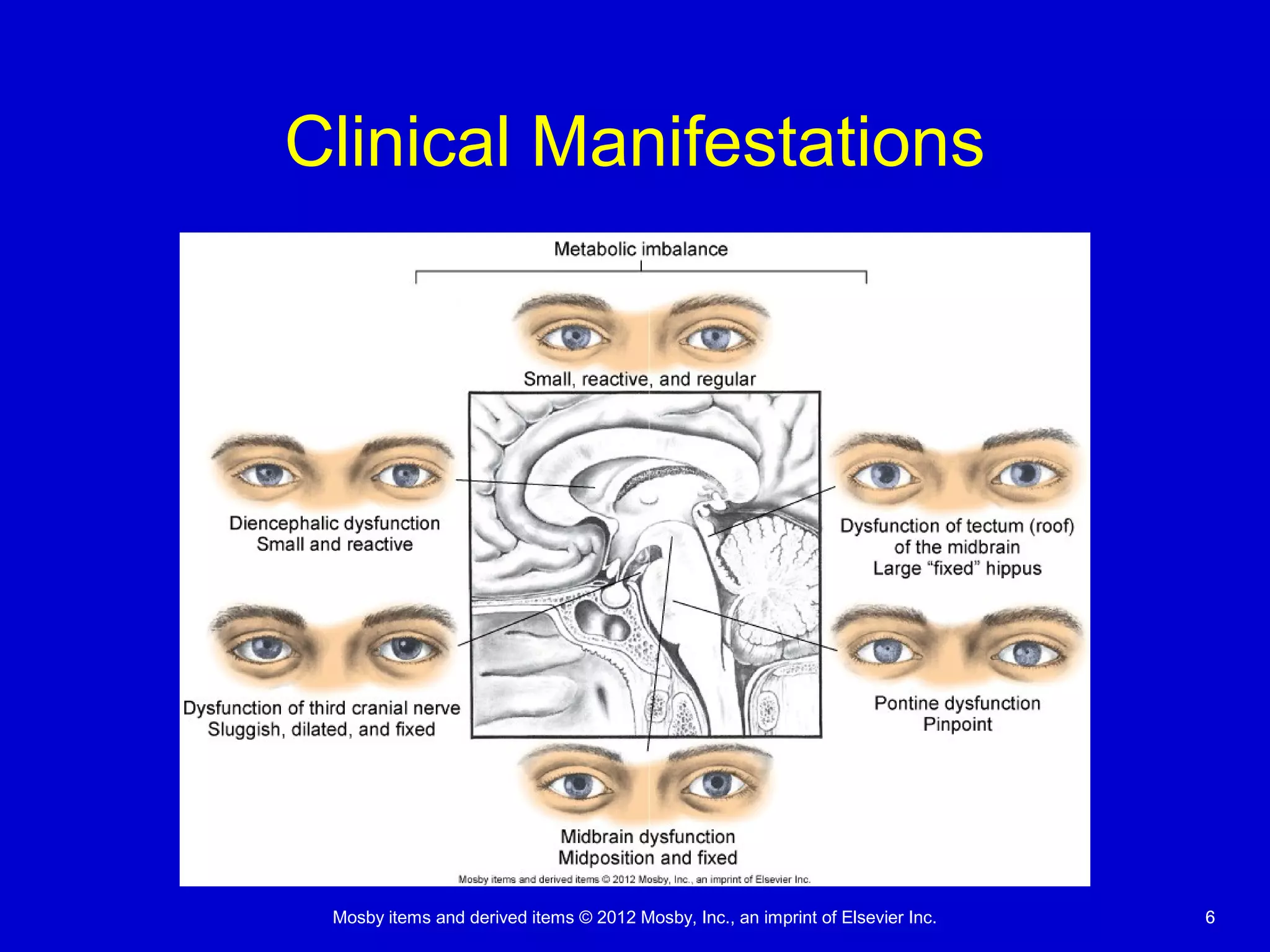
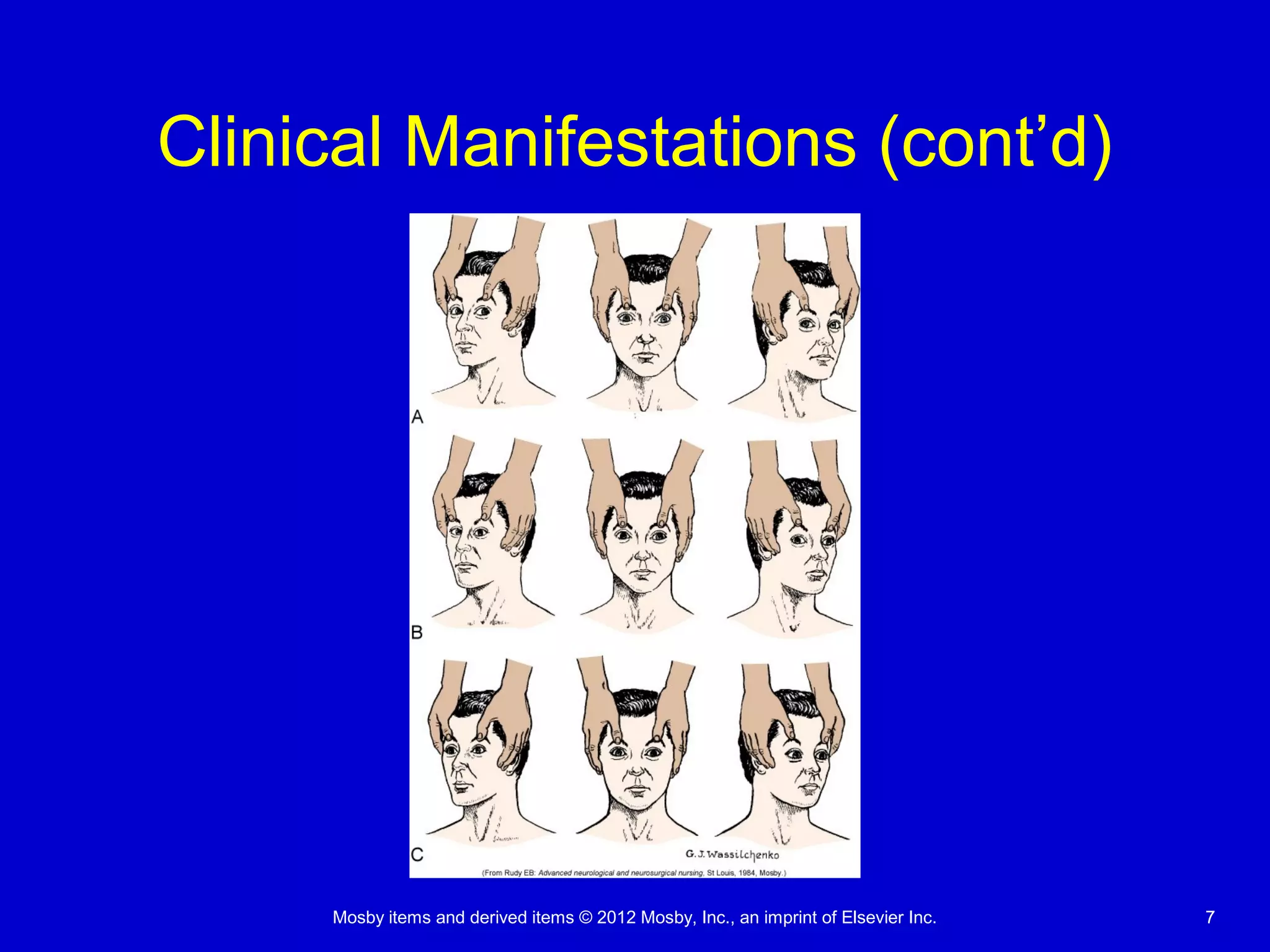
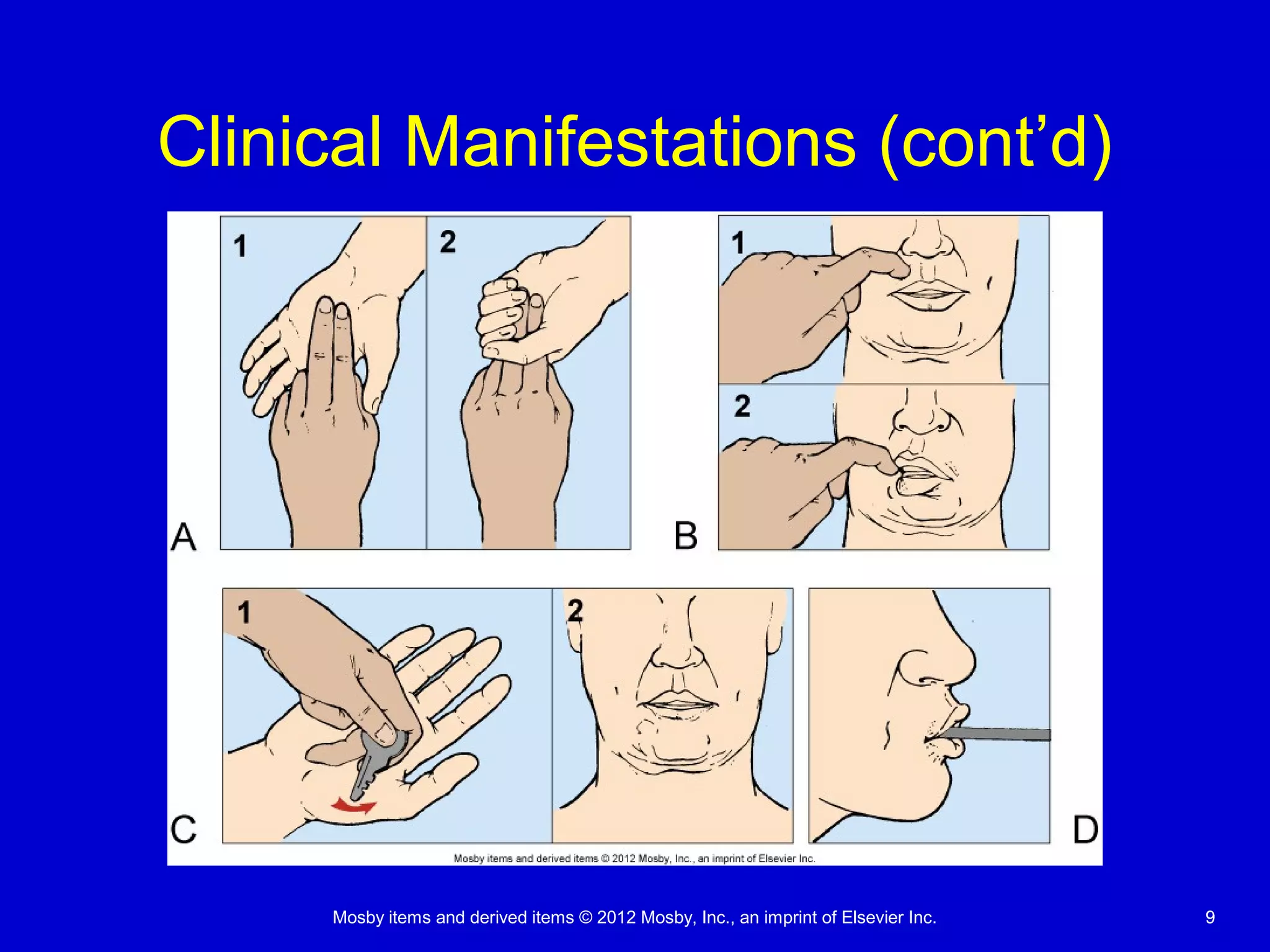
