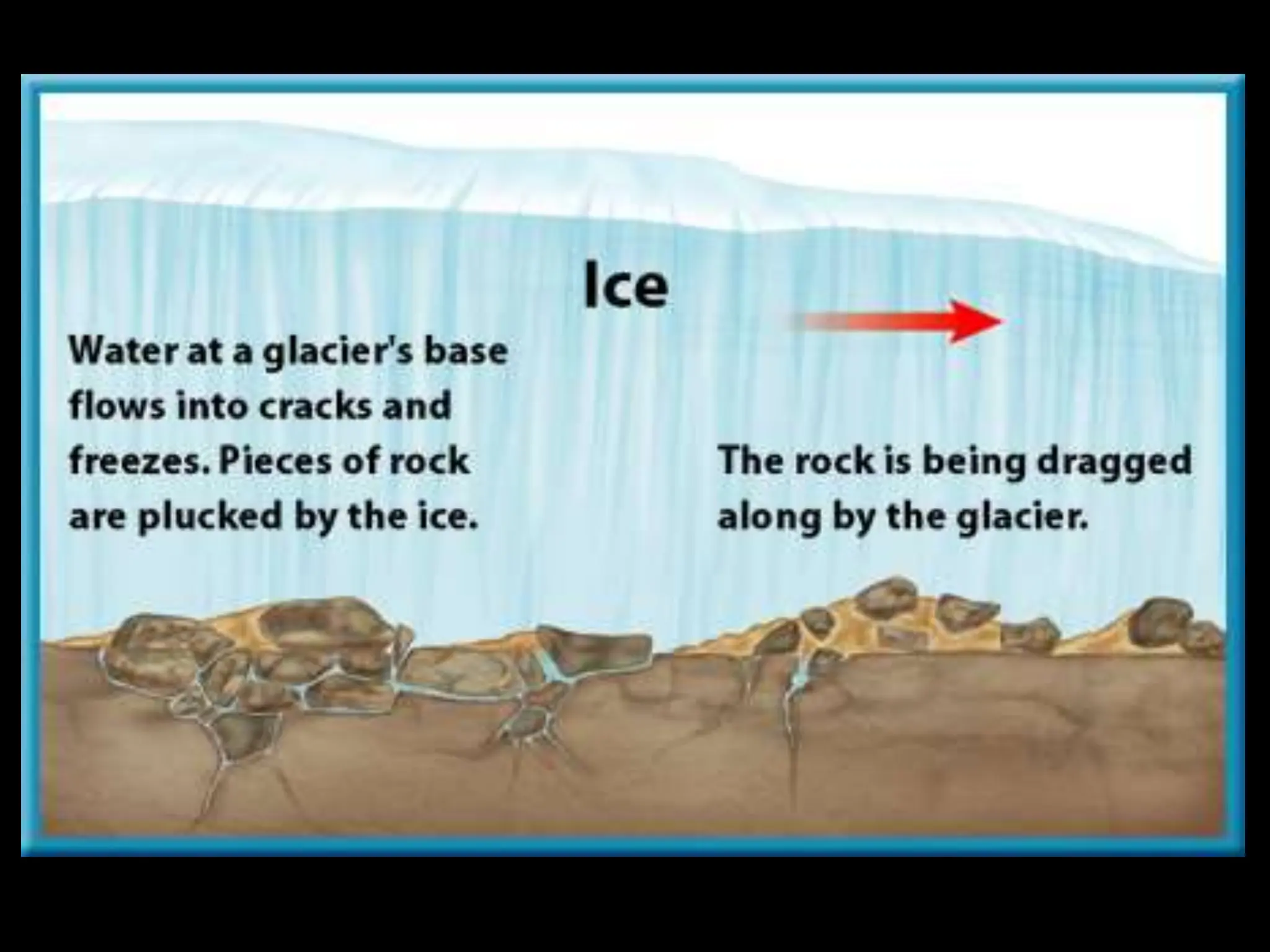
The document explains how weathering and erosion shape the Earth's surface through the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering, as well as the agents of erosion such as gravity, water, wind, and glaciers. It discusses various types of mass movement and the impacts of glaciers and wind on landforms, including mechanisms like plucking and abrasion. It further describes how rivers and waves contribute to erosion and the formation of features such as deltas and beaches.