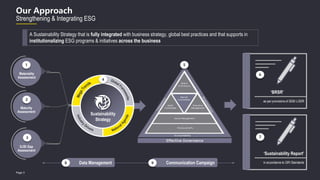
This document outlines Ujjivan Small Finance Bank's approach to strengthening environmental, social and governance (ESG) integration. It details the key activities the bank has undertaken, including a materiality assessment, benchmarking against peers, and assessments against the Dow Jones Sustainability Index and EY's Sustainable by Design framework. It establishes six pillars for the bank's ESG framework: sustainable operations, empowering communities, responsible finance, customer centricity, human capital, and effective governance. Under each pillar, focus areas and goals are defined for the short, medium and long term to guide the bank's sustainability strategy and reporting.


![Page 4
S. No. Activities Status Brief Update
1. Materiality Assessment Completed
• 177 stakeholders engaged i.e., 161 internal and 16 external
• Materiality matrix developed
2. Gap Assessment [ Benchmarking ] Completed
• Benchmarking completed using EY’s SbD criteria
• Four banks i.e. AU, IndusInd, HDFC & Cholamandalam
3. DJSI Assessment Completed
• Gap assessment conducted as per DJSI methodology
• Actions items identified under short, mid and long term
4. ESG Strategy and Roadmap In Progress
• Focus areas identified and ESG framework devised
• Long-term and short-term goals defined across focus areas
• Signoffs to be obtained for respective focus areas
• Implementation plan to be developed
5. Data Management In Progress
• Environment data collection template shared
• ESG dashboard (MIS) to be developed post finalization of goals / targets / implementation plan
6. Effective Governance In Progress
• Policies identified for updation / development
• OHS policy drafted; Sustainability, CoC, HR in progress
• Multi-tier governance to be developed
7. Capacity Building In Progress
• 1 workshop and 1 flyer released
• Other programs scheduled and to be taken subsequently
8. Drafting of BRSR Completed • Maiden BRSR drafted and finalized
9. Drafting of Sustainability Report In Progress • Data collection has been initiated; Draft report to be in place by end of August
Status Overview
Activities and Update](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-4-320.jpg)

![Page 7
Key ‘Takeaways’
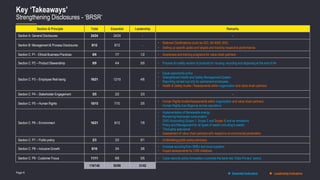
Defining ‘Materiality Assessment’
CV
To identify and prioritize aspects that are of relevance and significance to stakeholder and business
136
Employees
18
Department SPOC’s
5
NGOs
2
Investors
7
Customers
Engaged 170+ Internal & External Stakeholder
through various mediums
7
Leadership & Sr
Mgmt.
2
Suppliers
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANG
E]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
0.80
1.00
1.20
1.40
1.60
1.80
2.00
0.30 0.50 0.70 0.90 1.10 1.30 1.50 1.70 1.90 2.10
STAKEHOLDER
INFLUENCE
IMPACT ON USFB
Materiality Matrix
Responsible
Finance
Sustainable
Operations
Key Themes
Empowering
Communities
Effective
Governance
Governance Social
Environment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-7-320.jpg)



![Page 15
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 1 – Sustainable Operations – Sustainable by Operations [ 1 / 2 ]
• Streamline monthly monitoring and establish accounting across environment
KPIs (energy, emissions, waste, water)
• Continue the rigour of data reporting and monitoring
mechanism through automation process
• Identify relevant Scope 3 emissions categories & sources
• Explore the feasibility of Scope 3 emissions accounting in
alignment with GHG Protocol
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Environment
Monitoring
Mechanism
Sustainable by
Operations*
Responsible
Waste
Management
• Identify & categorize the wastes
• Prepare an inventory of the waste
• Handle and dispose in adherence to the laid down regulatory requirements
• Waste handling vendor contracts to be in place
• Guidelines in place on waste handling, storage and disposal
• Continue the rigour of waste management handling across
operations
• Explore and implement waste reduction / reusing options
• Achieve “Zero waste to landfill” status
• Retain Zero waste to landfill status
Energy /
Emissions/
Water
• Explore opportunities for resource optimization (energy & water)
• Renewable energy options to be explored especially for branches where
consumption is minimum
• Conduct Energy audit to identify energy saving opportunities.