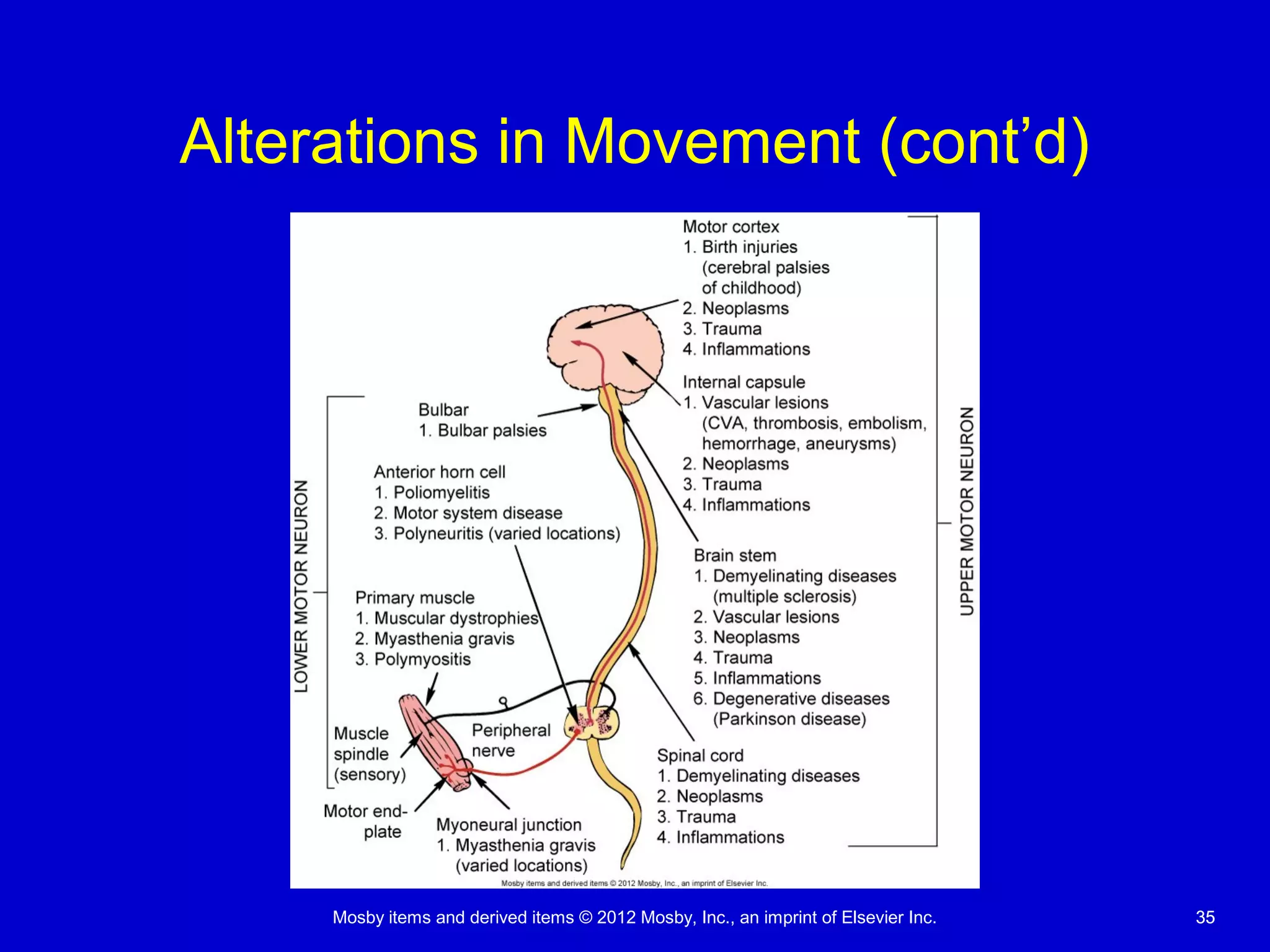
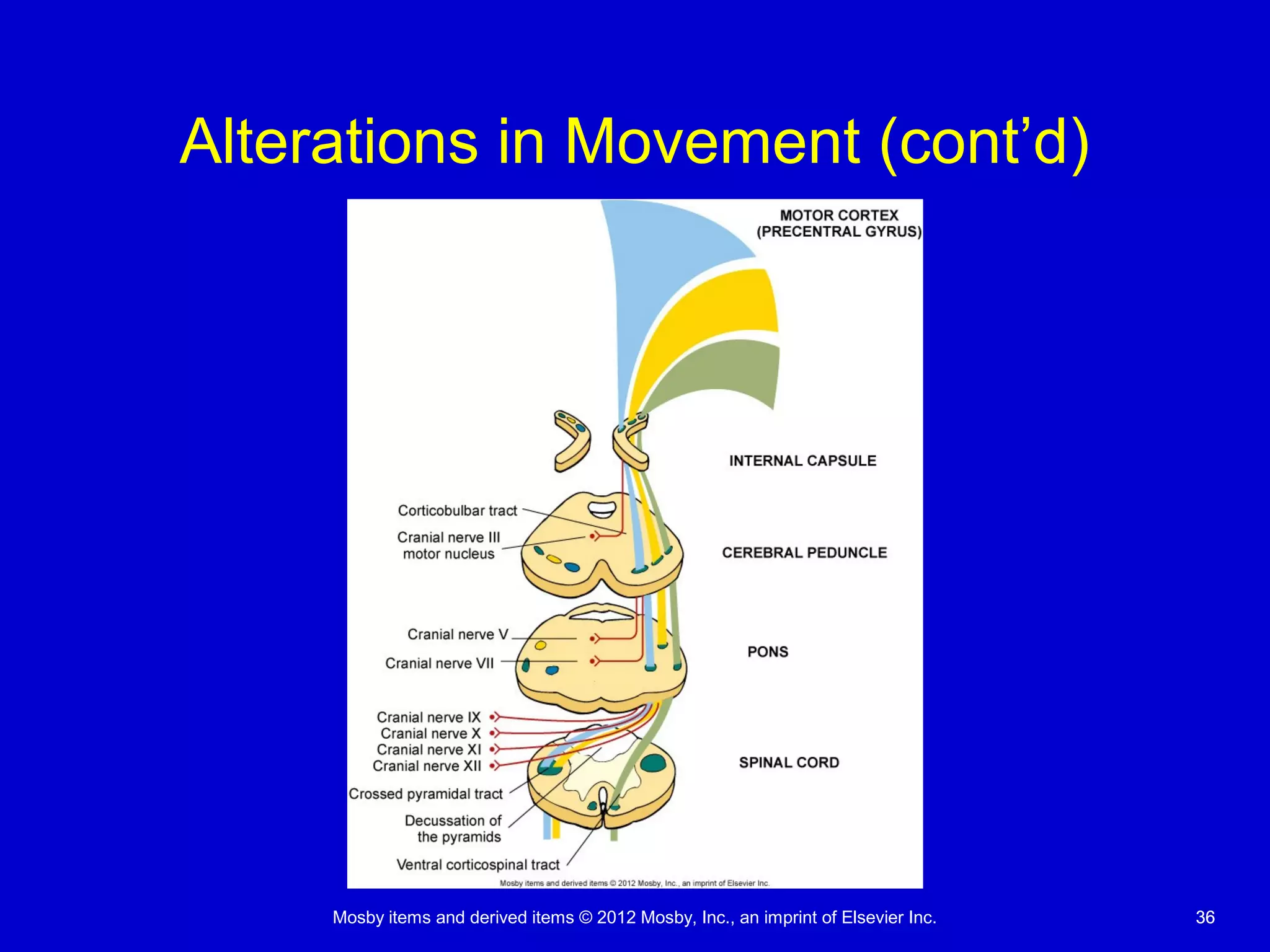
