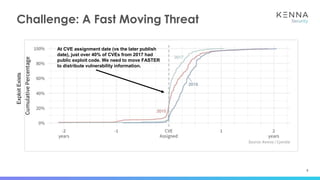
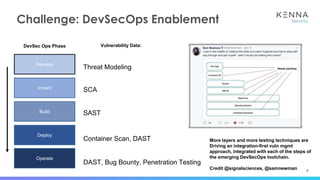
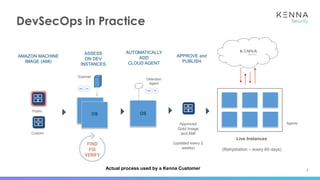
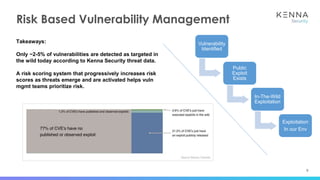
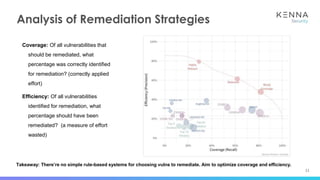
The document discusses vulnerability prioritization and prediction challenges in cybersecurity, highlighting increasing volumes of vulnerabilities and the need for a data-backed prioritization process. It emphasizes the importance of integrating multiple data sources for risk-based vulnerability management and the emerging need for effective remediation strategies. The document also advocates for using predictive models to enhance efficiency and coverage in vulnerability management efforts.