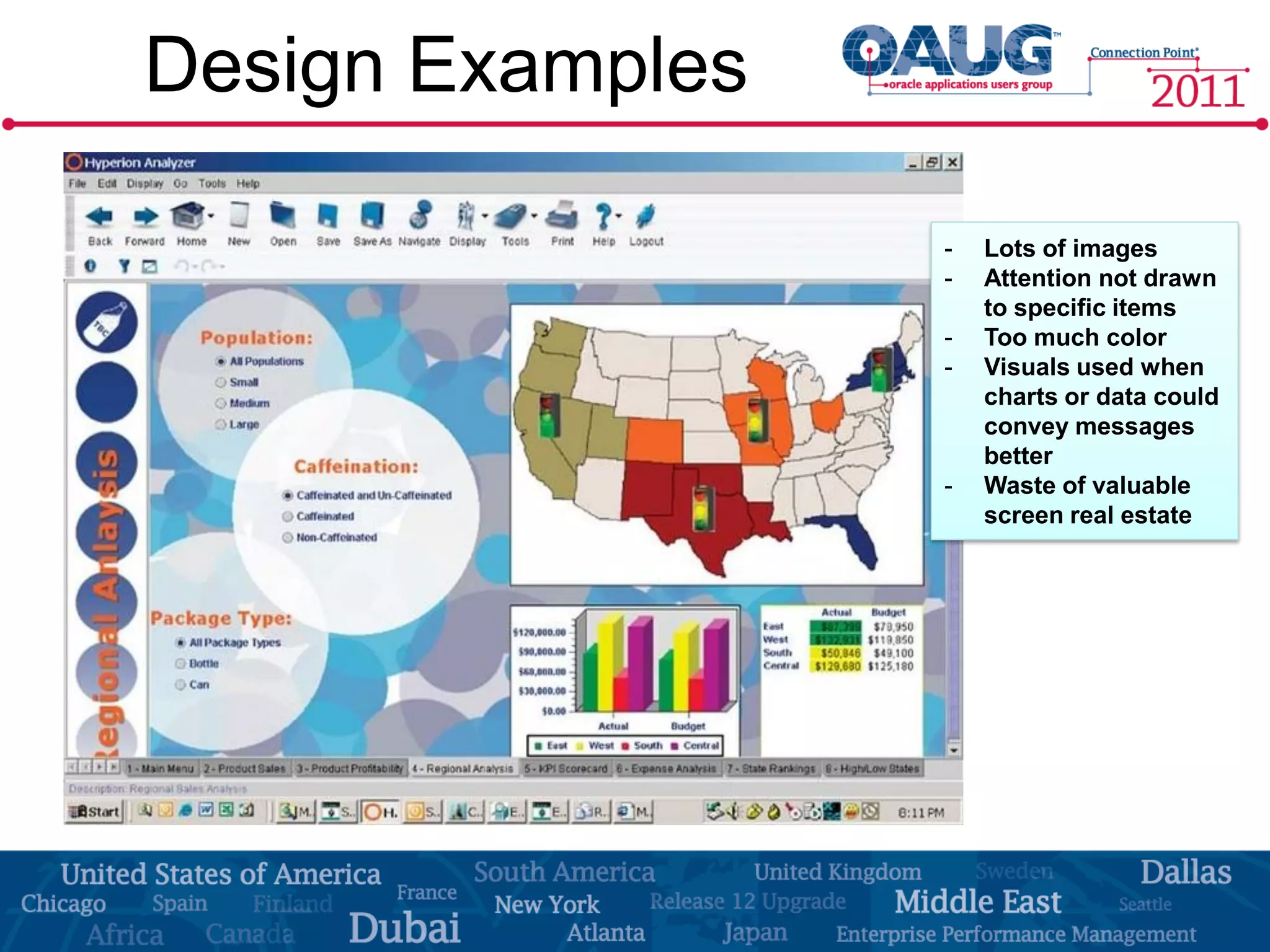
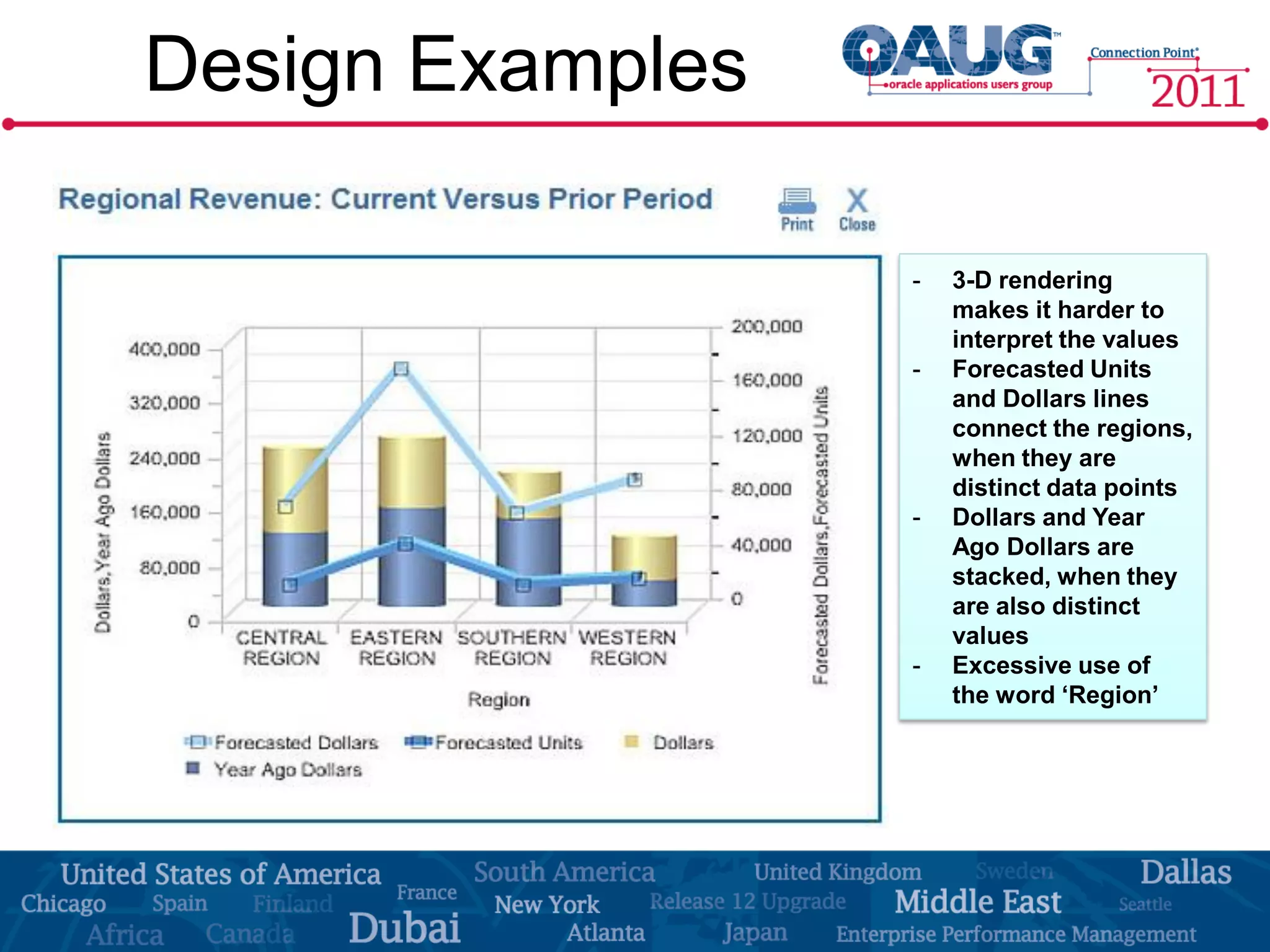
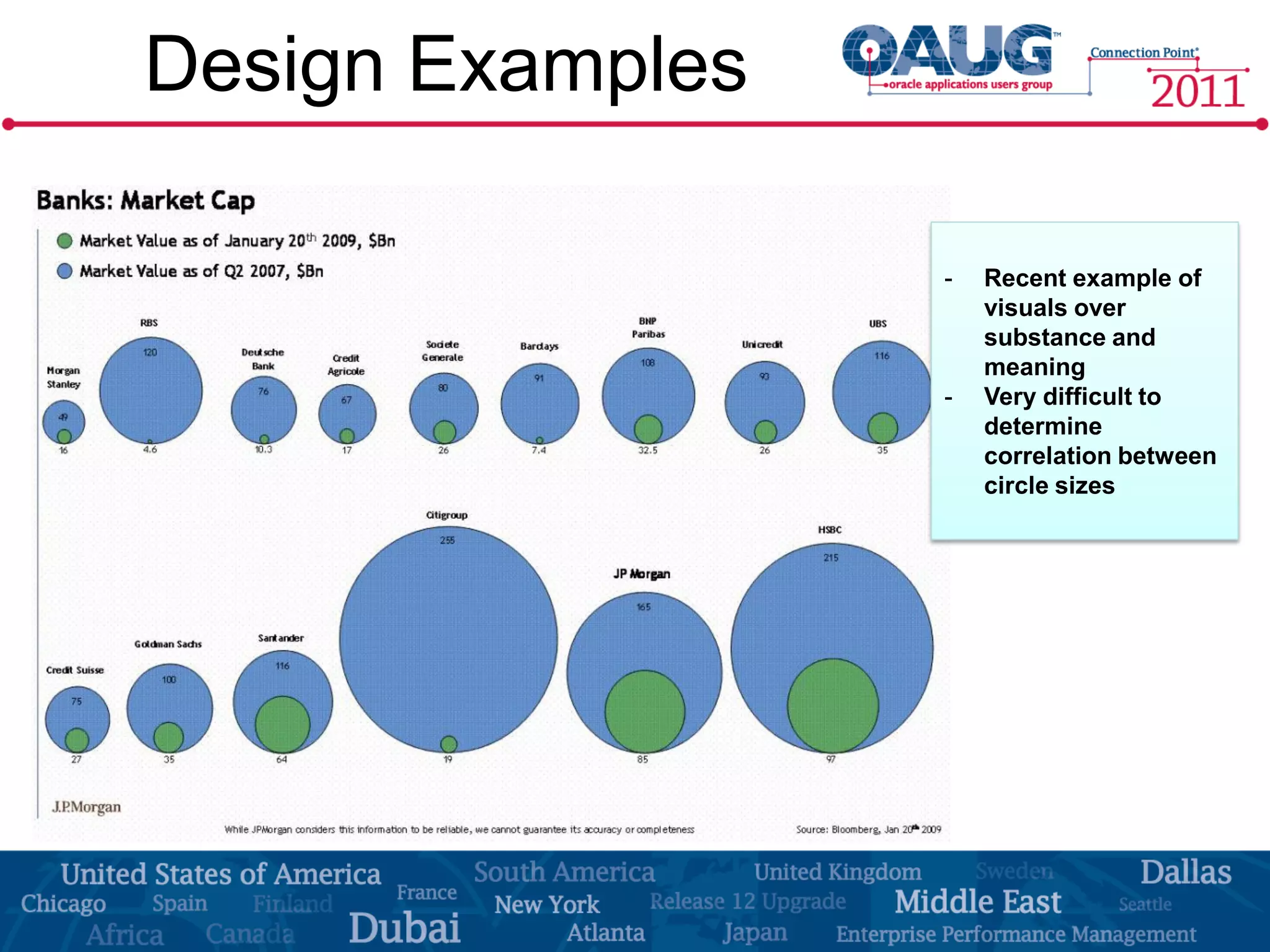
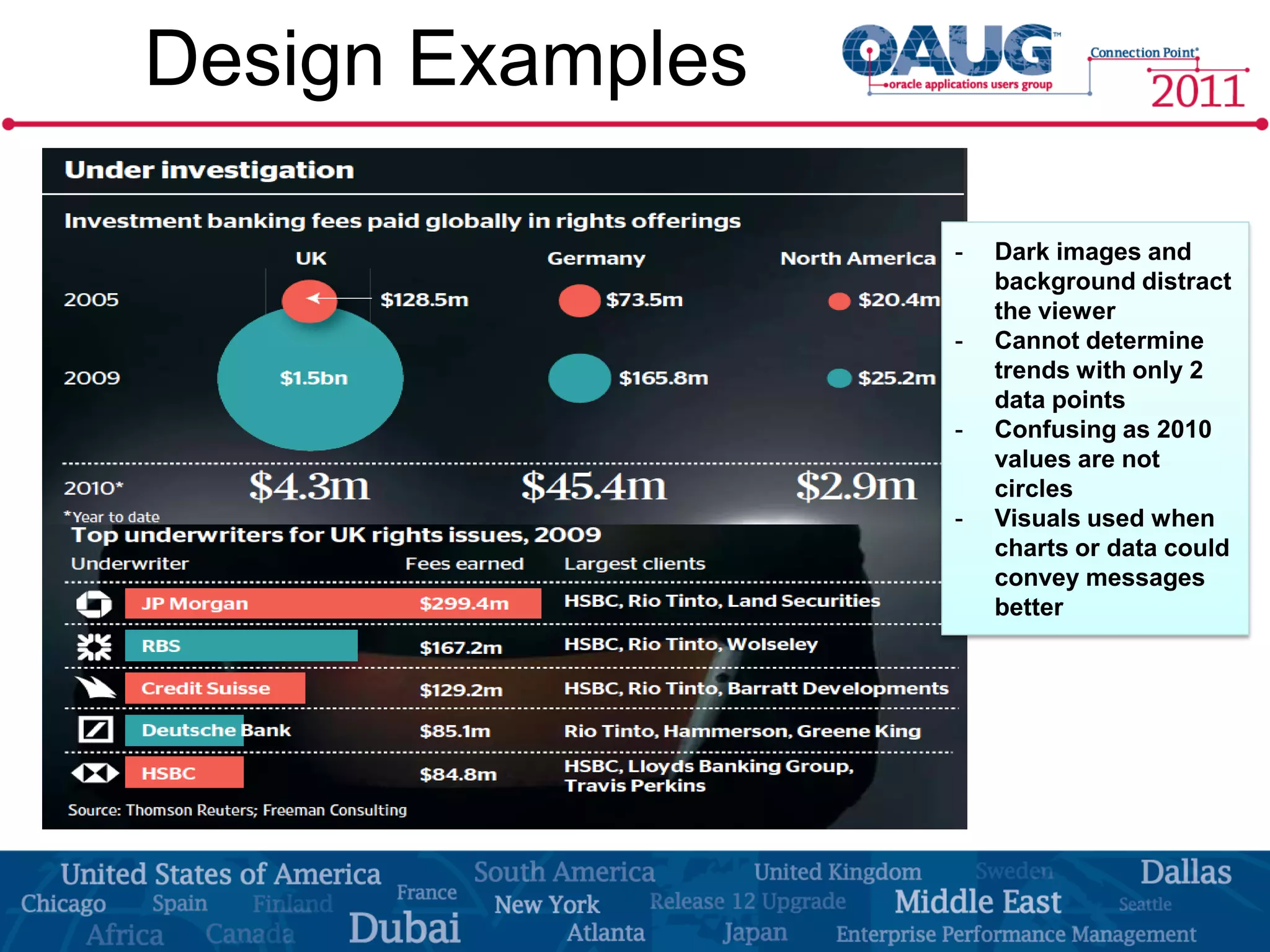
