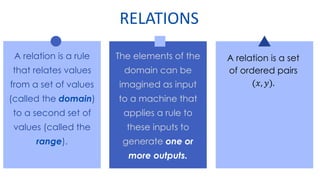
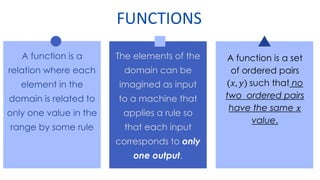
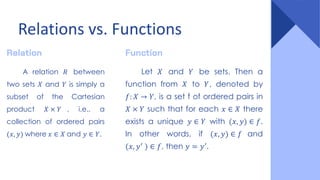
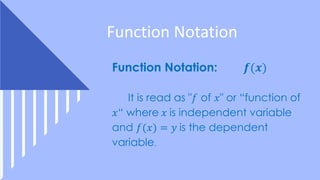
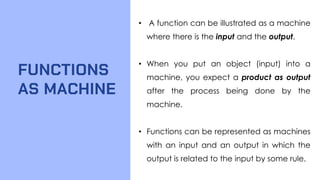
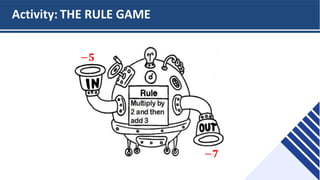
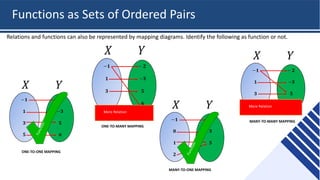
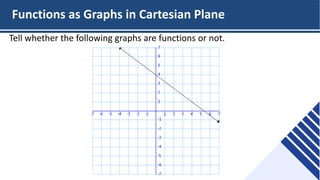
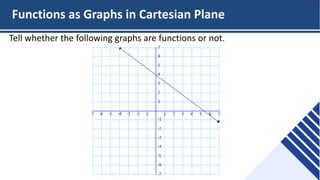
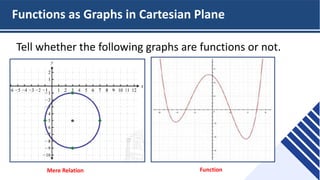
This document provides an overview of functions and their representations. It defines relations and functions, and notes that a function is a relation where each input maps to a unique output. It then discusses several ways to represent functions: as machines that take inputs and produce outputs according to a rule; as sets of ordered pairs; as mapping diagrams; and as graphs in the Cartesian plane. Examples are provided to illustrate functions versus relations for each representation. The overall purpose is to recall key concepts about functions and their graphical and symbolic representations.