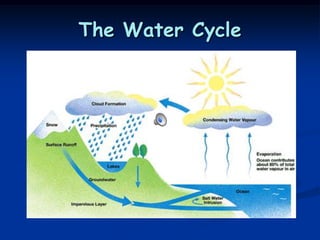
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. The sun heats water which evaporates as vapor into the air. Water vapor condenses into liquid water that falls as precipitation. Precipitation that does not soak into the ground becomes runoff that flows into bodies of water, completing the cycle as that water evaporates again.