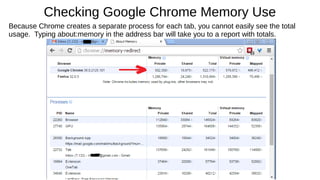
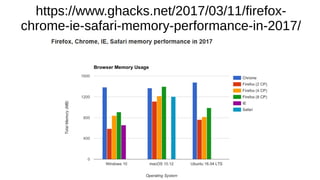
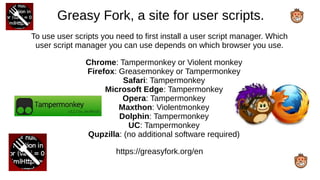
The document provides an extensive overview of web browsers, focusing on their definitions, functionalities, and fundamental components such as URLs and cookies. It highlights security concerns, browser performance, and best practices for safe browsing, including the use of password managers and privacy-focused search engines. Additionally, it offers various tips, tricks, and resources to optimize browser usage and security.



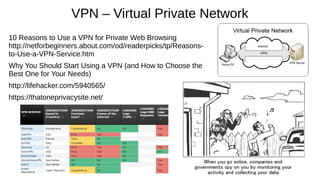
![What is a Web Browser?
“A web browser (commonly referred to as a browser) is
a software application for retrieving, presenting and
traversing information resources on the World Wide
Web. An information resource is identified by a
Uniform Resource IdentifierUniform Resource Identifier ((URI/URLURI/URL)) and may be
a web page, image, video or other piece of content.[1]
Hyperlinks present in resources enable users easily to
navigate their browsers to related resources.”
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_browser
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/browserbasicsd20-170518210718/85/Web-Browser-Basics-Tips-Tricks-Draft-20-Revised-5-18-17-6-320.jpg)


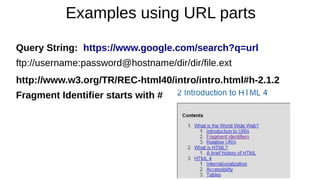
![What are the parts of a URL? (1)
scheme://domain:port/path?query_string#fragment_id
The scheme, often referred to as protocol, defines how the resource will be obtained. Examples
include http, https, ftp, file and many others. Although schemes are case-insensitive, the canonical form
is lowercase.
The domain name or literal numeric IP address gives the destination location for the URL. A literal
numeric IPv6 address may be given, but must be enclosed in [ ] e.g. [db8:0cec::99:123a].
The domain google.com, or its numeric IP address 173.194.34.5, is the address of Google's website.
The domain name portion of a URL is not case sensitive since DNS ignores case:
http://en.example.org/ and HTTP://EN.EXAMPLE.ORG/ both open the same page.
The port number, given in decimal, is optional; if omitted, the default for the scheme is used.
For example, http://vnc.example.com:5800 connects to port 5800 of vnc.example.com, which may be
appropriate for a VNC remote control session. If the port number is omitted for an http: URL, the
browser will connect on port 80, the default HTTP port. The default port for an https: request is 443.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/browserbasicsd20-170518210718/85/Web-Browser-Basics-Tips-Tricks-Draft-20-Revised-5-18-17-9-320.jpg)
![What are the parts of a URL? (2)
protocol://domain:port/path?query_string#fragment_id
The path is used to specify and perhaps find the resource requested. It is case-sensitive,
[13] though it may be treated as case-insensitive by some servers, especially those based
on Microsoft Windows.
If the server is case sensitive and http://en.example.org/wiki/URL is correct, then
http://en.example.org/WIKI/URL or http://en.example.org/wiki/url will display an HTTP 404
error page, unless these URLs point to valid resources themselves.
The query string contains data to be passed to software running on the server. It may
contain name/value pairs separated by ampersands, for example
?first_name=John&last_name=Doe.
The fragment identifier, if present, specifies a part or a position within the overall resource
or document.
When used with HTML, it usually specifies a section or location within the page, and used in
combination with Anchor Tags the browser is scrolled to display that part of the page.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uniform_resource_locator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/browserbasicsd20-170518210718/85/Web-Browser-Basics-Tips-Tricks-Draft-20-Revised-5-18-17-10-320.jpg)

![https: Secure Encrypted connections
“Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its
predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are
cryptographic protocols designed to provide
communication security over the Internet.[1] They
use X.509 certificates and hence asymmetric
cryptography to authenticate the counterparty with
whom they are communicating, and to exchange a
symmetric key. This session key is then used to
encrypt data flowing between the parties. This
allows for data/message confidentiality, and
message authentication codes for message
integrity and as a by-product, message
authentication.”
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_S
ecurity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/browserbasicsd20-170518210718/85/Web-Browser-Basics-Tips-Tricks-Draft-20-Revised-5-18-17-13-320.jpg)
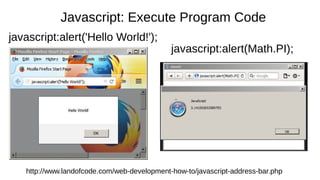


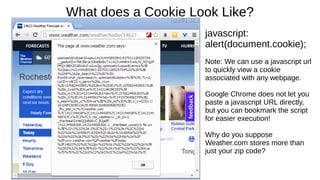
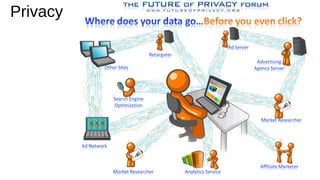
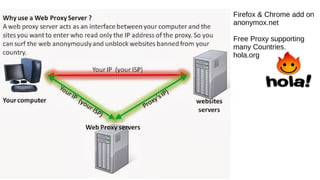
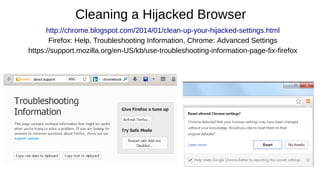
![Cookie Concerns
Snowden says the NSA uses QuantumCookies to ID Tor users.
A corrupt or invalid cookie can prevent access to a web site.
This slideshow is a nice introduction to Cookie issues:
http://www.slideshare.net/iamit/cookies-and-browser-exploits
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a type of computer security vulnerability
typically found in Web applications. XSS enables attackers to inject
client-side script into Web pages viewed by other users. [to steal
session cookies, and then private information like credit card numbers!]
“BEAST” (“Browser Exploit Against SSL/TLS”), CRIME, BREACH, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/browserbasicsd20-170518210718/85/Web-Browser-Basics-Tips-Tricks-Draft-20-Revised-5-18-17-23-320.jpg)