This document provides an overview of key concepts for designing and planning webpages, including:
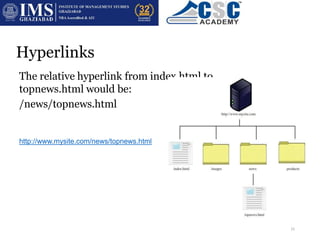
HTML is the code used to structure webpages and can be viewed by looking at a page's source code. Browsers interpret HTML to display webpages correctly and include features like bookmarks and history. URLs identify resources on the internet through a protocol, domain name, path, and filename. Hyperlinks allow users to navigate between webpages either within the same site or between different sites using absolute or relative links. Navigation options include entering URLs, using search engines, bookmarks, history, breadcrumbs, and forward/back buttons.