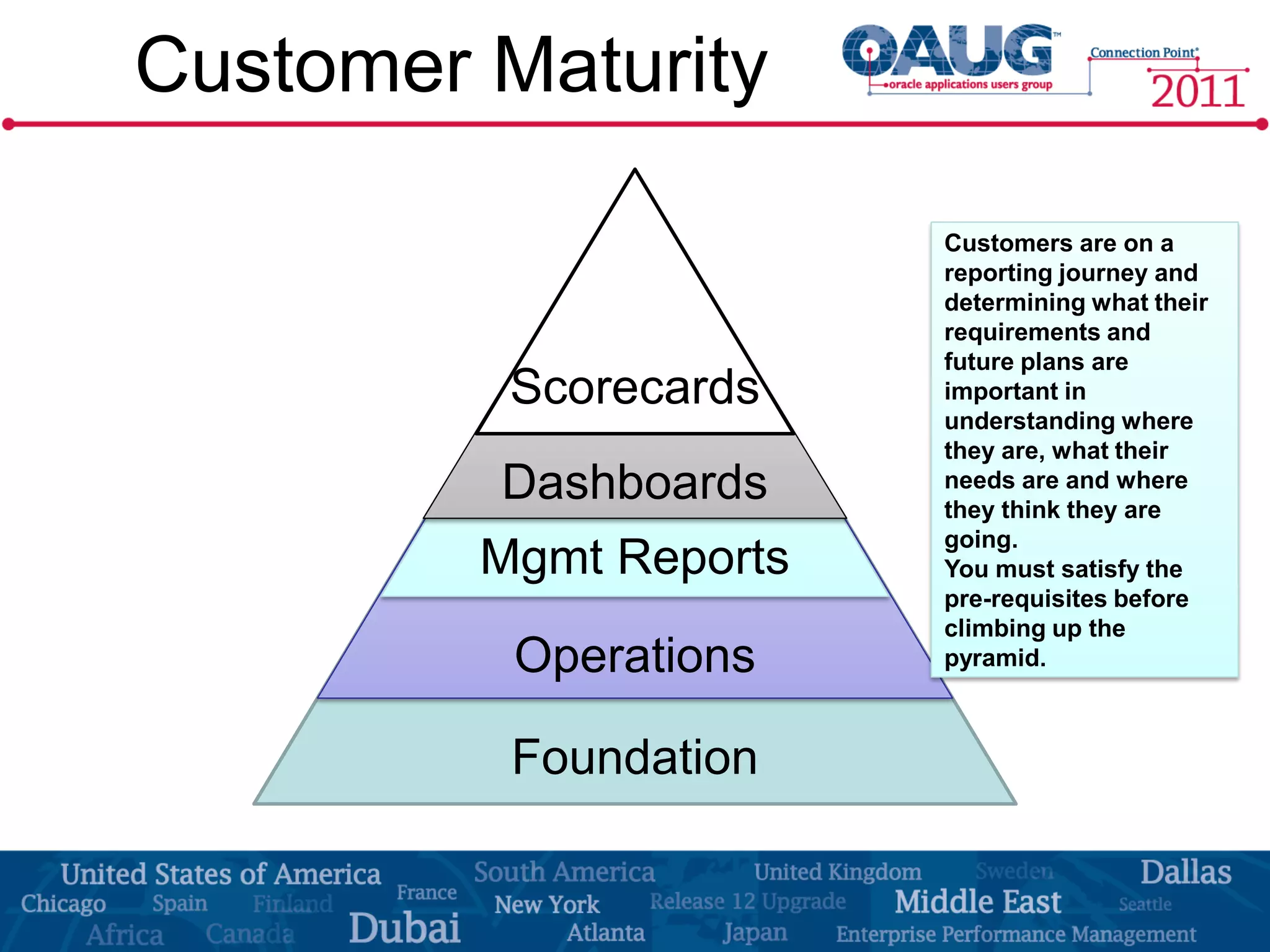
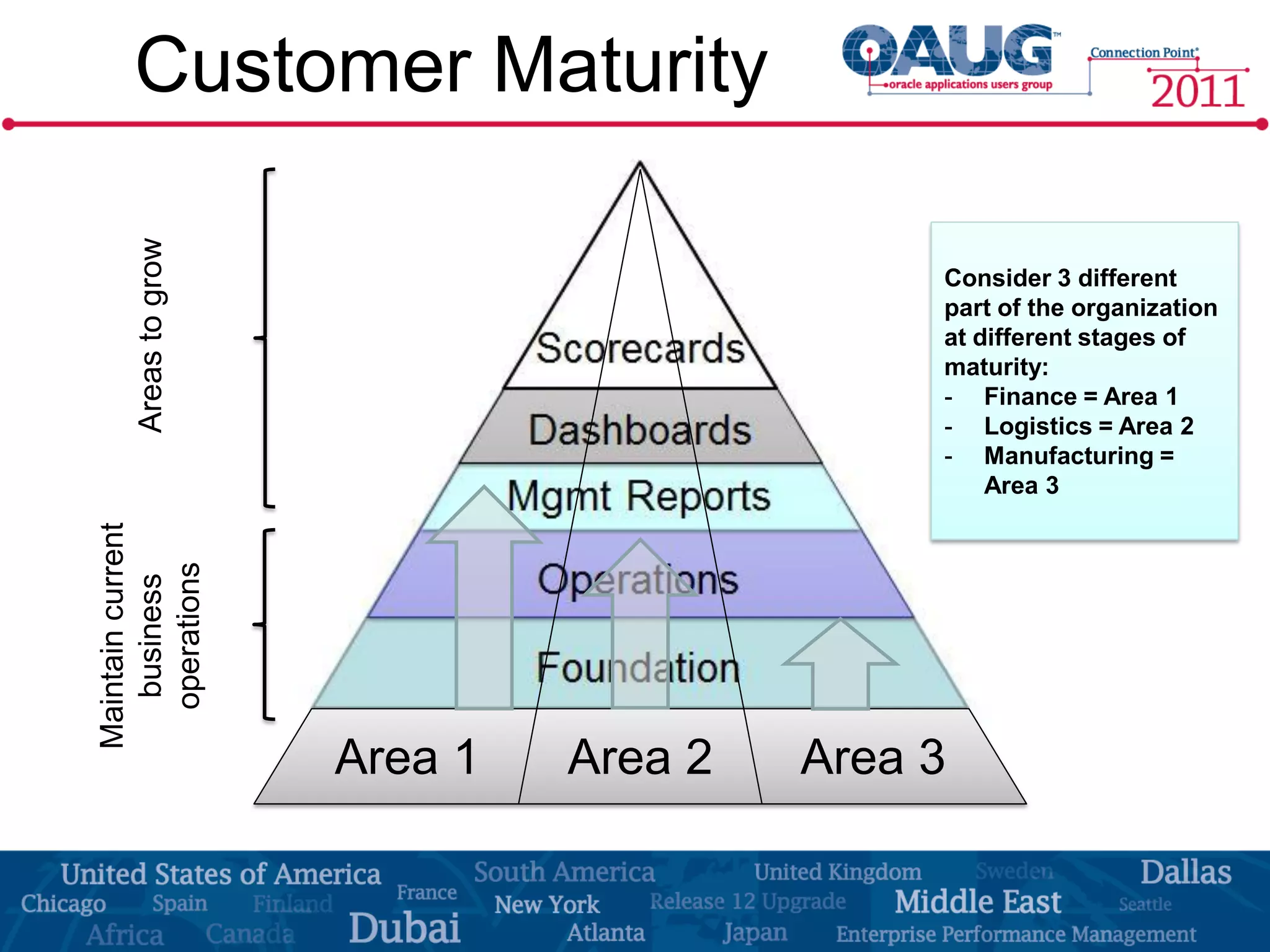
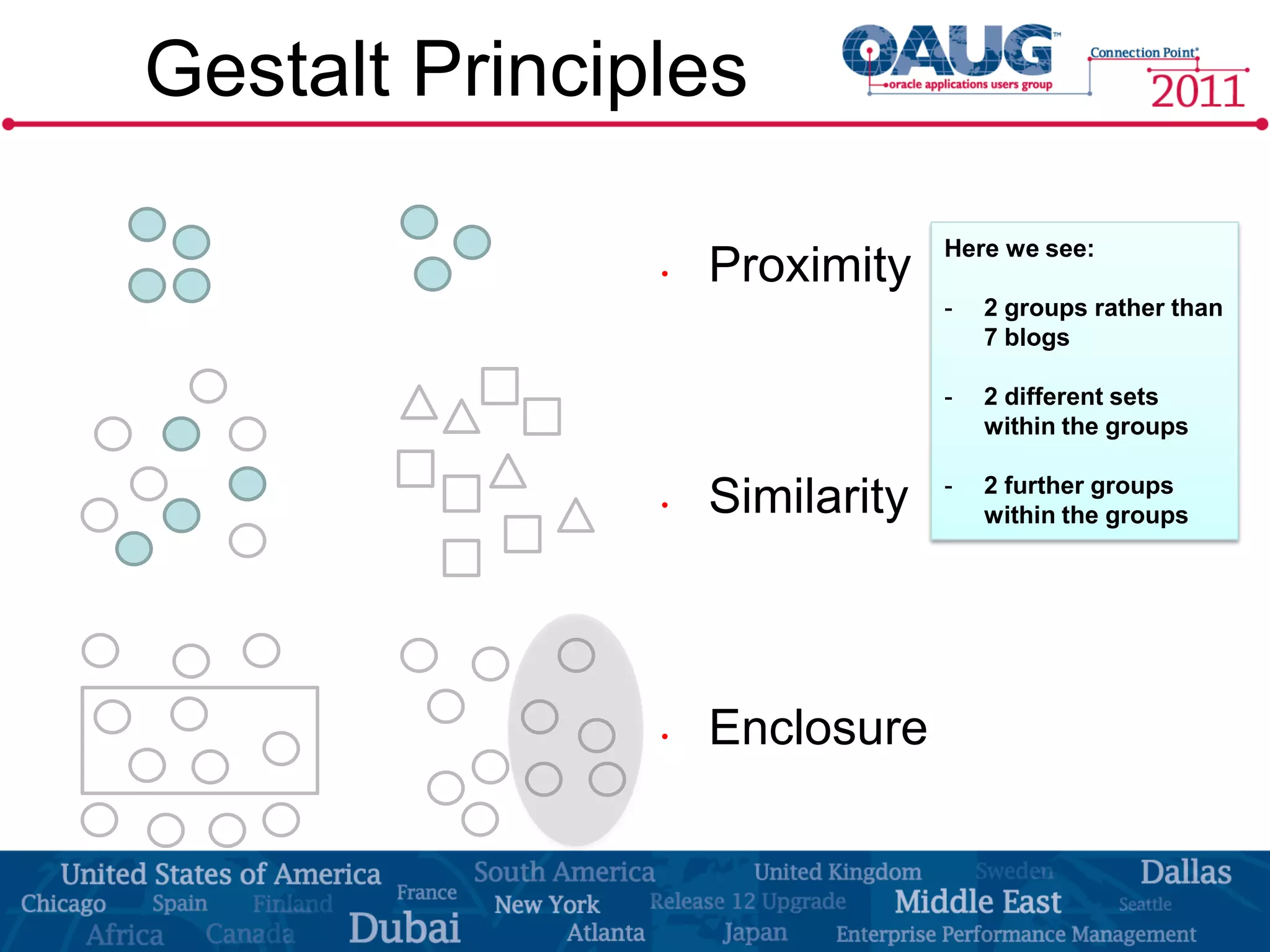
