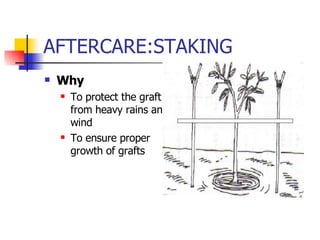
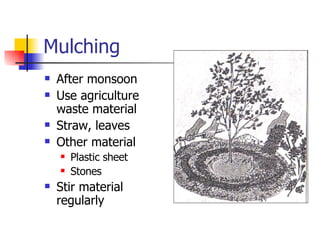
The document provides best practices for establishing and maintaining a Wadi programme, which involves planting fruit trees. It outlines recommendations for plot selection and marking, pit digging and filling, graft selection and planting, aftercare including staking, basin preparation, mulching, shade provision, and intercropping. Proper spacing, soil management, irrigation, and integrated pest management are emphasized.