• 100% offices to be equipped with Energy efficient lighting systems to
conserve energy
• 100% employees will be provided training on energy and water conservation
practices through awareness campaigns, training programs etc
• SOP to be defined for Resource optimization and renewable
alternatives as default across operations.
• Install Renewable energy (Solar PV) for selected offices
• Implement energy audit findings (applicable ones) across
operations and measure the energy reduction achieved,
• Achieve 5% reduction in power consumption compared to
FY’23
• Achieve 10% reduction in power consumption compared to FY’23
• Explore opportunities to reduce Scope 3 emissions, which are
emission intensive (Ex: Employee commutation, Business travel
etc.)
Goal 2030 20% reduction in Power consumption
Target 2028 15% reduction in Power consumption
Target 2026 10% reduction in Power consumption
*Goals and targets are w.r.t to FY’2023 baseline
Focus Area SPOC
Ms. Almas Fatima,
National Manager
Admin & Infrastructure Dept](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![Page 16
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 1 – Sustainable Operations – Sustainable by Design [ 2 / 2 ]
• Develop guidelines on sustainable green design concepts
such as energy efficient fittings, alternate materials in
accordance with global frameworks
• Define KPIs scoring mechanism
• Address the gaps/opportunity areas basis the pilot
assessment.
• Automation of Internal processes : Moving towards
manual to automated process for processes (Ex: digital
invoices, Digital employee visiting cards, dual printing,
and digital application forms)
• Implement GREEN building guidelines for selected
office and declare it as a “Model Green branch“
• Review and update the guidelines as per the
learning’s from “model Green branch”
• Explore the feasibility of obtaining IGBC certification
(Green building) for selected office location
• 20% automation of Internal process across 100%
offices and reduce paper consumption by 20%
• Certification of select branches in alignment with national
standards - IGBC
• 50% automation of Internal process across 100% offices
and reduce paper consumption by 50%
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Green
Branches /
Offices
Sustainable by
Design
Goal 2030
10% of total office area (Ujjivan offices) to achieve ‘Green
Building’ certification
Target 2028
5% of total office area (Ujjivan offices) to achieve ‘Green Building’
certification
Target 2026 One select office as “GREEN Building” certified
Focus Area SPOC
Ms. Almas Fatima,
National Manager
Admin & Infrastructure Dept](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-16-320.jpg)



![Page 20
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Talent Management [ 1 / 4 ]
• Increase Training Hours per Employee - from 29
Hours to 30.5 Hours
• Creating ESG awareness as part of new employee
orientation
• Increase the participation % through E-learning
modules
• Increase Training Hours per Employee- from 30.5
Hours to 32 Hours
• Enable Global learning platform for self learning
• Increase Training Hours per Employee - from 32
Hours to 34 Hours
• Provide learning grant for individual development
areas
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Learning &
Development
Talent
Management
Talent attraction
and retention
• Achieve talent retention rate through:
o Job Rotation policy for key roles
o Career development programs
o Sabbatical Leave for individuals
o Introduction of work life balance policy
o Ensuring employee avail mandatory leave to
create work life balance across all levels (>60%)
o Disclose total Employee turnover rate with a
breakdown of Age, Gender, Management level
and Race
• Control voluntary employee attrition rate up to 25%
• Achieve talent retention rate through:
o Ensuring eligible employee avail mandatory
leave to create work life balance across all levels
(>70%)
o Implement policies and employee support
programs such as Work from home (WFH)
working options
• Control voluntary employee attrition rate up to 25%
• Achieve talent retention rate through:
o Ensuring eligible employee avail mandatory leave
to create work life balance across all levels (>80%)
o Track the usage of People Analytics for Strategic
Workforce Planning by:
o Identifying current workforce skills gaps
o Identifying flight risks to improve retention
• Control voluntary employee attrition rate up to 25%
Goal 2030 --
Target 2028 --
Target 2026 34 hours per employee training
Focus Area SPOC
Ms. Shini Ashok, National Manager –
Learning & Talent Management
HR Department](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-20-320.jpg)
![Page 21
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Diversity, Equity & Inclusion [ 2 / 4 ]
• Achieve *gender diversity upto 22%.
o Introduction of “Unpause” model to welcome
women with a career break
o Develop Diversity policy and communicate
across the organization
o Conduct training on gender neutrality for
supervisors for facilitating non-discrimination
awareness against married or pregnant women
• Achieve gender diversity upto 24%.