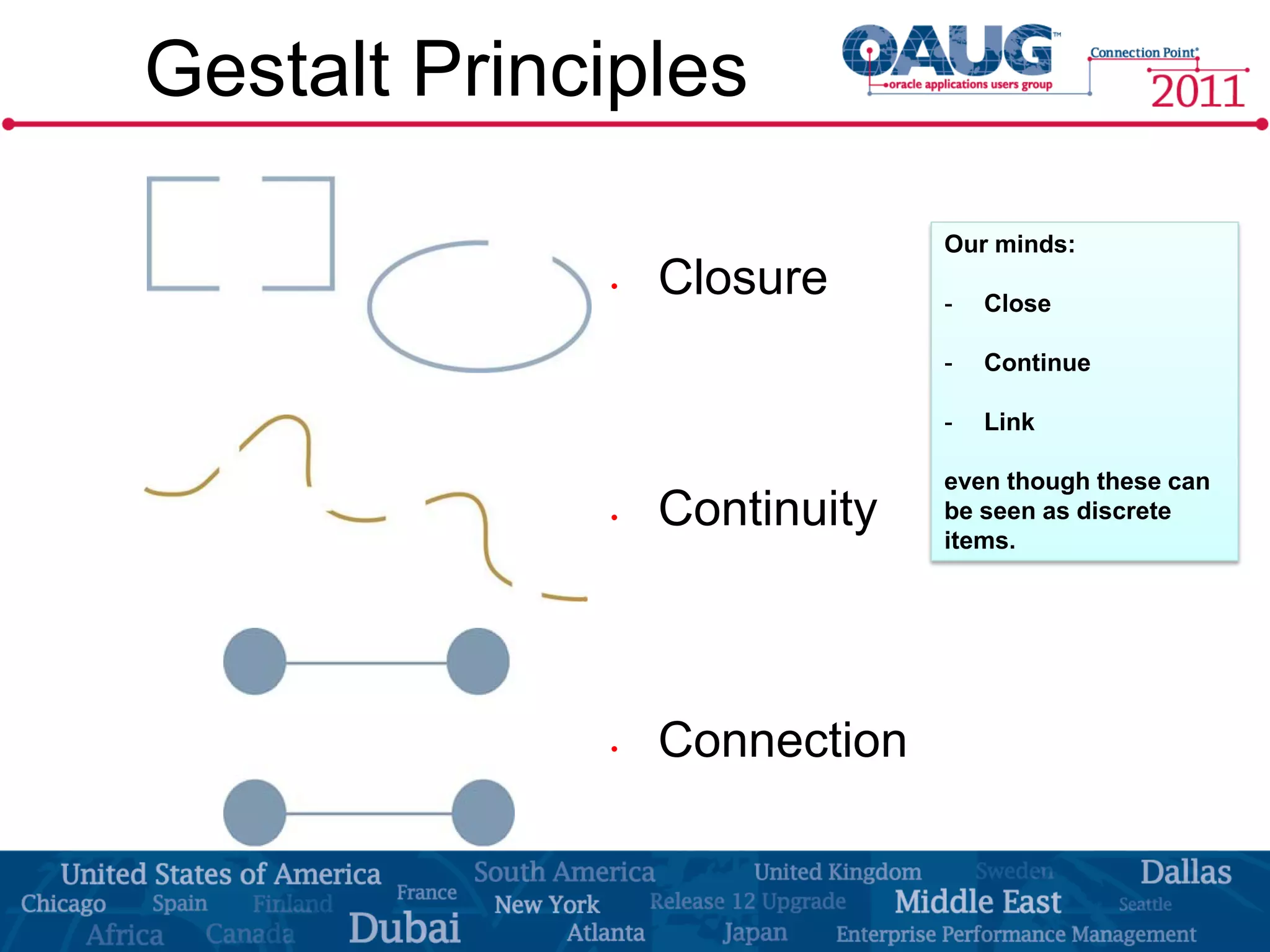
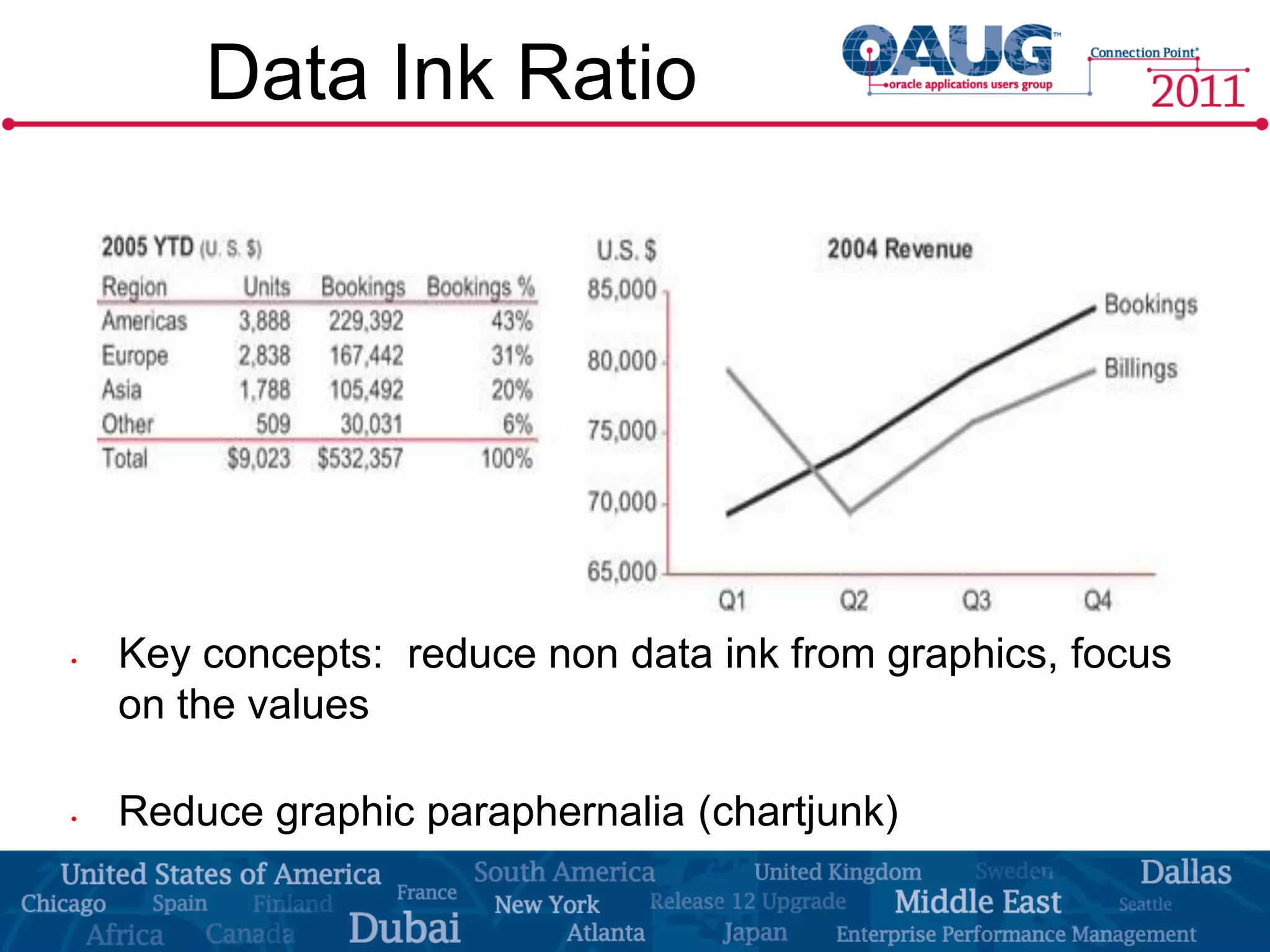
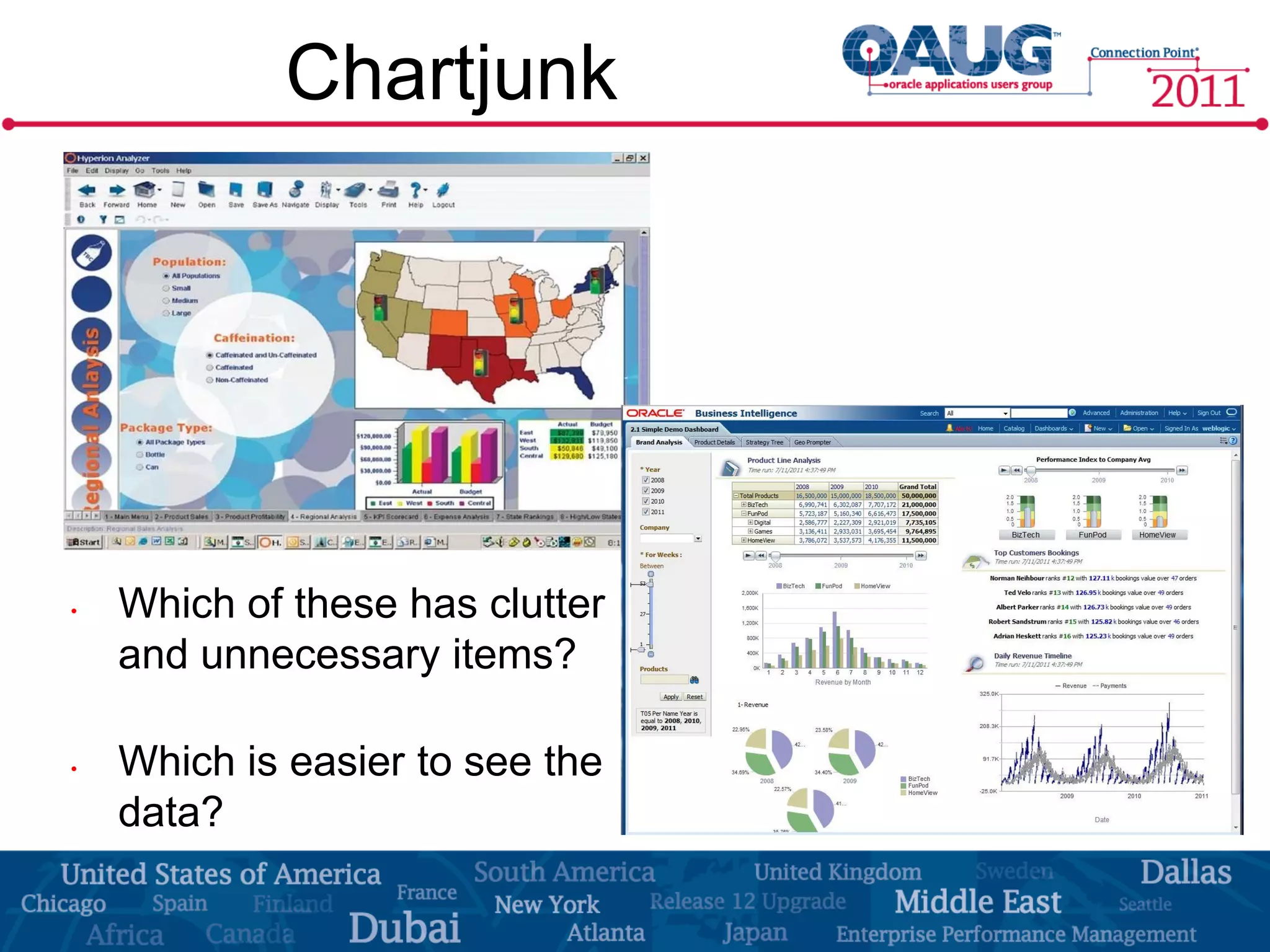
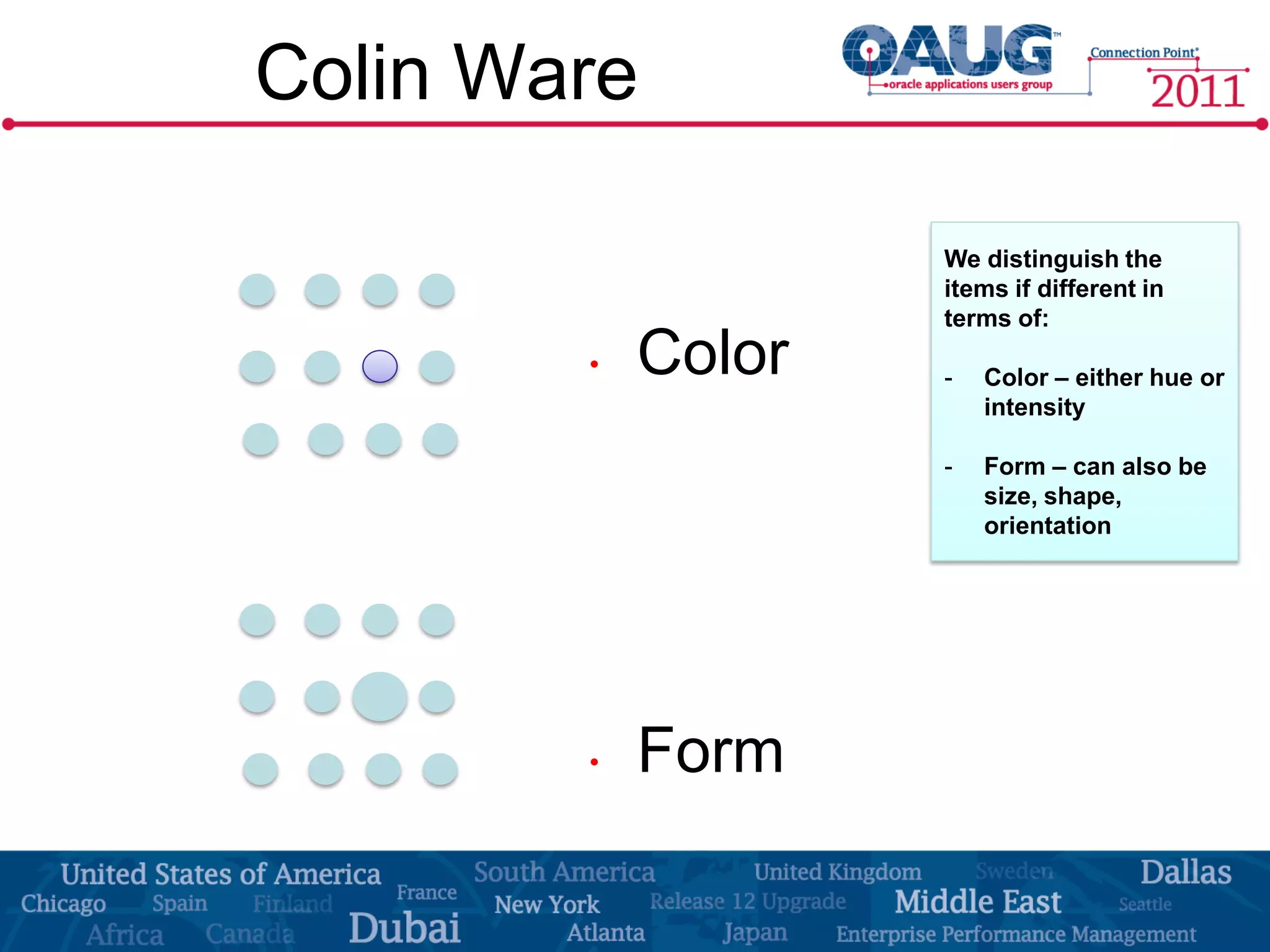
