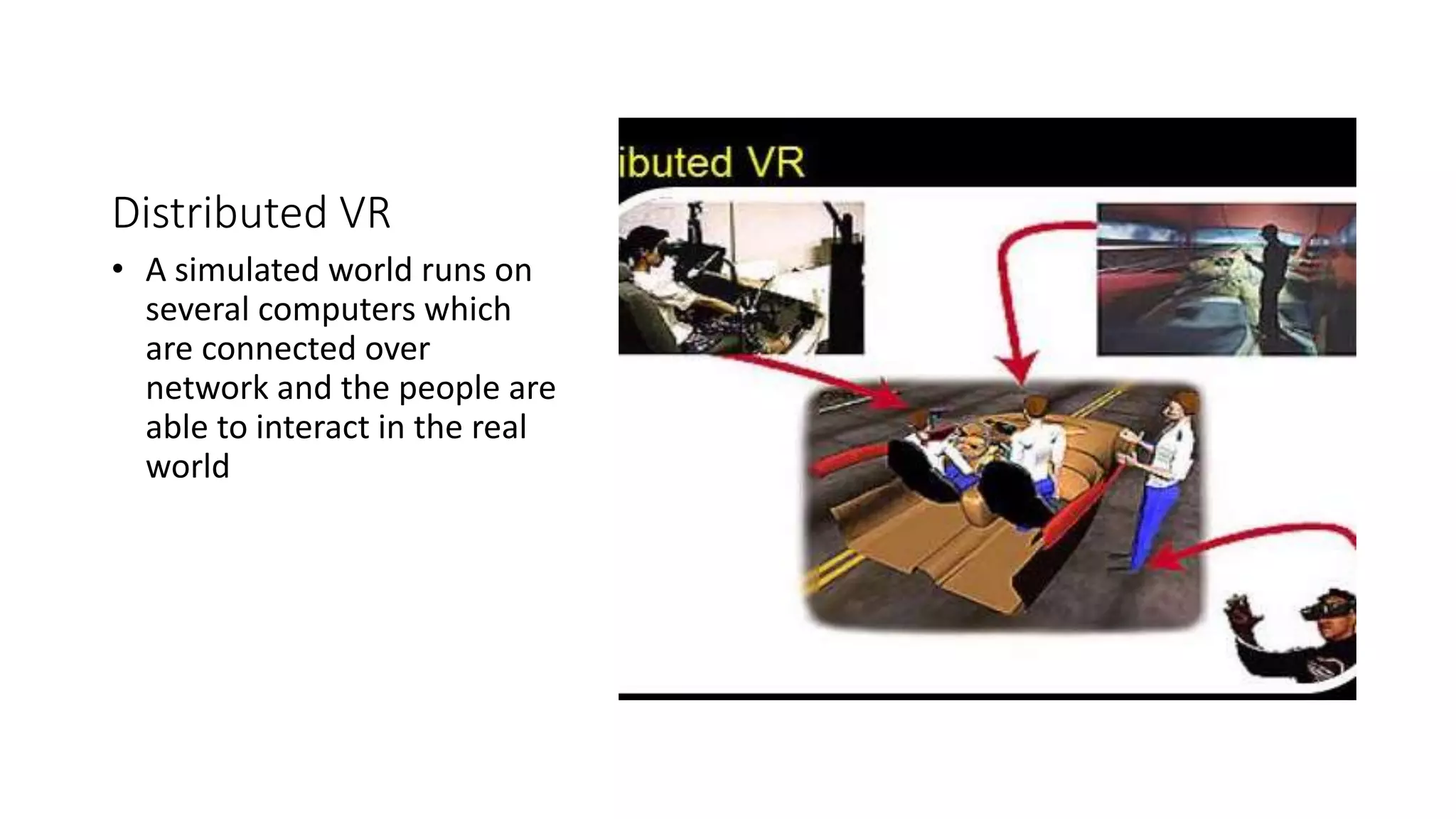
VRML is a modeling language used to create interactive 3D virtual worlds that can be experienced online through the World Wide Web. It allows users to define 3D objects and environments using nodes that represent 3D geometric shapes, cameras, lights, textures, and controls. Scenes are constructed by connecting these nodes together in a hierarchical graph structure. VRML files can be viewed using plugins for web browsers that render the 3D world and allow navigation and interaction with objects. Example applications include entertainment, education, product visualization, and virtual reality simulations.





