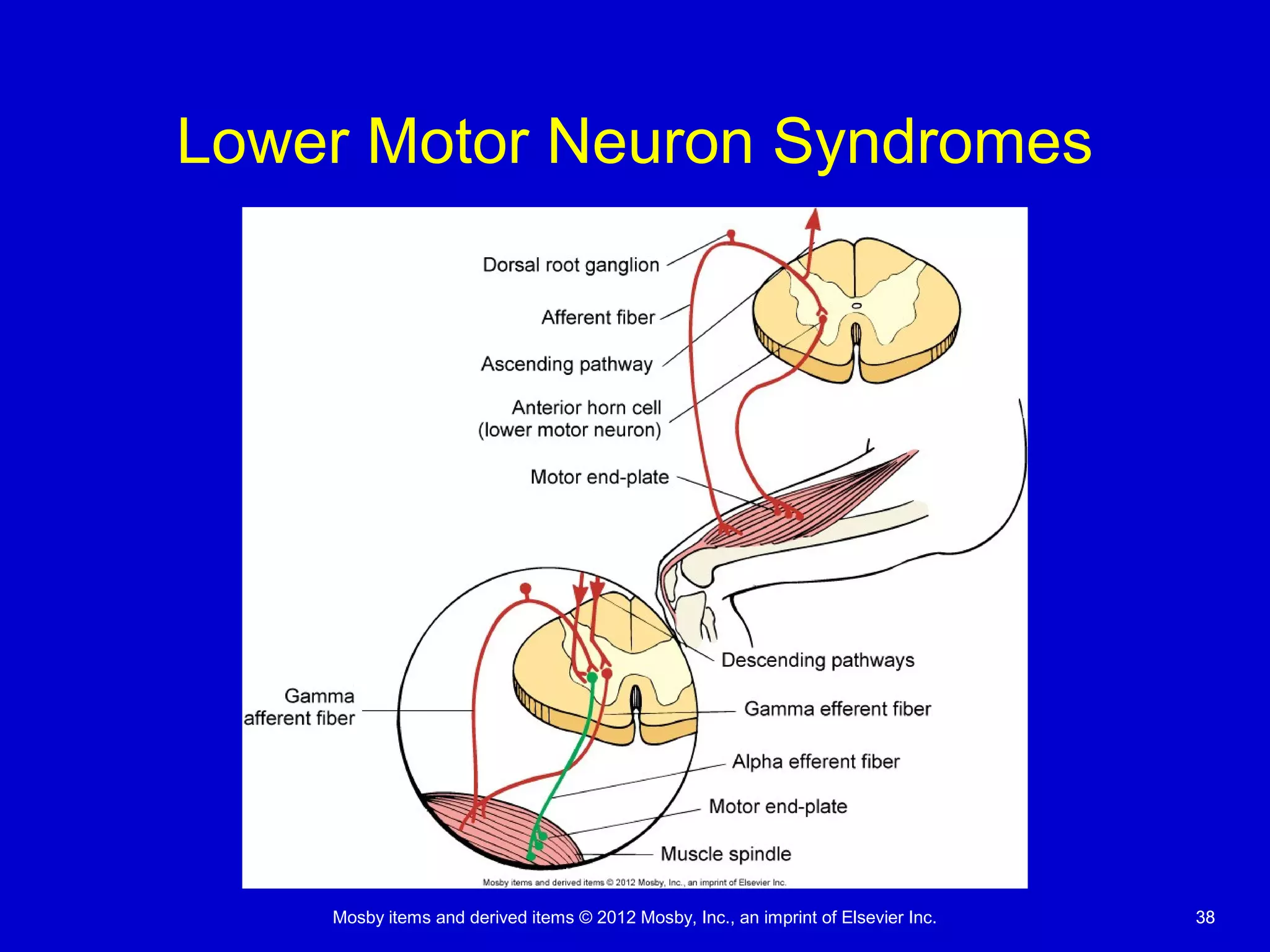
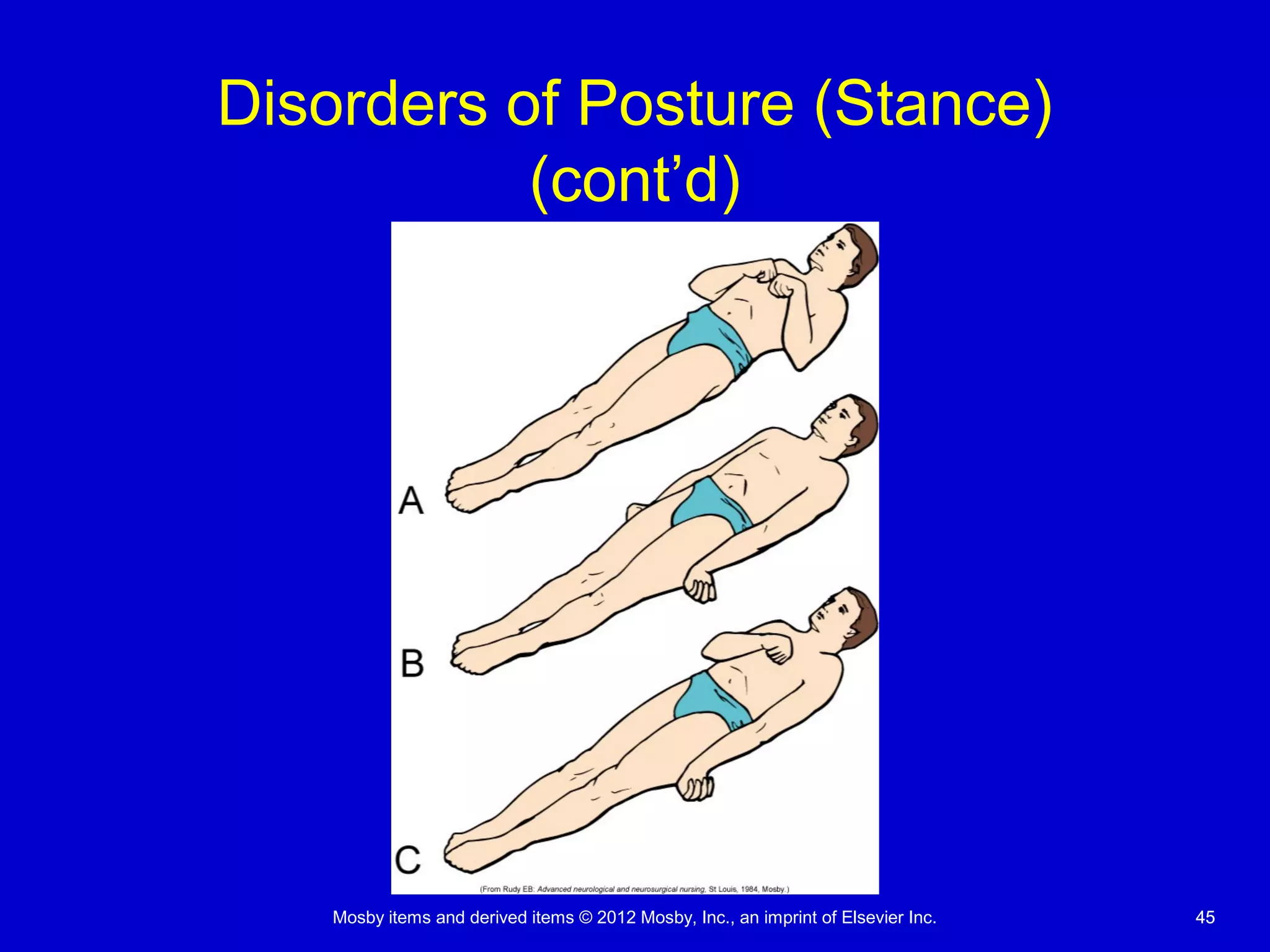
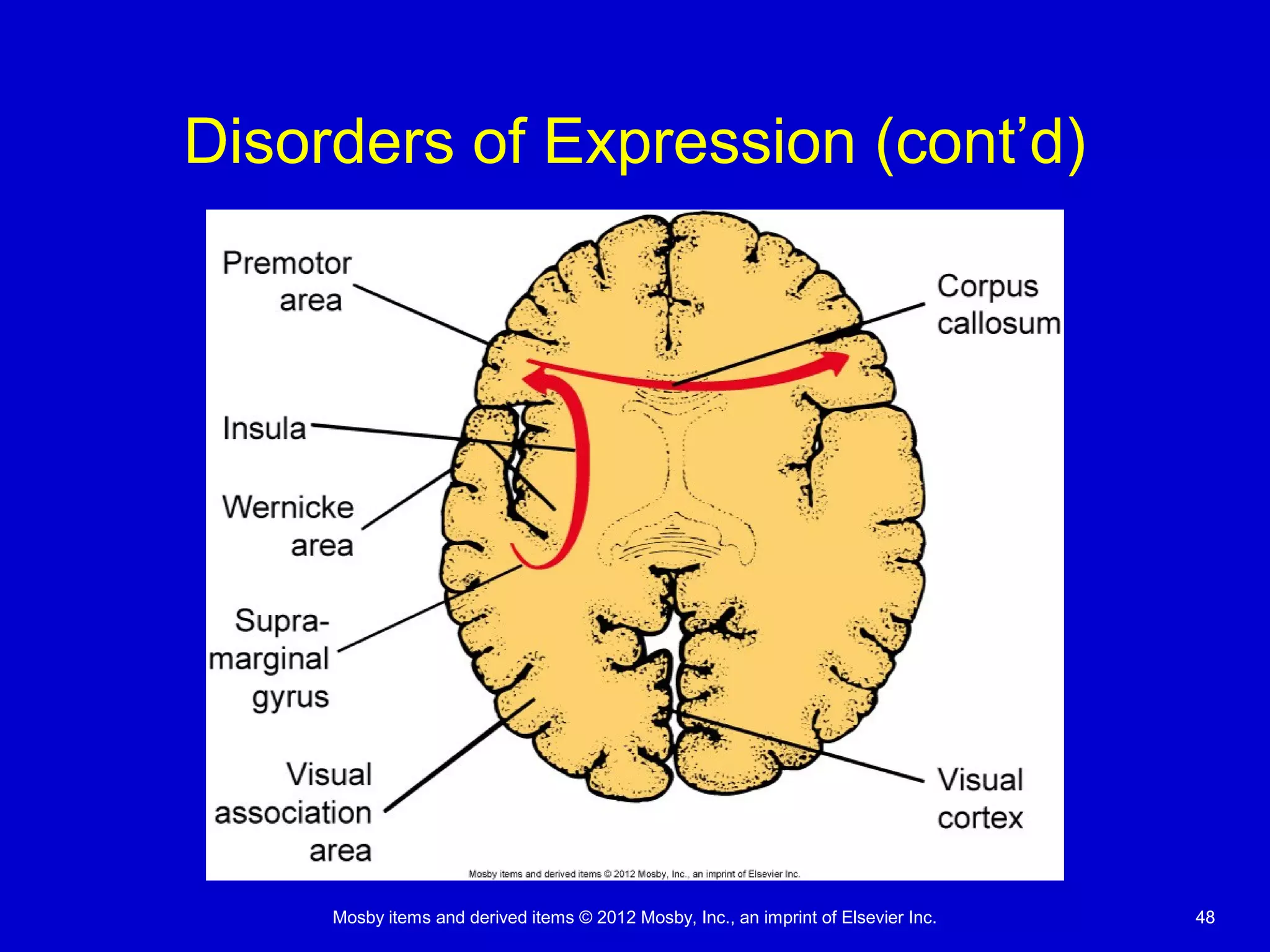
