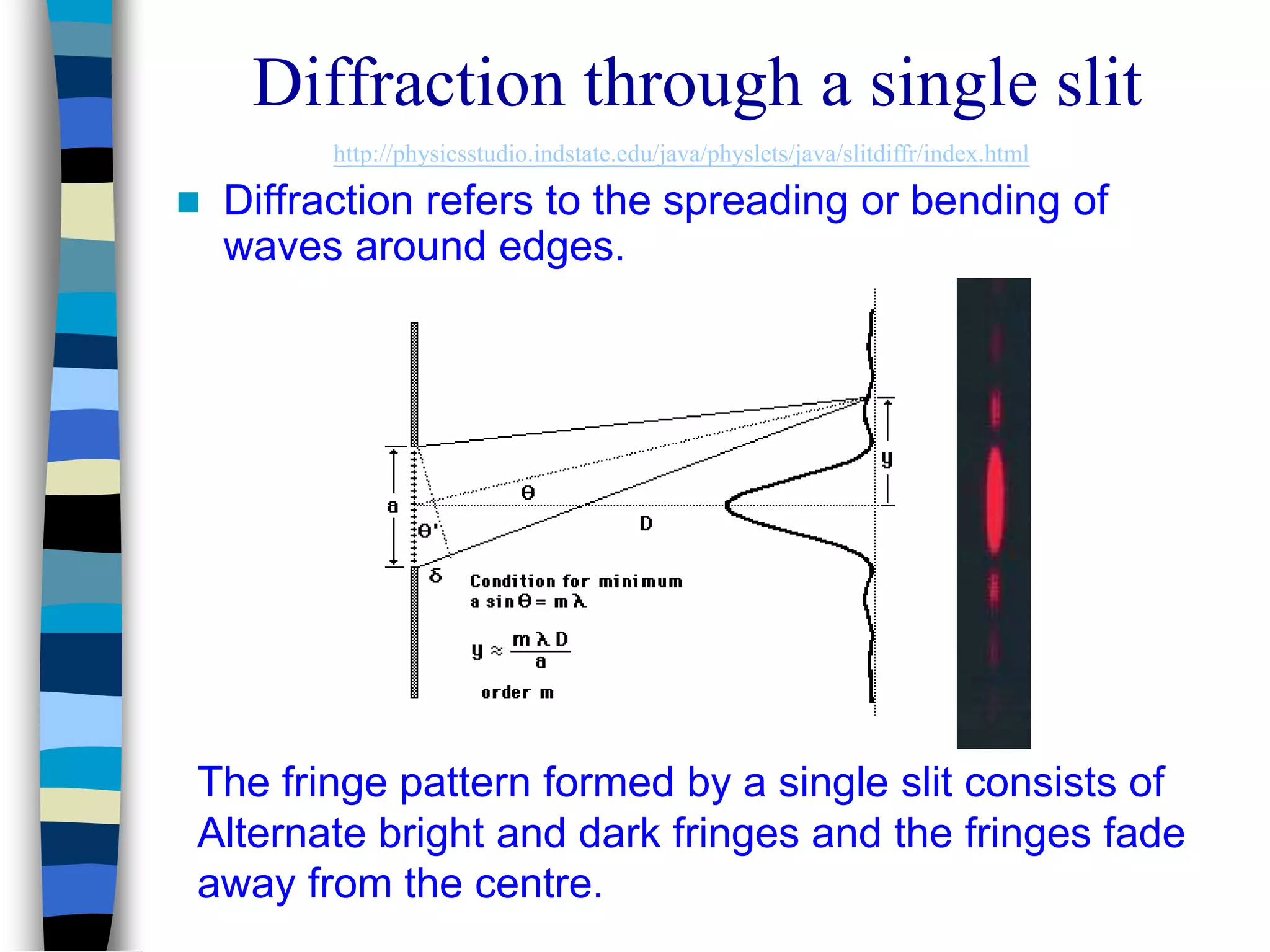
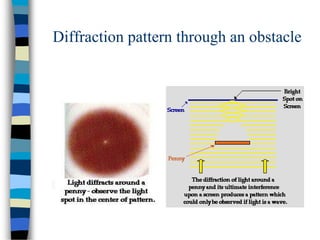
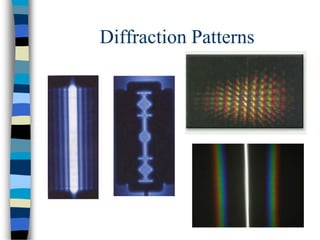
1) Diffraction refers to the spreading or bending of waves around edges, which results in a characteristic fringe pattern from a single slit consisting of alternate bright and dark fringes that fade from the center.