![Texture with
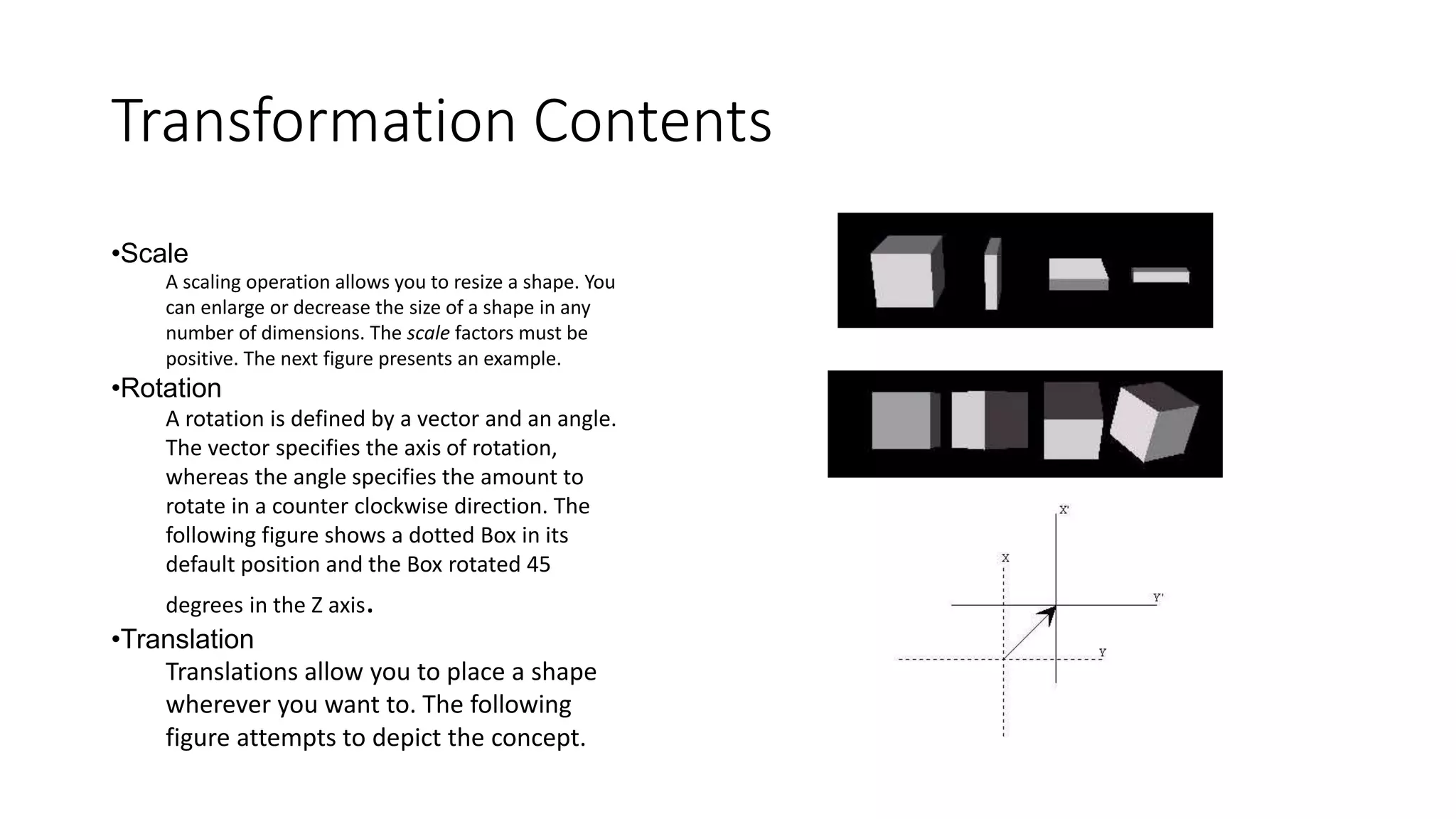
