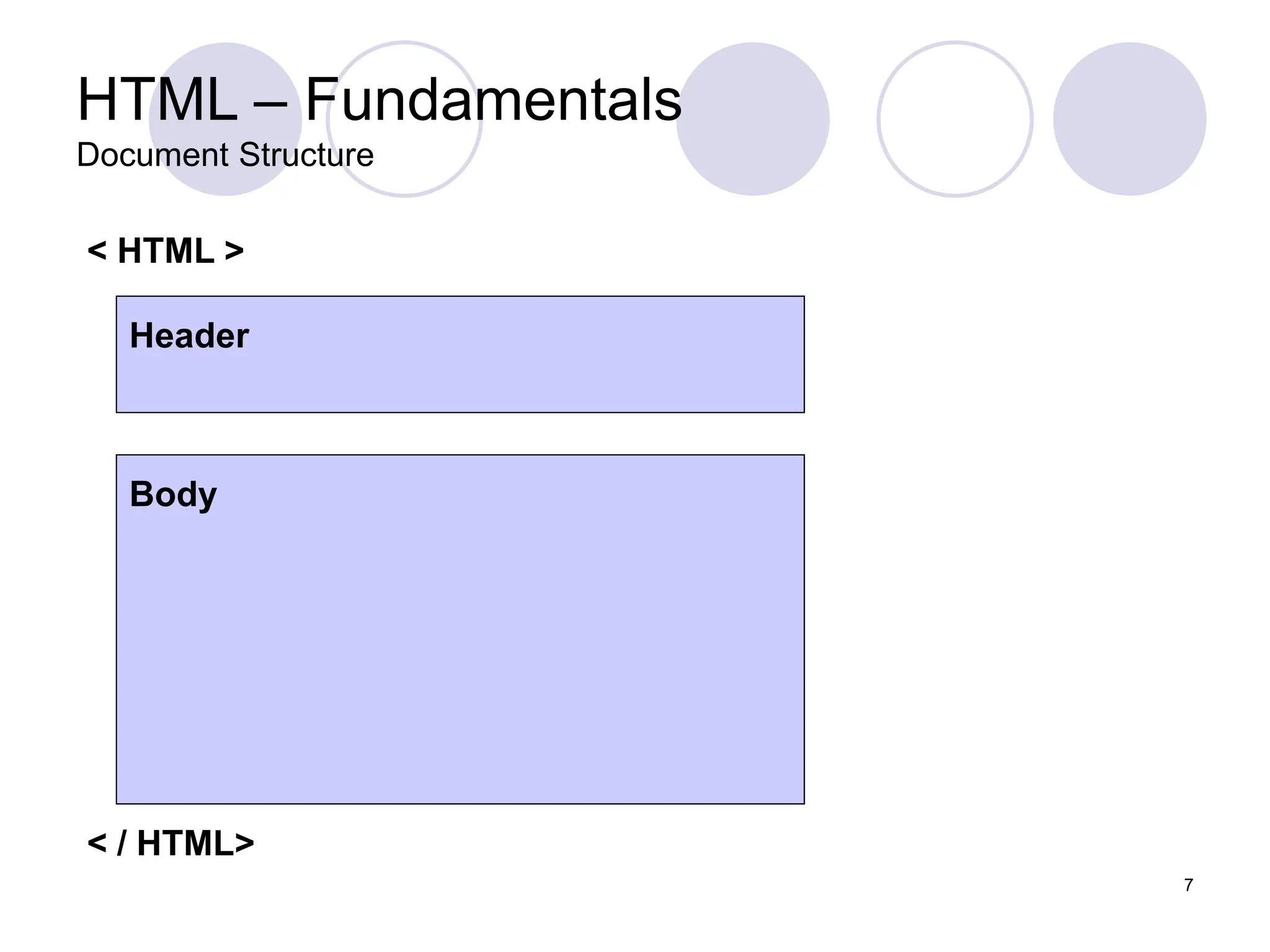
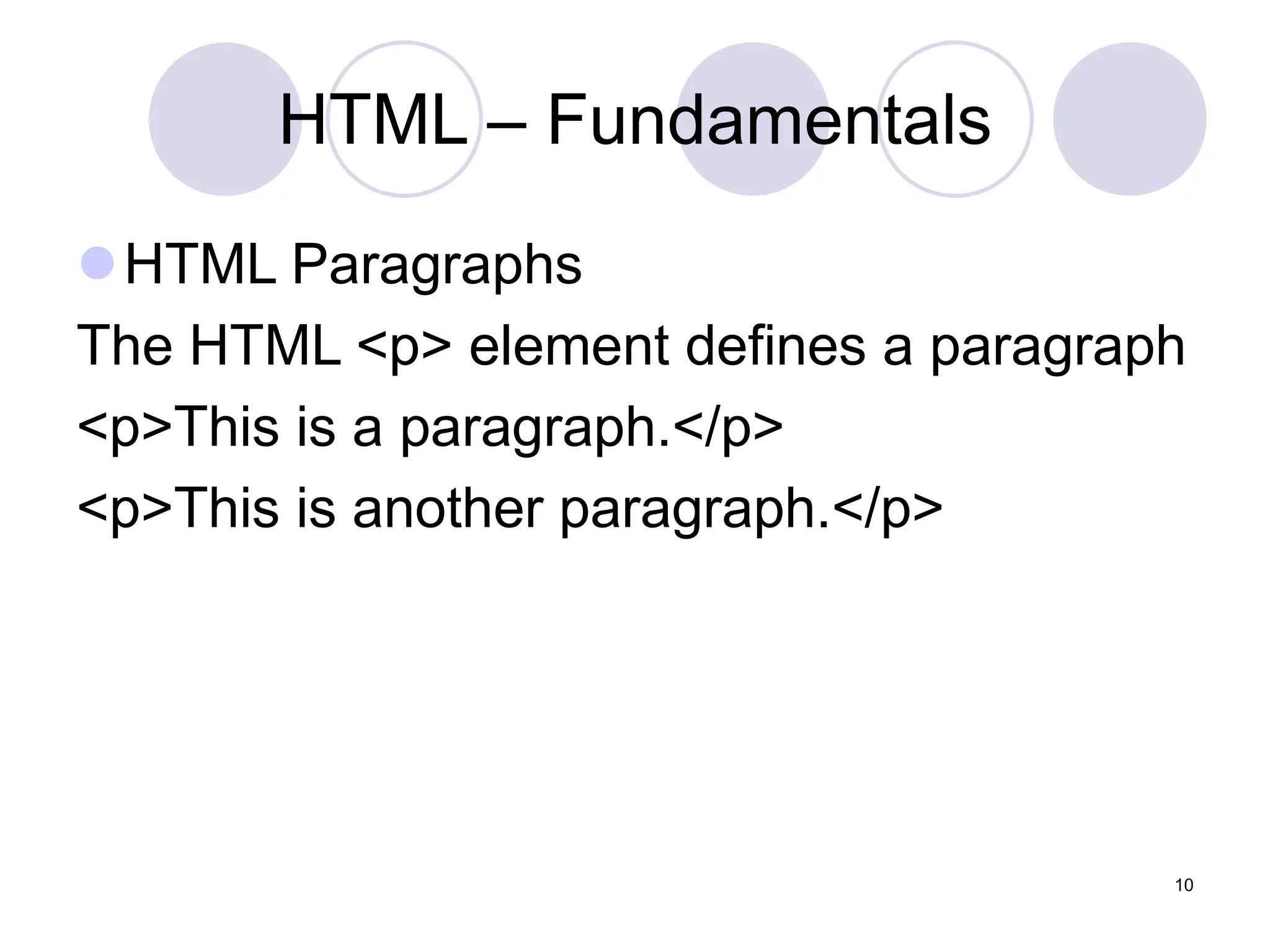
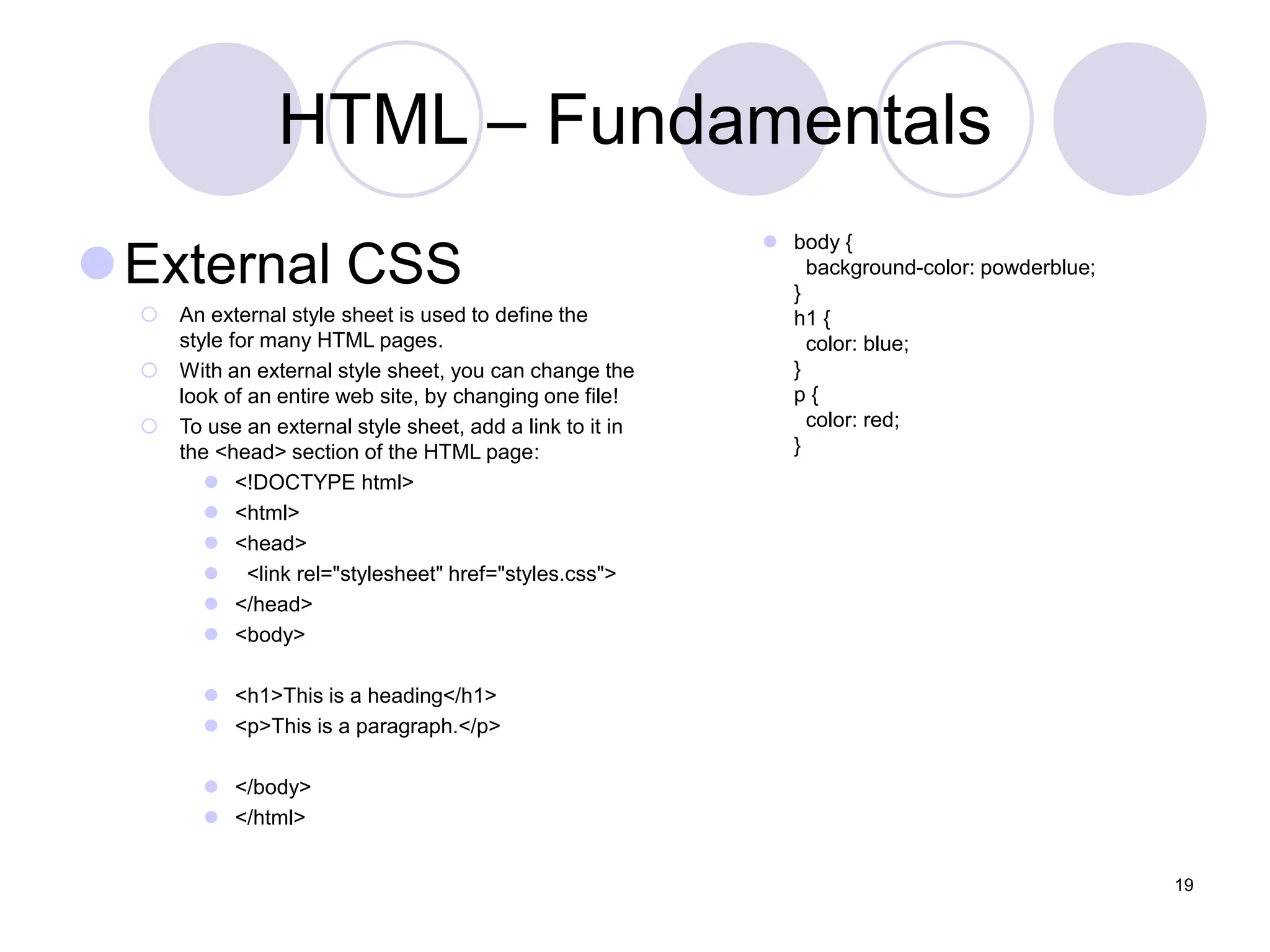
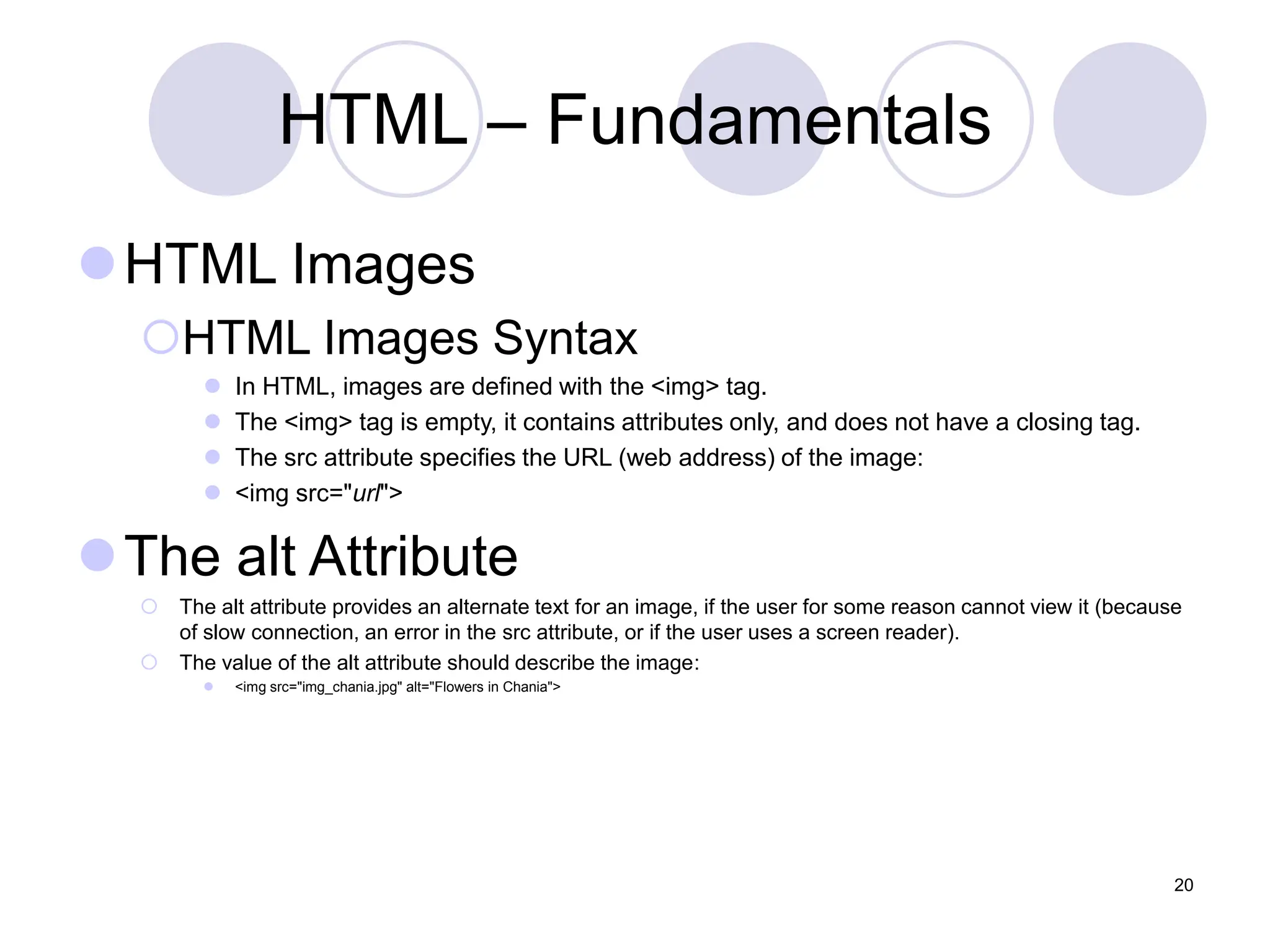
This document is a lecture on web design by Muhammad Waheed, covering essential technologies and tools for creating websites, specifically HTML and CSS fundamentals. It discusses HTML structure, elements, styles, and the use of CSS for styling web pages, including inline, internal, and external methods. The content also includes information on images, attributes like class and id, and advanced CSS background properties.