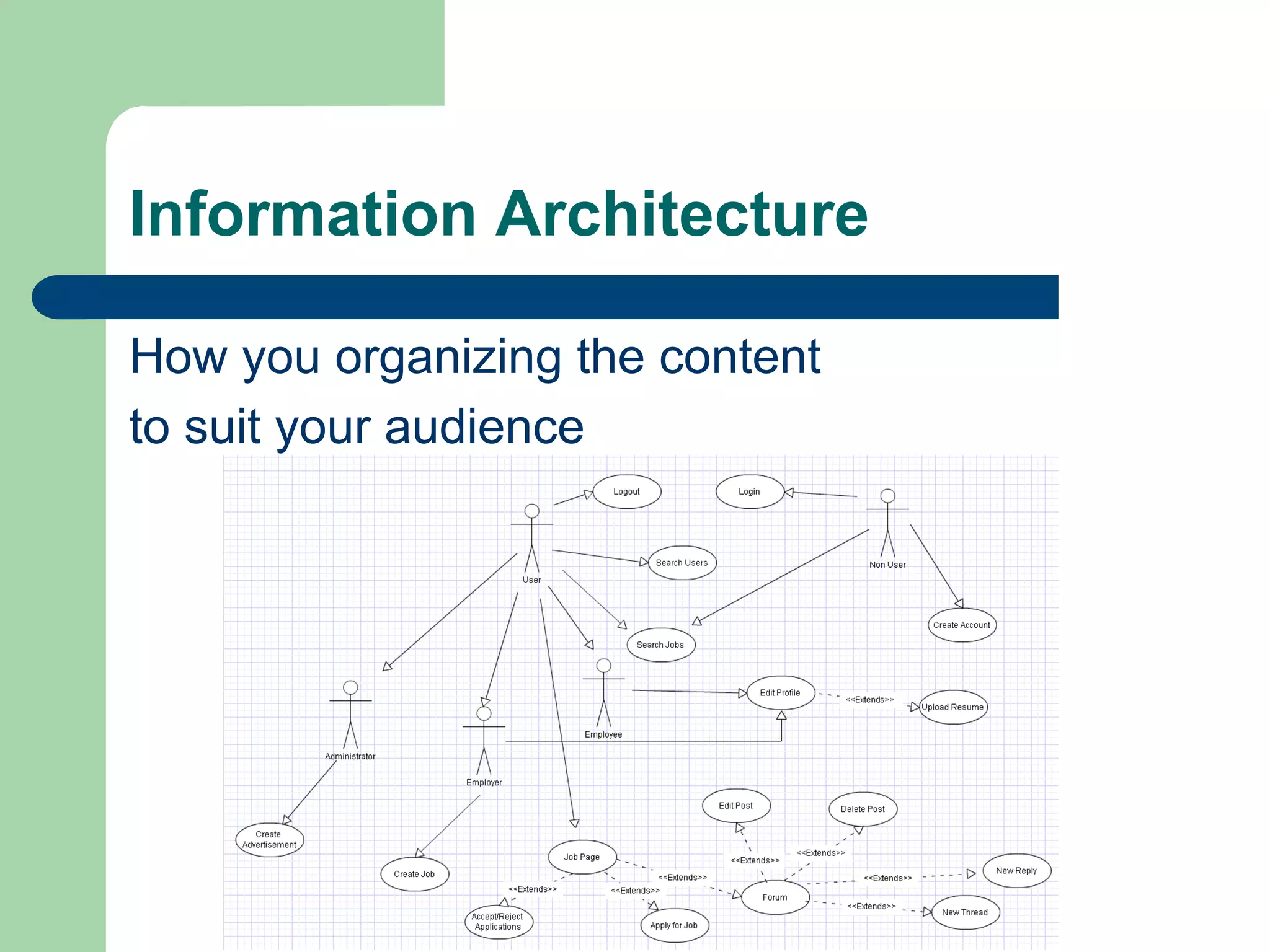
The document outlines essential planning strategies for creating successful multimedia presentations, highlighting the importance of a well-structured plan that comprises 80% planning and 20% production. Key elements include defining the purpose, identifying the target audience, developing specifications, and creating design strategies tailored to user needs. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for thorough audience analysis and content organization to enhance user engagement and effectiveness.