o Identification of “women only” position in
agreement with the HODs to drive women hiring
in their respective departments
o Derive action plan for hiring women/ disabled/
marginalised
o Introduce reward scheme for referring women in
leadership role
• Achieve gender diversity upto 26%.
o Conduct “women only” hiring campaigns
o Recognise teams, managers and leaders for driving
DE&I
FY24 FY25 FY 26
DE&I
Diversity, Equity &
Inclusion
Goal 2030 --
Target 2028 Achieve gender diversity upto 30%
Target 2026 Achieve gender diversity upto 26%
Focus Area SPOC
Manas Satapathy, National Manager
– Talent Acquisition
HR Department
*Gender diversity specified above, refers to women workforce only](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![Page 22
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Human rights [ 3 / 4 ]
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Human Rights
Goal 2030 -
Target 2028
Completion of the remediation actions of the identified
risk areas.
Target 2026 Complete implementation of the HRDD
• Develop the human rights policy and communicate
across relevant stakeholders
• Develop a human rights due diligence framework and
identification of the potential risks and impact of the
same.
• Conduct due diligence process to proactively identify
potential impacts and risk relating to respecting
human rights
• Report on human rights mitigation and remediation
activities
• Implement processes to mitigate human rights risks
• Number of sites with mitigation plans
• Type of remediation actions taken
Human Rights
Focus Area SPOC
Prasanna Venkatesen, National Manager –
HR operations
HR Department](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-22-320.jpg)
![Page 23
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Health, Safety and Wellbeing [ 4 / 4 ]
• Develop OHS management system
• Program Deployment (e.g., Ergonomics, healthy
lifestyle, health talks by experts, fitness programs,
defensive driving etc.,)
• Conduct accident investigation & preventive action at
Ujjivan office locations
• Conduct electrical safety audit across Ujjivan offices.
• Road safety focused program to be rolled out across
operations focussing more on field staff
• Monitor the accident rate at Ujjivan office locations
• Conduct employee Survey and develop Employee
Wellness Index
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Employee
Overall
Wellness
Initiatives
Health, Safety &
Wellbeing
Goal 2030
Zero Accidents – Ujjivan office locations
Target 2028
Target 2026
Focus Area SPOC
Manjunath V,
Lead – Payroll & Compliance
HR Department](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-23-320.jpg)

![Page 25
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Data Privacy and Cyber Security [ 1 / 4 ]
Align policies and procedures with global standards
like ISO 27001:2022 (inclusive of business
contingency plan, incident response procedures
and periodic testing)
Obtaining ISO 27001:2022 Certification
Ensuring Sustenance of ISO 27001:2022
certification
Implementation of data Privacy Framework as per
Indian Privacy Law
Assessment in place to ensure alignment with ISO
27001:2022
Indian Privacy Law Compliance
Strengthen the security posture of the Bank to continue
to remain Cyber Attack/ Breach Free.
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Privacy and
Information
Security
Management
Data Privacy &
Cyber Security
Goal 2030
Zero Data Security Breaches
Target 2028
Target 2026
Focus Area SPOC
Mr. Shailesh Tiwari,
Cyber Governance Manager
Information Security Risk
Department](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-25-320.jpg)
![Page 26
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Governance [ 2 / 4 ]
Design a multi-tier ESG governance structure
Develop roles and responsibilities for each
position
Increase the Board Independence further from
the current 66%
Continuous review and update of governance
structure
Further increase in board diversity ratio
To continue to adhere to highest standards of
governance to ensure 100% compliance
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Governance
Structure
Governance
Goal 2030
Robust Governance Structure, beyond compliance
Target 2028
Target 2026
Focus Area SPOC
Kshama Algure, Assistant Company
Secretary
Corporate Secretary Department](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-26-320.jpg)
![Page 27
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Ethics & Compliance [ 3 / 4 ]
Identify, review and develop areas requiring policy as
per ESG trends/external requirements.
100% implementation of policies developed in
FY'24
Regular review and update of policies at set
frequencies
Regularly update policies at set frequencies
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Business Ethics
‘Programs and initiatives identified. However, no Goal / Target defined
for the same’
Ethics &
Compliance
Compliance
Management
Automation of Contract Management that reduces
turnaround time in execution of contracts and
streamlines the contract management system.
Implement Litigation Management Software that
eases monitoring of cases involving the Bank.
