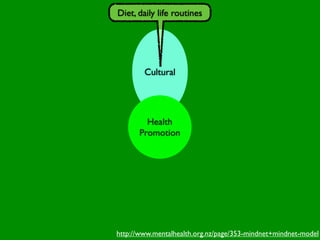
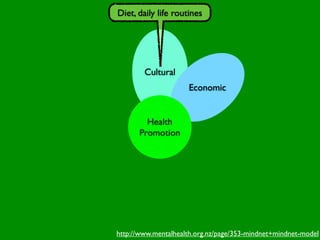
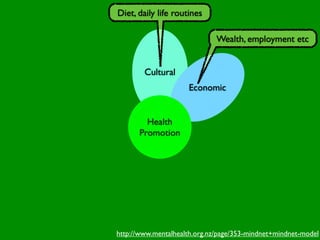
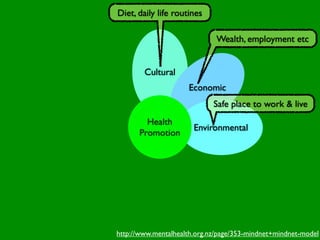
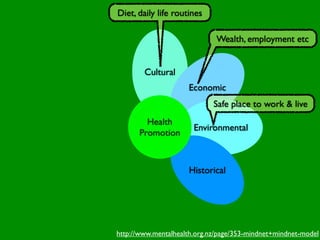
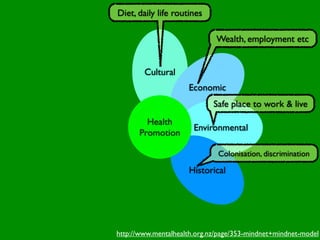
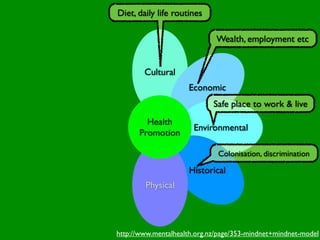
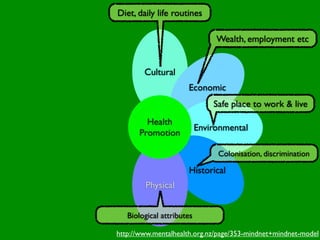
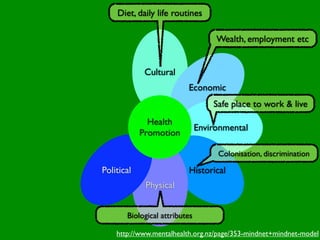
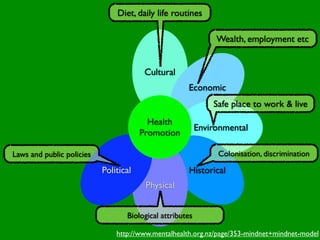
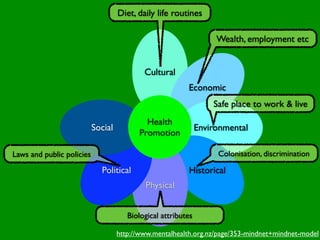
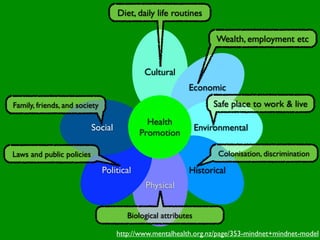
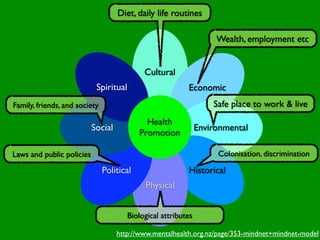
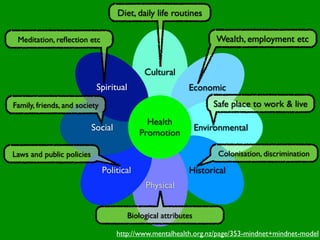
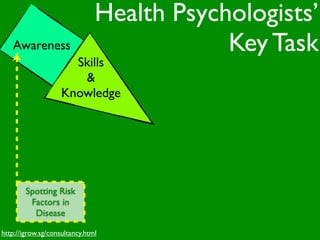
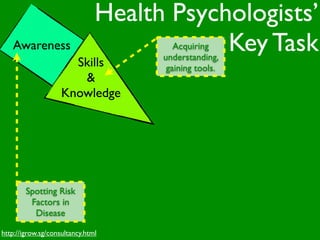
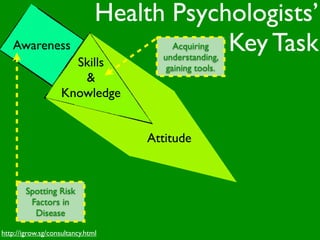
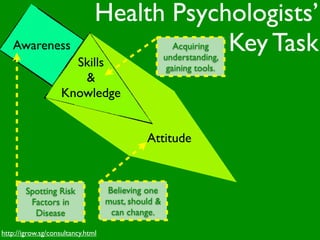
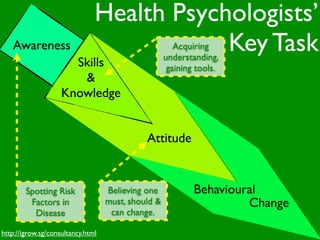
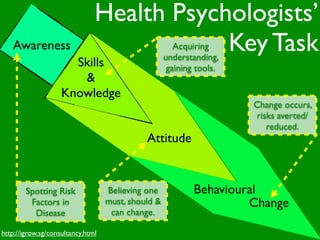
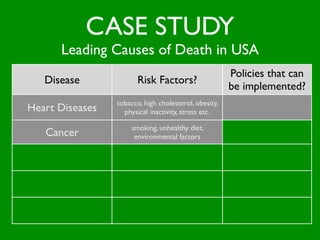
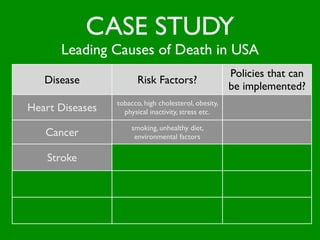
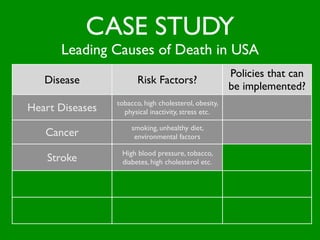
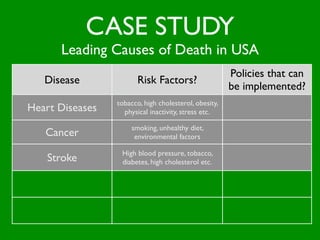
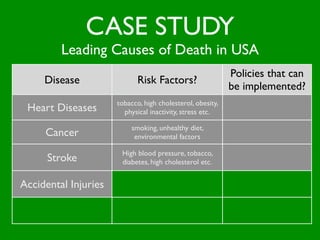
