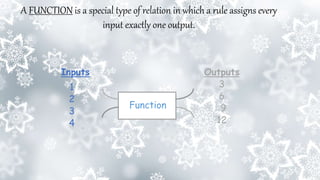
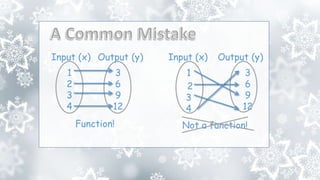
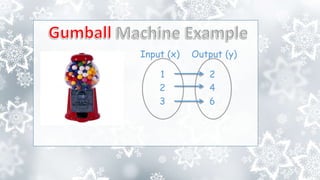
This document provides an overview of a math unit on functions. The unit will introduce students to the concept of functions, including defining functions, determining domain and range, evaluating functions, calculating slope, and representing functions in different ways. The unit consists of 4 lessons: defining functions, evaluating functions, comparing functions, and using functions to model linear relationships. Key learning objectives are outlined. Essential questions ask why functions are represented in multiple ways and how functional properties and operations are useful.