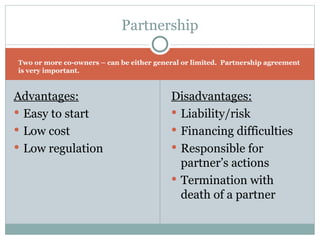
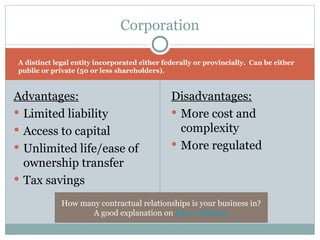
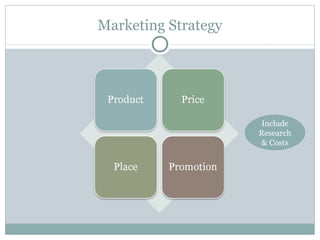
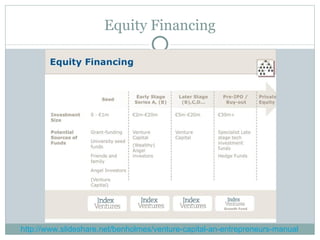
This document discusses different legal forms of businesses including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. It provides advantages and disadvantages of each structure. It also summarizes the key components of a business plan including an executive summary, business strategy, marketing strategy, operational plan, and financial forecasts. The document notes that financing options for businesses include personal funds, bank financing, government grants, angel investors, and venture capitalists.