Digitisation of stamping through external vendor to
avoid storage of physical stamp papers.
Continue advisory in the best interest of Bank and mitigate
legal risks to avoid any fines, penal actions by statutory
authorities against the Bank.
Focus Area SPOC
Kshama Algure, Assistant Company Secretary
Ms. Megha, Manager - Legal
Corporate Secretary Department & Legal
Team](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-27-320.jpg)
![Page 28
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Risk Management [ 4 / 4 ]
• Risk management education for non-executive
directors
• Enhance disclosure on risk management practices
(risk governance policy, risk training programs)
• Disclosure in accordance with TCFD requirements
• Develop a framework for ESG aspects in
credit/lending business
Integrating climate related risk in the risk
management process as per global frameworks
• Focused training throughout the organization on
risk management principles
• Inclusion of Risk management criteria in the HR review
process for all employees
• *Due diligence process to identify risk & impact relating
to human rights
• Assessment of potential human rights issues across
business activities
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Risk & Crisis
Management
Risk
Management
Goal 2030 Achieve transformative stage in the risk maturity ladder
Target 2028
-
Target 2026
Focus Area SPOC
Rakesh Kalyanram,
Lead - Risk
Risk Management Team
*This point is included in HR goals as well](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-28-320.jpg)


![Page 32
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 6 – Responsible Finance – Green Finance [ 1 / 2 ]
Conduct market survey and identify the
requirements of green products
Develop criteria for Green products/responsible
finance.
Identify responsible finance products (ex: lending
for rain water harvesting, Biogas plant, EV & CNG
vehicle, Solar water heater, ECO friendly buildings,
Solar PV, composting facility etc).
Develop KPIs on Green products outreach (e.g. no.
of beneficiaries, GHG emission
reduction, reduction in fresh water withdrawal etc.)
• Roll out the pilot product and monitor the impact
created across defined KPIs.
• Basis the pilot product, relook the criteria.
• Set goals and targets against the KPIs for
evaluation.
• Launch of green products portfolio.
• Measure the KPIs to assess the performance against the
targets.
• Communicate the performance both externally and
internally at fixed intervals (external assurance).
• Explore options releasing Green bonds/green deposits,
Sustainability linked loans.
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Green Finance
Green Finance
Goal 2030 xx% revenue from green product portfolio
Target 2028 xx% revenue from green product portfolio
Target 2026 Devise criteria for Green Finance
Focus Area SPOC
To be nominated
Business Team](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-32-320.jpg)
![Page 33
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 6 – Responsible Finance – Inclusive Finance [ 2 / 2 ]
• Simplifying loan application processes making it
easier for small businesses & individuals to access
financing
• Develop Strategy to provide financial services for
aspiring entrepreneurs/ MSME enterprises in rural
areas.
• Explore and define an action plan to expand the
micro-finance portfolio in Tier 2 & Tier 3 cities.
• Digital solutions and literacy programs to streamline
transactions in the micro-finance sector.
• Basis strategy, release financial products in the
market to support entrepreneurs/ MSME
enterprises.
• Collaborate with funds, foundations and development
finance Institutions to support projects in sectors like
agriculture, micro-finance, health care etc.
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Inclusive
Finance
Inclusive Finance
Goal 2030 Expanding reach & impact
Target 2028 -
Target 2026 -
Focus Area SPOC
To be nominated
Business Team](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-33-320.jpg)

![Page 35
Building the ‘Framework’
Aspects Cutting Across – Transparency & Disclosures [ 1 / 3 ]
• Dedicated webpage on sustainability to display the
activities under ESG domain
• In addition to the Sustainability Report and BRSR,
TCFD two pager to be appended to existing
Sustainability Report
• Continue the rigour on Sustainability Report in
alignment with GRI Standard, BRSR and TCFD
• External assurance as per ISAE 3000 and AA 1000
AS (2008) Standards
• Integrated reporting in alignment with global frameworks
like GRI/TCFD/IIRC
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Reporting
framework
Disclosures
ESG Indices
• Internal assessment and readiness towards S&P
Global CSA (DJSI) to reach ~40 score*
• Maiden S&P Global CSA (DJSI) assessment
• Continue to participate on S&P Global CSA
(DJSI) assessment
Goal 2030 Aspire to reach top quartile on S&P Global CSA (DJSI)
Target 2028 60 score on S&P Global CSA (DJSI)
Target 2026 -
Focus Area SPOC
D Srividhya, Manager, CSR
Kshama Algure, Assistant
Company Secretary
Social Service Department
and
Corporate Secretary Team
*Above is an indicative score as the DJSI questionnaire gets updated annually](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-35-320.jpg)
![Page 36
Building the ‘Framework’
Aspects Cutting Across – Stakeholder Engagement [ 2 / 3 ]
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Stakeholder
Engagement
Goal 2030
100% digital invoices from vendors with spend of Rs. 1 Cr or
higher
Target 2028 -
Target 2026 Top quartile across all stakeholder group satisfaction surveys
Quarterly engagement with investors - 5 among top 15
Quarterly engagement with Sell-side analyst (minimum
5 nos.)
