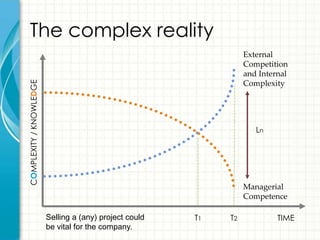
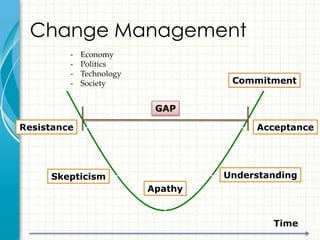
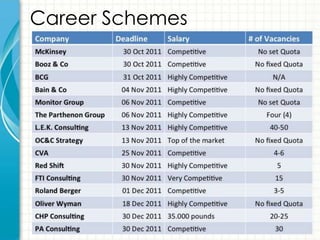
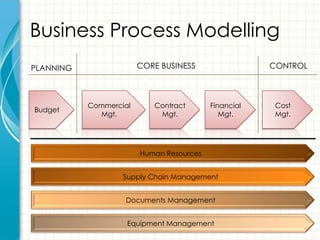
This document provides an overview of consulting as a profession. It begins with defining consulting as the business of giving expert advice to other professionals, typically in business matters. It then discusses what qualities and skills are required to become a consultant, such as time management, commitment to results, and communication skills. Finally, it shares some of the author's personal experiences working as a management consultant for various companies.