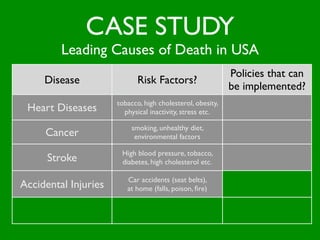
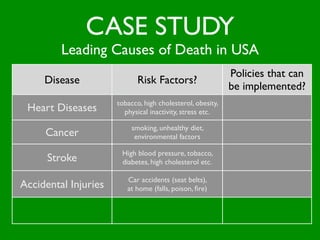
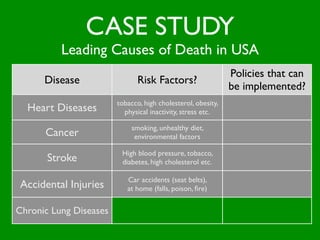
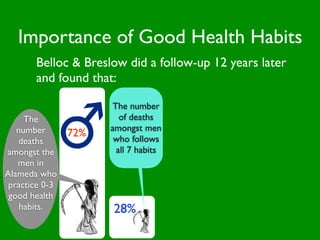
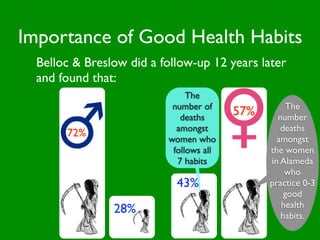
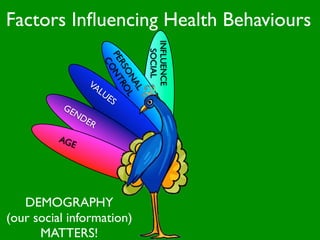
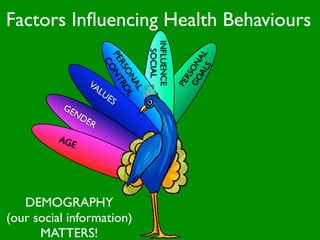
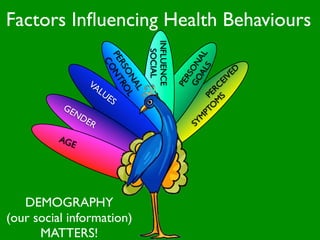
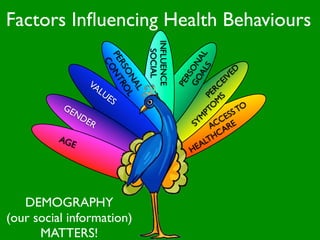
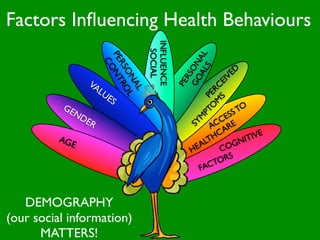
The document discusses health behaviors and health promotion. It states that health behaviors are actions taken to maintain or improve health, while health promotion refers to the belief that good health requires personal and collective commitment. It then outlines the MindNet model, which shows that health is influenced by biological, physical, social, economic, cultural, historical, environmental, political and spiritual factors. Finally, it states that key tasks of health psychologists include building awareness, acquiring skills and knowledge, and spotting risk factors for disease.