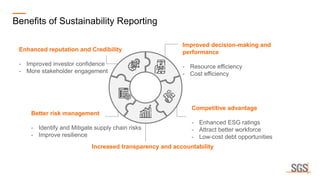
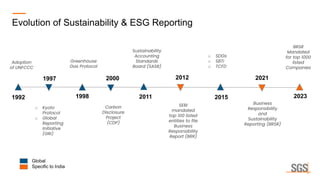
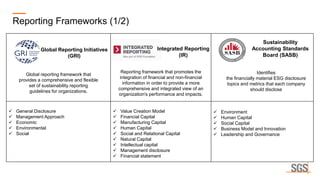
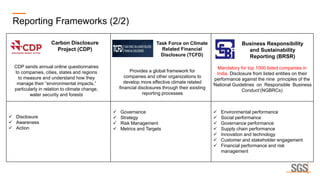
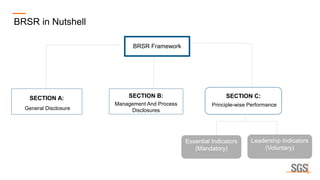
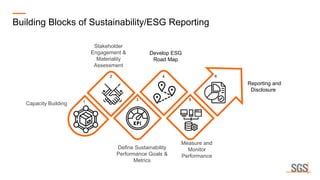
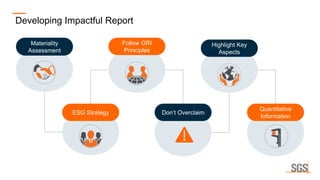
This webinar discusses sustainability reporting and ESG frameworks. It covers key concepts around sustainability, ESG, and reporting. The webinar agenda includes an overview of sustainability and ESG concepts, navigating the sustainability reporting landscape, common reporting frameworks like GRI, SASB, TCFD, and India's BRSR framework. It provides guidance on effective sustainability reporting, including stakeholder engagement, materiality assessment, goal-setting, and disclosure. The webinar is delivered by experts from SGS India, who also describe SGS' ESG advisory and assurance services that can help companies with their sustainability journey and reporting.