Quarterly engagement with investors - 7 among top 15
Quarterly engagement with Sell-side analyst (minimum
7 nos.)
Quarterly engagement with investors - 10 among top 15
Quarterly engagement with Sell-side analyst (minimum 8
nos.)
Investors
Develop and incorporate ESG requirements in the
contracts/agreements executed with vendors through
vendor Code of Conduct
Develop SoP for vendor assessment and capture the
scores as part of the vendor assessment
Conduct capacity building on vendor code of
conduct and assessment for strategic vendor
partners
Shift to digital invoices to cover 50% vendors with
spend of Rs. 1 Cr or higher
Involve and engage with strategic vendors (50%) to
implement eco-friendly initiatives
Shift to digital invoices to cover 80% vendors with spend of
Rs. 1 Cr or higher
Vendors
Focus Area SPOCs
• Mr. Deepak Shivprakash Khetan, National Manager- Investor
Relations, Financial Planning & Strategy;
• Ms. Apoorva Padmanabh, Manager- Service Quality
Compliance;
• Mr. Sriram Srinivasan- Digital Banking;
• Mr. Zubair Ullah, Head- Digital Channels;
• Mr. Tahir Khan, National Manager- Procurement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-36-320.jpg)
![Page 37
Building the ‘Framework’
Aspects Cutting Across – Digital Transformation [ 3 / 3 ]
Implement new digital solutions such as end-to-end
Digital Fixed Deposit, Digital Savings/Current
Account, personalised banking services using video
banking solutions
Bringing 35 lakhs+ customers into digital banking
space and achieve digital transactions (volume) of
35 crores by including 12 lakh+ new users on any
one of the digital platform
Bringing 50 lakhs+ customers into digital banking
space and achieve digital transactions (volume) of
50 crores by including 15 lakh+ new users on any
one of the digital platform
Bringing 65 lakhs+ customers into digital banking space
and achieve digital transactions (volume) of 75 crores by
including 18 lakh+ new users on any one of the digital
platform
100% digitalisation for Asset & Liability business and
Digital Lending Solutions, thereby moving towards paper
less banking services
FY24 FY25 FY 26
Digital
Transformation
Digital
Transformation
Goal 2030
Bringing 1 crore customers into digital banking space and achieve digital
transactions (volume) of 100 crores.
Target 2028 -
Target 2026
Bringing 65 lakhs+ customers into digital banking space and achieve
digital transactions (volume) of 75 crores.
Focus Area SPOCs
• Mr. Sriram Srinivasan- Digital Banking;
• Mr. Zubair Ullah, Head- Digital Channels;
Digital Banking Dept](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-37-320.jpg)








![Page 47
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 1 – Sustainable Operations – Sustainable by Operations [ 1 / 2 ]
Sustainable by
Operations
Establish and drive sustainable practices across built environment with an objective to minimize resource usage
and also impact associated – Emissions, Waste & Water
Key waste mgmt. measures:
• Introduce digital visiting cards
since FY22
• Replaced single use plastic
bottles with refillable glass
bottles at all offices
• Responsible usage of
compressed wood modulars in
all offices
• E-waste generated disposed only
through authorised entities &
recyclers
• Procure e-devices only from
certified manufacturers that
comply with regulations on
hazardous substances’ disposal
The Govt. notified various rules for Plastic
Waste Management, e-Waste Management,
Construction and Demolition Waste
Management, Metals Recycling etc.
