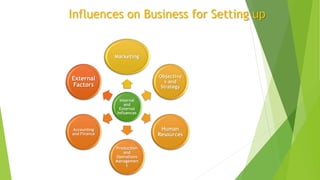
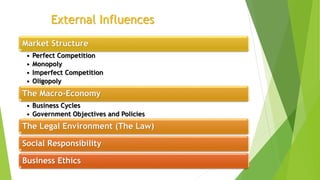
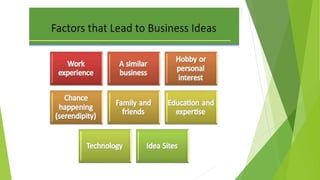
This document provides an overview of topics related to setting up a business, including the meaning and definitions of business, objectives of business, forms of business organization, and how to set up a business. It discusses the economic and social objectives of business, and covers factors that influence business like marketing, human resources, production, accounting, and external factors. It also describes the main forms of business organization like sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies. Finally, it outlines the key steps to setting up a business, such as conducting market research, writing a business plan, finding funding, choosing a location and structure, and marketing the business.