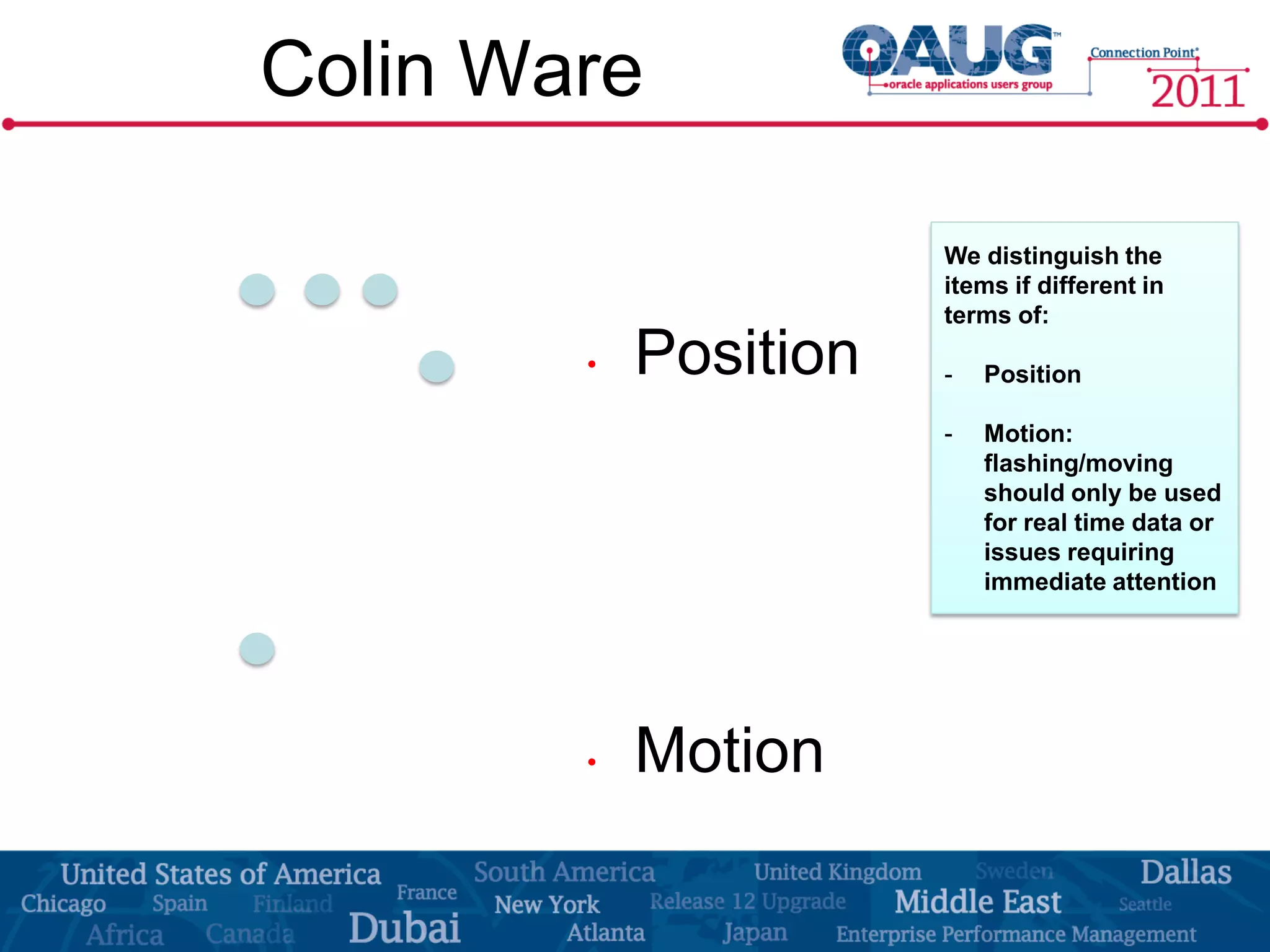
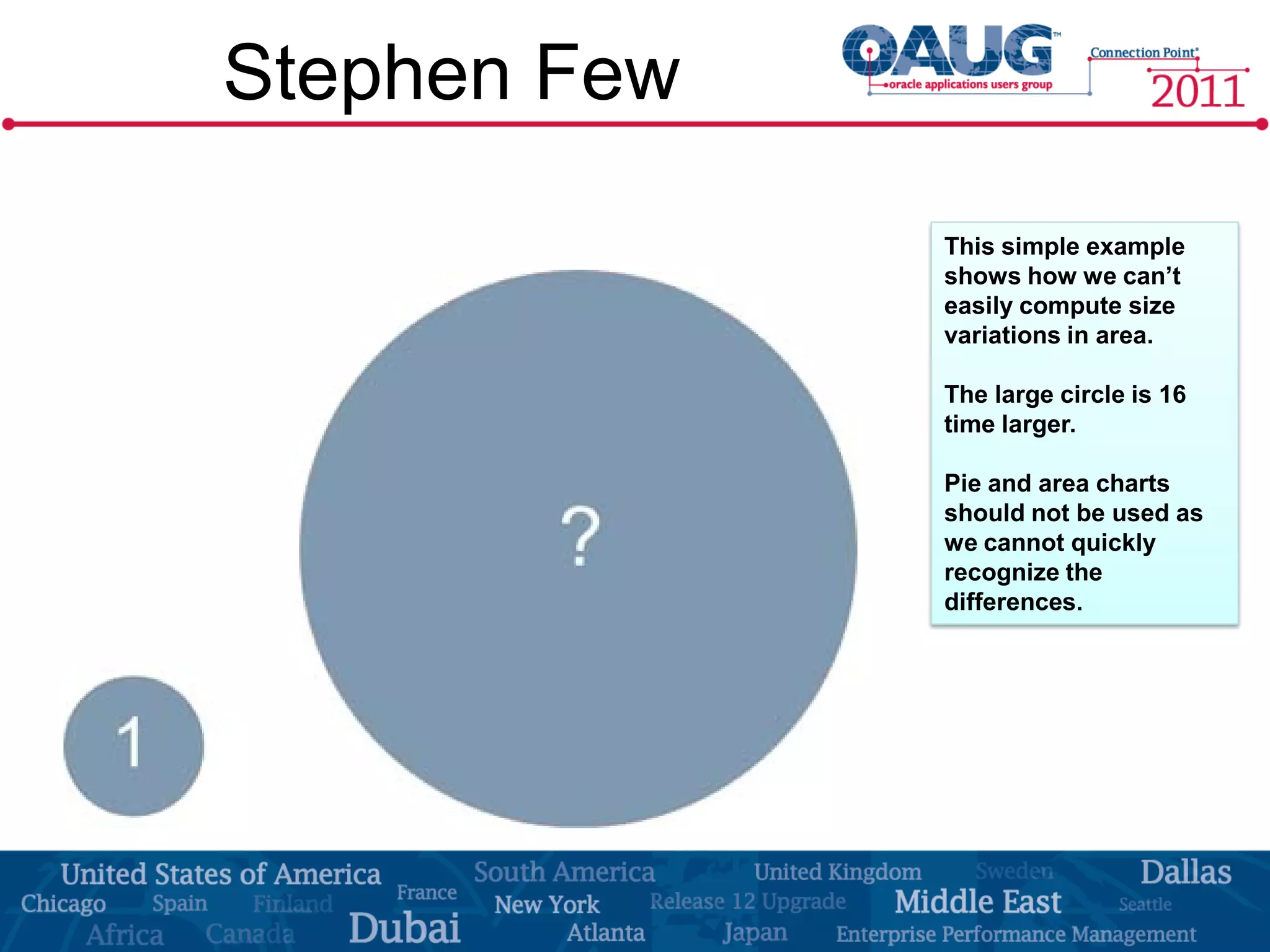
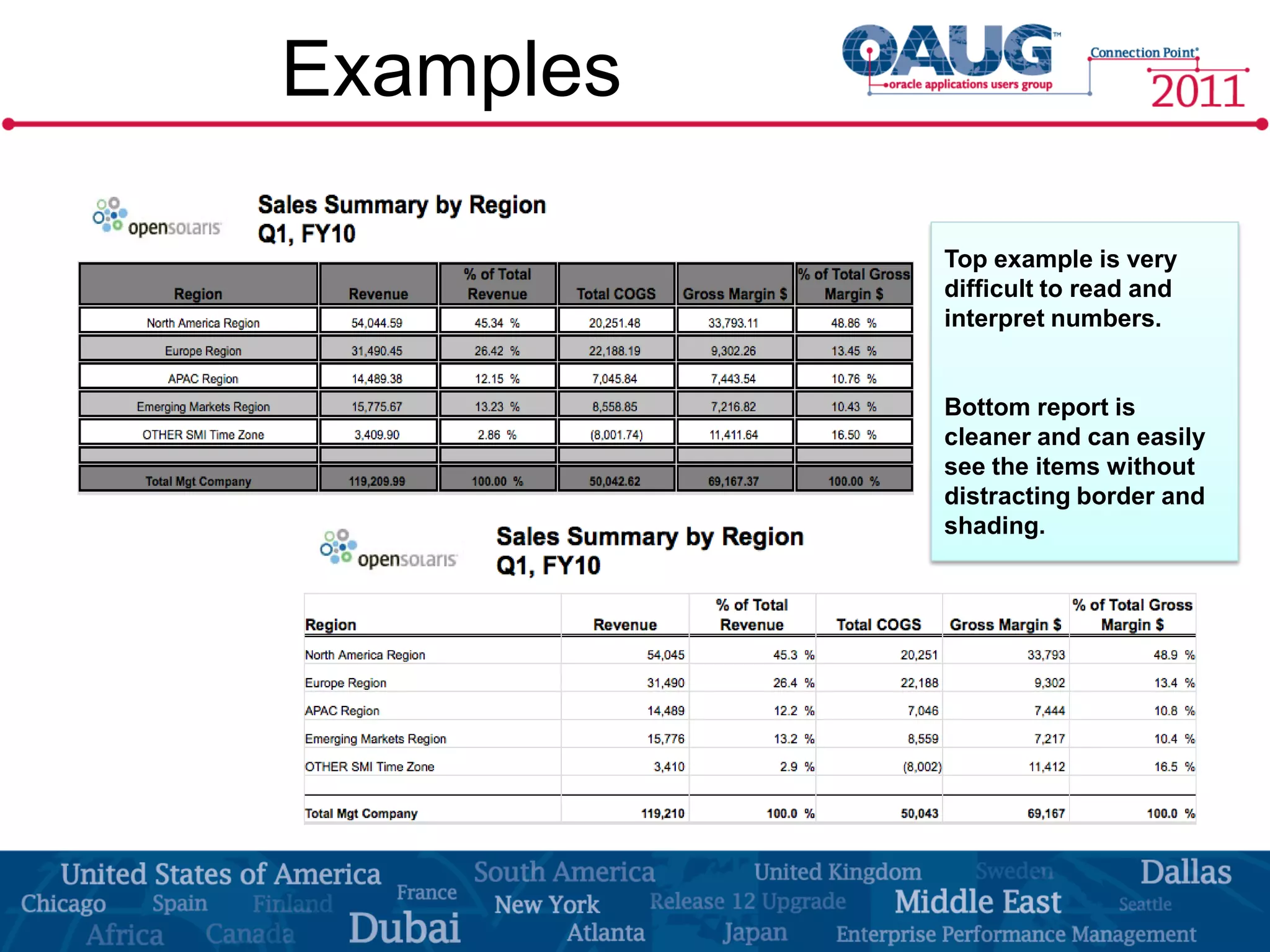