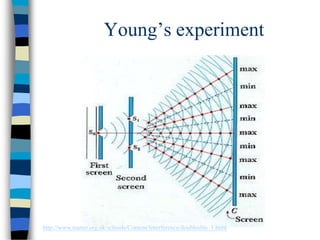
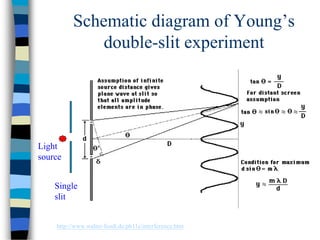
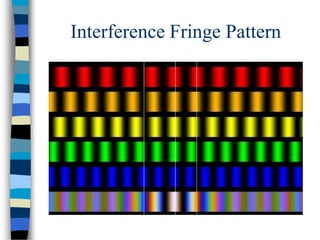
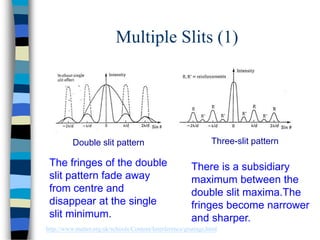
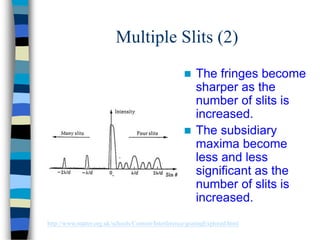
2) Young's double-slit experiment demonstrated the principle of interference, which requires coherent sources, equal amplitudes, and a small path difference between waves. Multiple slits produce sharper, narrower fringes.
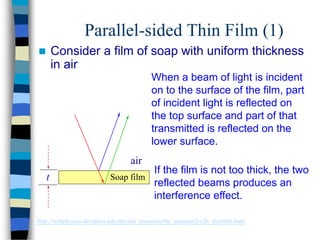
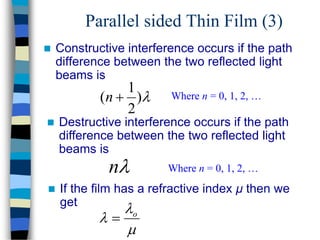
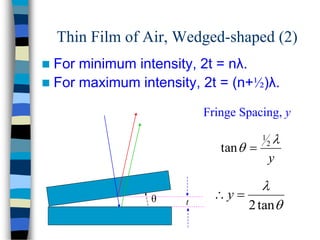
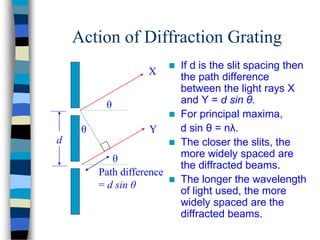
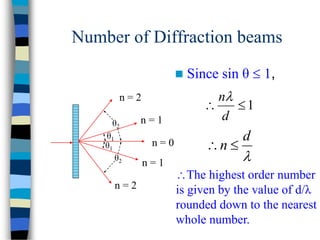
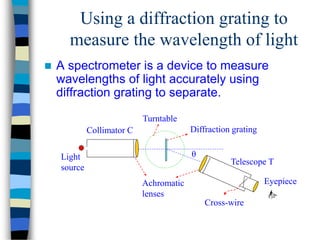
3) Thin films can produce interference patterns through the constructive or destructive interference of light reflecting off the top and bottom surfaces, with the thickness determining the colors observed. Diffraction gratings consist of many parallel slits and split light into multiple beams.