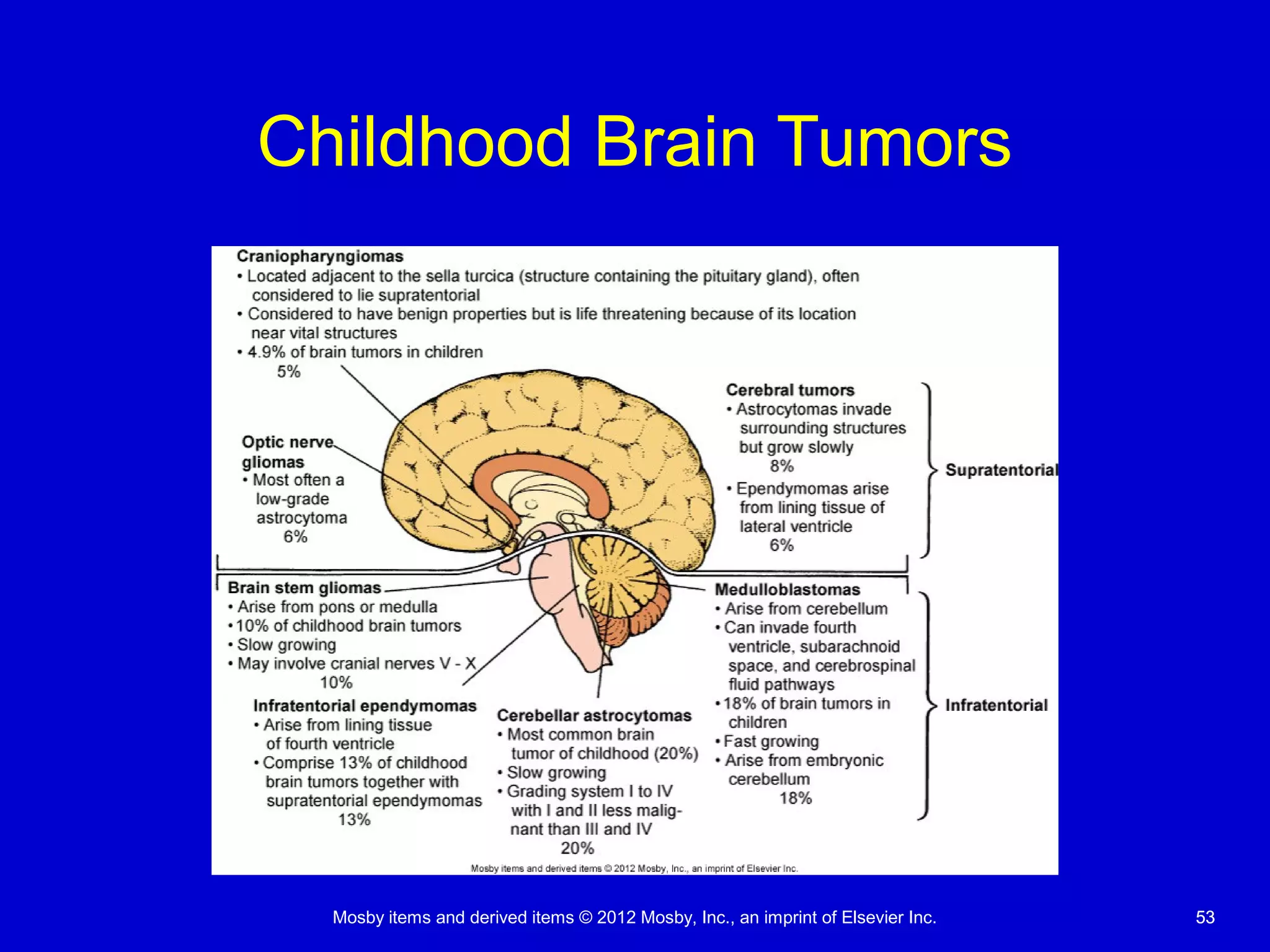
This document discusses various alterations in cognitive systems, cerebral hemodynamics, and motor function. It covers topics like alterations in arousal and consciousness, including coma. It also discusses increased intracranial pressure, herniation syndromes, cerebral edema, hydrocephalus, seizures, alterations in movement such as paresis and paralysis, and disorders of gait and posture. Finally, it briefly mentions reviewing differences in the nervous system of children compared to adults and covers childhood brain tumors.