Formed 11 committees, led by the concerned
line ministries & comprising officials from
MoEFCC, NITI Aayog, domain experts,
academics and industry representatives for 11
focus areas
The committees will prepare comprehensive
action plans for transitioning from a linear to a
circular economy in their respective focus areas
India Driving Transition from Linear to
Circular Economy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-47-320.jpg)
![Page 48
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 1 – Sustainable Operations – Sustainable by Design [ 2 / 2 ]
Sustainable by
Design
Environmentally conscious or responsible built space, which is purposefully designed to reduce the overall
environment footprint during & after its construction phase
Key sustainable workspace initiatives:
• Recycle old furniture & utilise only certified green-
wood furnishings
• Afforestation Strategy: Focused on enhancing green
cover in offices & beyond its periphery
• Insulation in offices to reduce heat at workplaces to
reduce energy consumption
• Adopted energy-efficient systems by installing LEDs
in offices, branches & outlets
• Natural ventilation through modern architectural
designs
• Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) & Variable
Refrigerant Volume (VRV) systems are integrated &
installed in the ACs in all Offices
• Responsible usage of compressed wood modulars in
AU’s offices which are environmentally benign,
reusable, & recyclable.
LEED Gold certified offices in Mumbai and
Bhubaneswar.
In addition, new buildings in Mohali, Kolkata
Palava and Mumbai (Maharashtra) premises
are being constructed to meet IGBC Gold
certification standards.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-48-320.jpg)
![Page 49
Corporate Social
Responsibility
Supporting essential workers and vulnerable sections of society
through focused interventions like education, skilling, healthcare
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 2 – Empowering Communities – Corporate Social Responsibility [ 1 / 1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-49-320.jpg)
![Page 50
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Talent Management [ 1 / 4 ]
Talent
Management
Companies are evaluated on their workforce talent requirements and their ability to
attract, retain, and develop a highly skilled workforce.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-50-320.jpg)
![Page 51
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Diversity, Equity & Inclusion [ 2 / 4 ]
Diversity, Equity &
Inclusion
Culture of inclusion and belonging for everyone in an organization irrespective of
gender, ethnicity, race, religion, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-51-320.jpg)
![Page 52
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Human Rights [ 3 / 4 ]
Human Rights
Rights inherent to all human beings, regardless of race, sex, nationality, ethnicity,
language, religion, or any other status.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-52-320.jpg)
![Page 53
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 3 – Human Capital – Health, Safety and Wellbeing [ 4 / 4 ]
Health, Safety &
Wellbeing
Promoting resilient and transformative culture where workplace allows people to
perform and develop in a safe and healthy ecosystem
FY2021-22 was again a very
challenging year for the entire
nation and the global economy in
particular, due to repeated waves of
COVID-19 pandemic, global
conflicts & ensuing economic
disruptions.
One of the key focus areas of the
Human Resources function during
the financial year was to enable
employee well-being and also
ensure business continuity for
superior customer service.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-53-320.jpg)
![Page 54
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Data Privacy and Cyber Security [ 1 / 4 ]
Data Privacy &
Cyber Security
Due to the current trend of digitization, it is crucial that access to network, IT systems and data is assured at all times eliminating
threat to confidential data and customer privacy in terms of data theft & loss
Data
Privacy &
Cyber
Security](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-54-320.jpg)
![Page 55
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Governance [ 2 / 4 ]
Governance
This pillar evaluates the impact companies' corporate governance and business ethics practices have on investors.
The companies are assessed on all Governance Key Issues, including Ownership & Control, Board, Pay, Accounting,
Business Ethics, and Tax Transparency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-55-320.jpg)
![Page 56
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Ethics & Compliance [ 3 / 4 ]
Ethics & Compliance An ongoing process of monitoring and assessing systems to ensure they comply with regulatory and industry requirements
UK
• FCA is consulting on corporate disclosure of
climate risks and is focusing on ‘greenwashing’
• TCFD mandated for companies listed on
premium exchange from January 1, 2021 and to
extend to all UK companies by 2025
• Social value legislation and climate legislation for
procurement
• Non-Financial Reporting Directive – expected to
cover 50k entities
• EU Taxonomy for Sustainable Activities
Hong Kong
• The Securities & Futures Commission announced its
Strategic Framework for Green Finance in 2018, with
a focus on climate-related disclosure and the
integration of ESG into investment processes by asset
managers
Germany
• Bafin published guidance in December
2019 on how FS firms should manage
sustainability risks, with a focus on climate
Singapore
• Monetary Authority of Singapore - exploring ways to
incorporate climate-related risks
• SGX introduced sustainability on a “comply-or-
explain” basis to its listing rules.