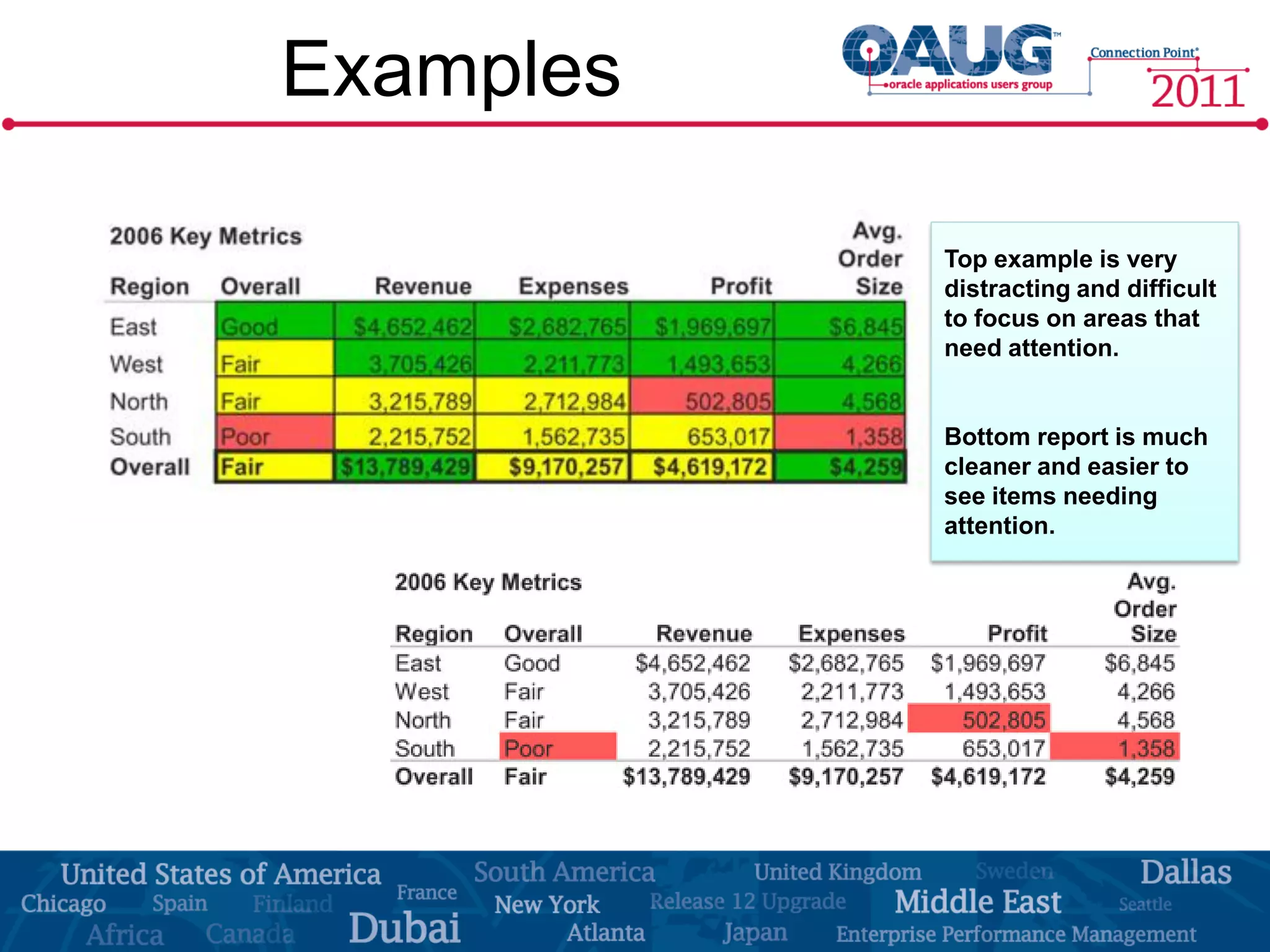
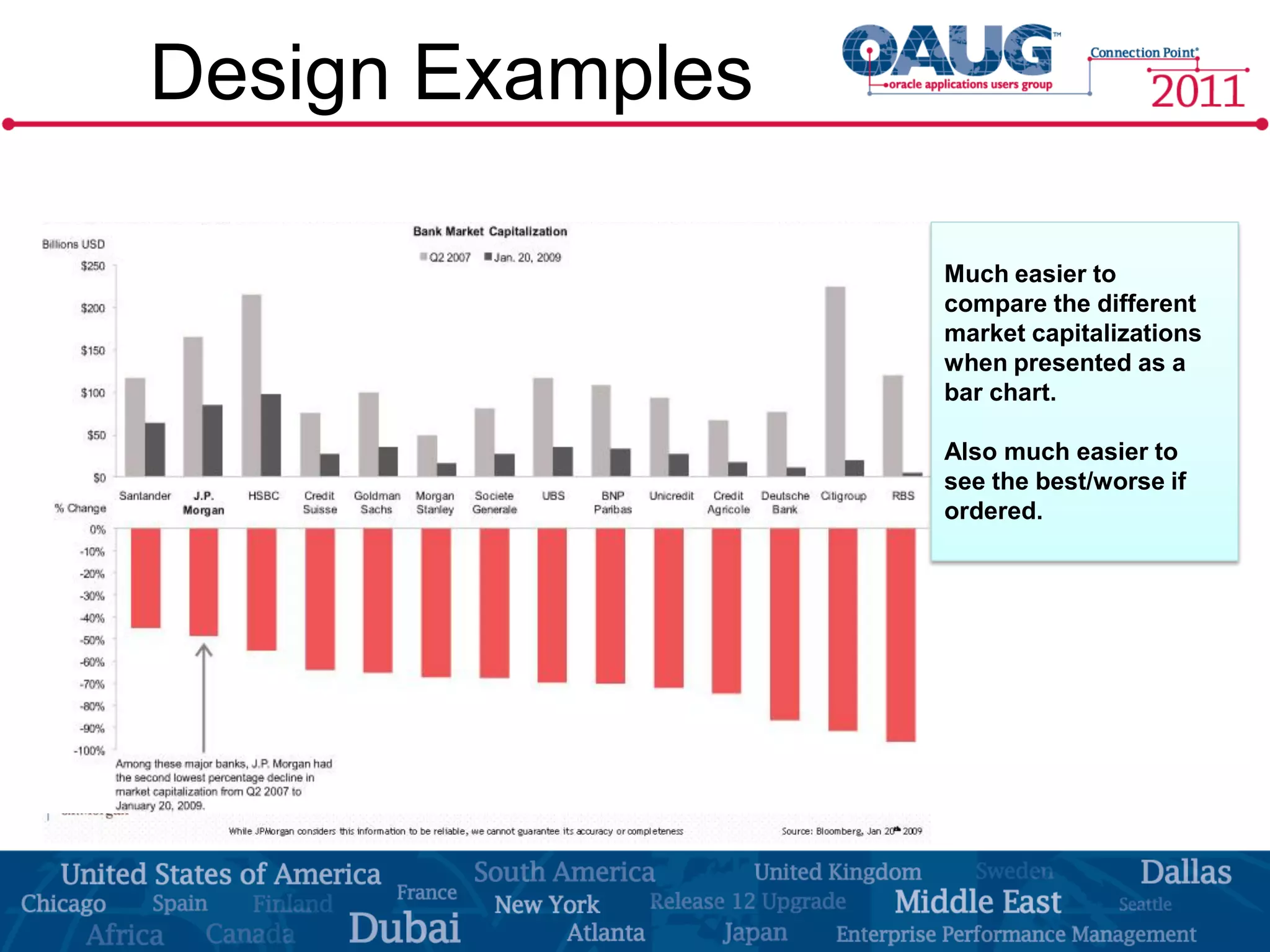
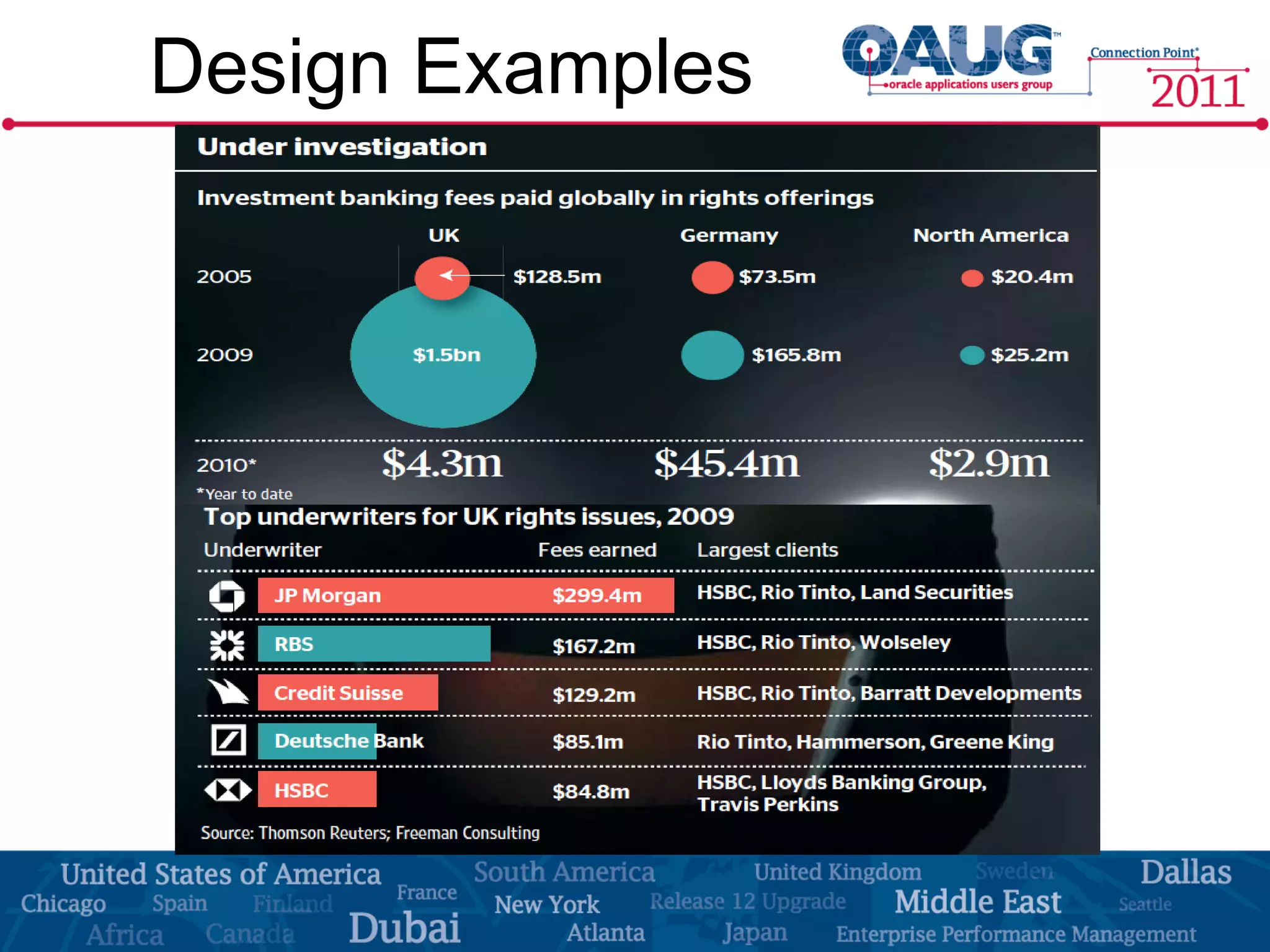
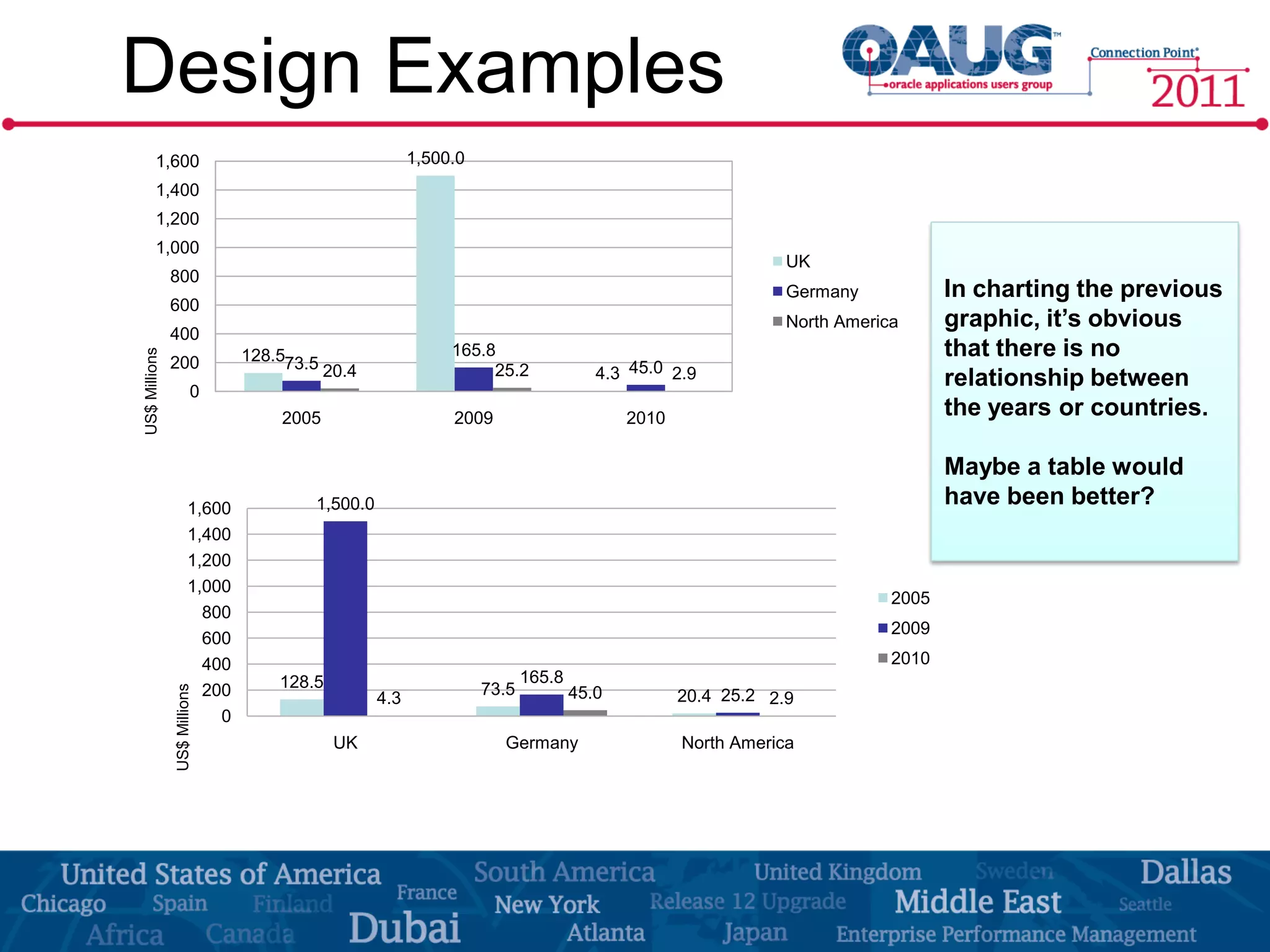
The document discusses the significance of effective data visualization in delivering actionable insights, emphasizing good design principles and user requirements. It highlights customer maturity stages and the need for clarity while reducing distractions in data presentation for better decision-making. Key insights from experts like Edward Tufte and Colin Ware illustrate the impact of design on data interpretation.