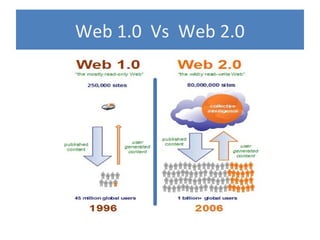
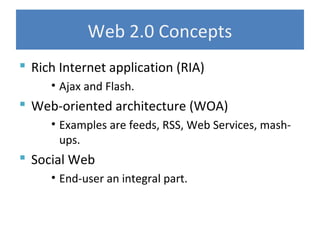
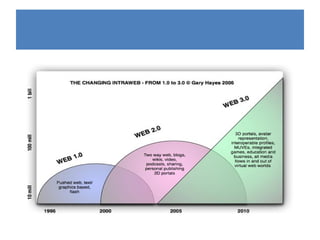
Web 2.0 refers to second-generation internet-based services that allow users to collaborate and share information online, unlike earlier static websites. It enables a read-write web where users can generate content through blogs, photos, videos and other media. Key concepts include rich internet applications using AJAX and Flash, web services, user-generated content, and social networking where users are an integral part of websites.