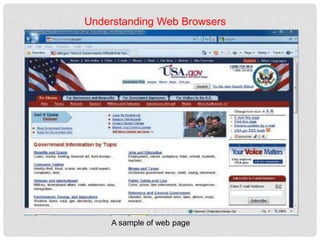
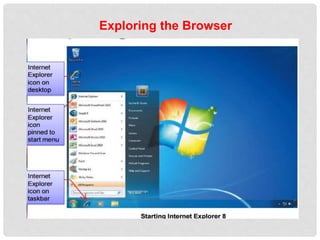
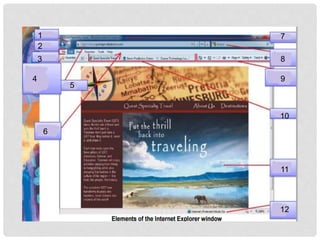
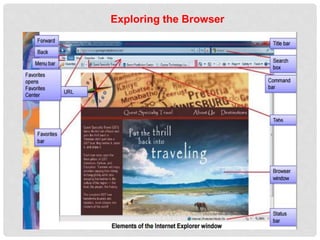
The document provides an overview of how to use the Internet Explorer web browser. It defines key browser terminology like websites, web pages, hyperlinks and URLs. It explains how to access and navigate websites using Internet Explorer. Features of Internet Explorer mentioned include displaying web pages, searching the internet, and saving or sharing web content. The document also gives a brief introduction to computer networks and how the internet connects millions of computers worldwide.