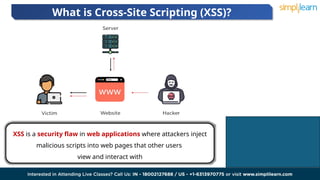
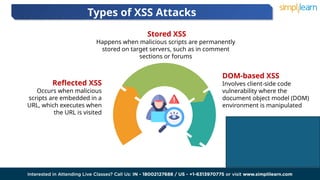
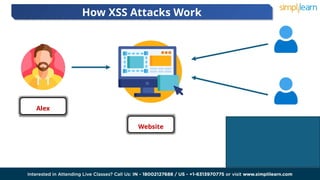
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a security vulnerability in web applications where attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages. There are three main types of XSS: reflected, stored, and DOM-based, which allow attackers to manipulate web application content and steal sensitive information. The consequences of XSS attacks can include reputational damage, legal issues, and significant financial losses for affected companies.