• SGX is aligning its disclosure requirements in line
with TCFD
Australia
• Australian Securities & Investments
Commission - disclosure provisions to
climate-related risks, reflecting TCFD
recommendations
India
• SEBI introduced Business Responsibility and
Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) regulations.
• It will be mandatory for top 1000 listed
companies (by net-worth) from FY23 (voluntary
from FY22)
United States
• US Senate - ESG Disclosure Simplification Act
of 2021
• SEC Announces Enforcement Task Force
Focused on Climate and ESG Issues
• SEC requests Public input on Climate
Disclosures
Europe Union
• Sustainable Finance Action Plan
• Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulations
Switzerland
• Mandates Climate Reporting for
public companies, banks and
insurance entities over a
threshold – aligned with TCFD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-56-320.jpg)
![Page 57
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 4 – Effective Governance – Risk Management [ 4 / 4 ]
Risk & Crisis
Management
Assessment and management of the risks associated
with climate change/extreme weather and its impacts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-57-320.jpg)
![Page 58
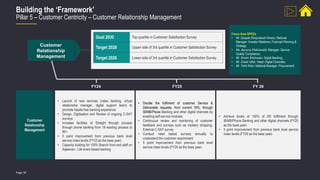
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 5 – Customer Centricity – Customer Relationship Management [ 1 / 1 ]
Customer Relationship
Management
Manage customers and better understand their needs in order to
provide the right solutions in a timely manner
• Customer-centric approach
• Seamless, easy, fast & transparent service
• Continuous client interaction by using
both digital and non-digital channels
• More than 70% of client requests in March
2022 were raised through digital channels
and overall 95% of the requests got resolved
within one day](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-58-320.jpg)
![Page 59
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 6 – Responsible Finance – Green Finance [ 1 / 2 ]
Green Finance Green financing is to increase level of financial flows to sustainable development priorities
• In 2017, the State Bank of India (SBI) launched a green bond worth ₹1,000 crore (US$125 million). The proceeds
from the bond were used to finance renewable energy projects
• In 2018, HDFC Bank launched a green loan scheme worth ₹5,000 crore (US$625 million). The scheme is designed
to finance energy efficiency projects in commercial buildings
• In 2019, ICICI Bank launched a sustainable investment fund worth ₹1,000 crore (US$125 million). The fund invests in
companies that are working to promote sustainable development](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-59-320.jpg)
![Page 60
Building the ‘Framework’
Pillar 6 – Responsible Finance – Inclusive Finance [ 2 / 2 ]
Inclusive
Finance
Availability and equality of opportunities to access financial services. It refers to a process by which individuals and businesses can
access appropriate, affordable, and timely financial products and services.
Improving
Access
Improving
Usage
Enhancing
Quality
Financial
Inclusion
31% branches in
unbanked rural
centres
1,93,000+
customers
provided financial
services under
Jan Dhan Yojana
600+ financial
literacy camps
at rural
branches
Digital
Inclusion
39,000+ AU 0101
registration in
unbanked rural
centres
40,000+ UPI
transacting
customers in
unbanked rural
centres
20,000+
merchants
onboarded on
UPI QR codes
in unbanked
rural centers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-60-320.jpg)
![Page 61
Building the ‘Framework’
Aspects Cutting Across – Transparency & Disclosures [ 1 / 3 ]
Transparency &
Disclosures
Ensuring data completeness, accountability and data transparency to all
relevant stakeholders and available in a timely manner.
Disclosures- India
BRSR is mandatory for the top
1000 listed entities
ESG investing to tackle the risk
of greenwashing including
mandating ESG schemes to
invest at least 65% of AUM
Core BRSR mandates 49
parameters for ESG reporting
Reasonable assurance made
mandatory under core BRSR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-61-320.jpg)
![Page 62
Building the ‘Framework’
Aspects Cutting Across – Stakeholder Engagement [ 2 / 3 ]
Stakeholder
Engagement
Focus on engaging with internal and external stakeholders and creating value for them](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-62-320.jpg)
![Page 63
Building the ‘Framework’
Aspects Cutting Across – Digital Transformation [ 3 / 3 ]
Digital
Transformation
Integration of digital technology throughout all aspects of an organization, results in
significant changes to how the organization functions and delivers benefits to its clients](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esgframework-231008035123-ac5259a1/85/ESG-Framework-pptx-63-320.jpg)