The webinar covered search engine marketing strategies, including:
1) An overview of search engine marketing and the anatomy of search engine results pages, which include paid and organic search listings.
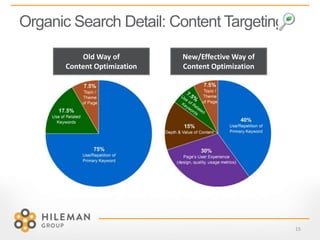
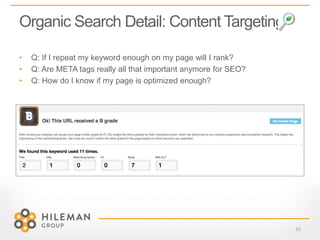
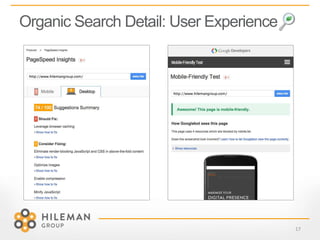
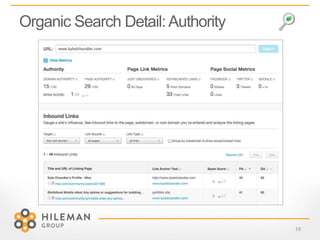
2) Details on optimizing for organic search through content targeting, user experience, and external links to a website.
3) How paid search works on a pay-per-click auction model and tips to improve quality scores without increasing budgets.
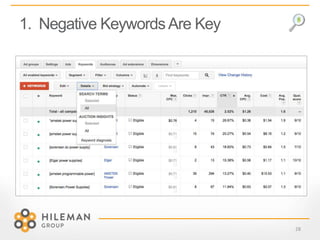
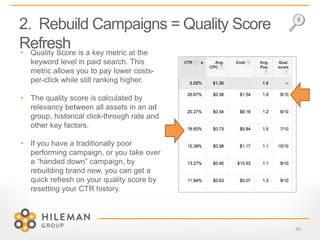
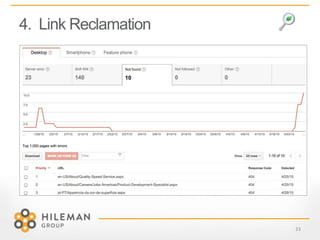
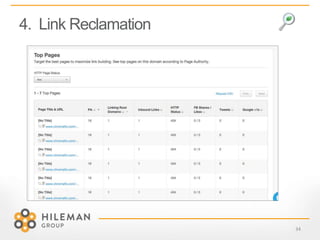
4) Key tips for 2015 like using negative keywords, rebuilding campaigns for quality score refreshes, and leveraging remarketing lists and link reclamation.
![[Webinar]
SearchEngineMarketing101](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-sem101-150521142510-lva1-app6891/85/Search-Engine-Marketing-101-1-320.jpg)