Transformation
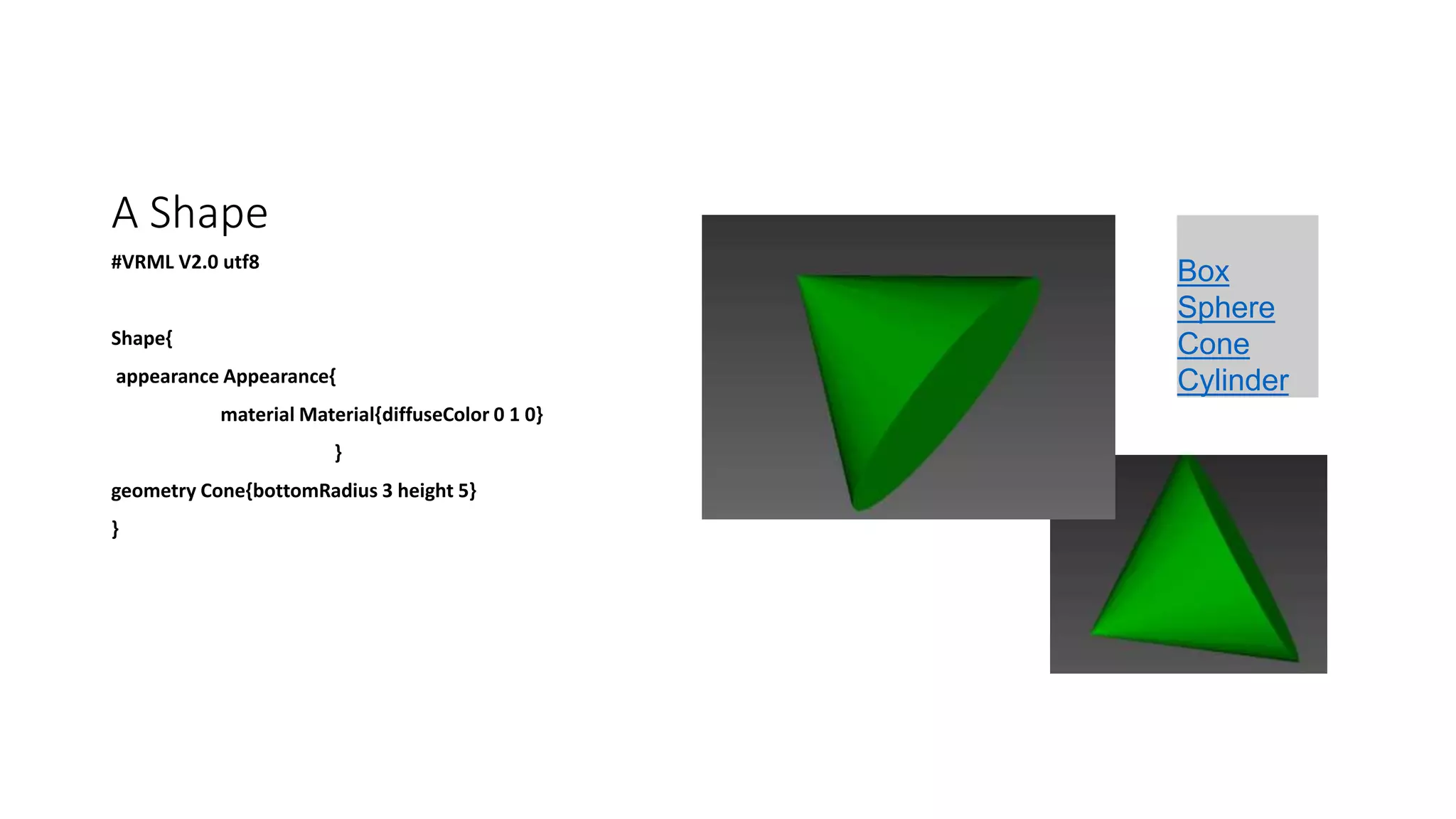
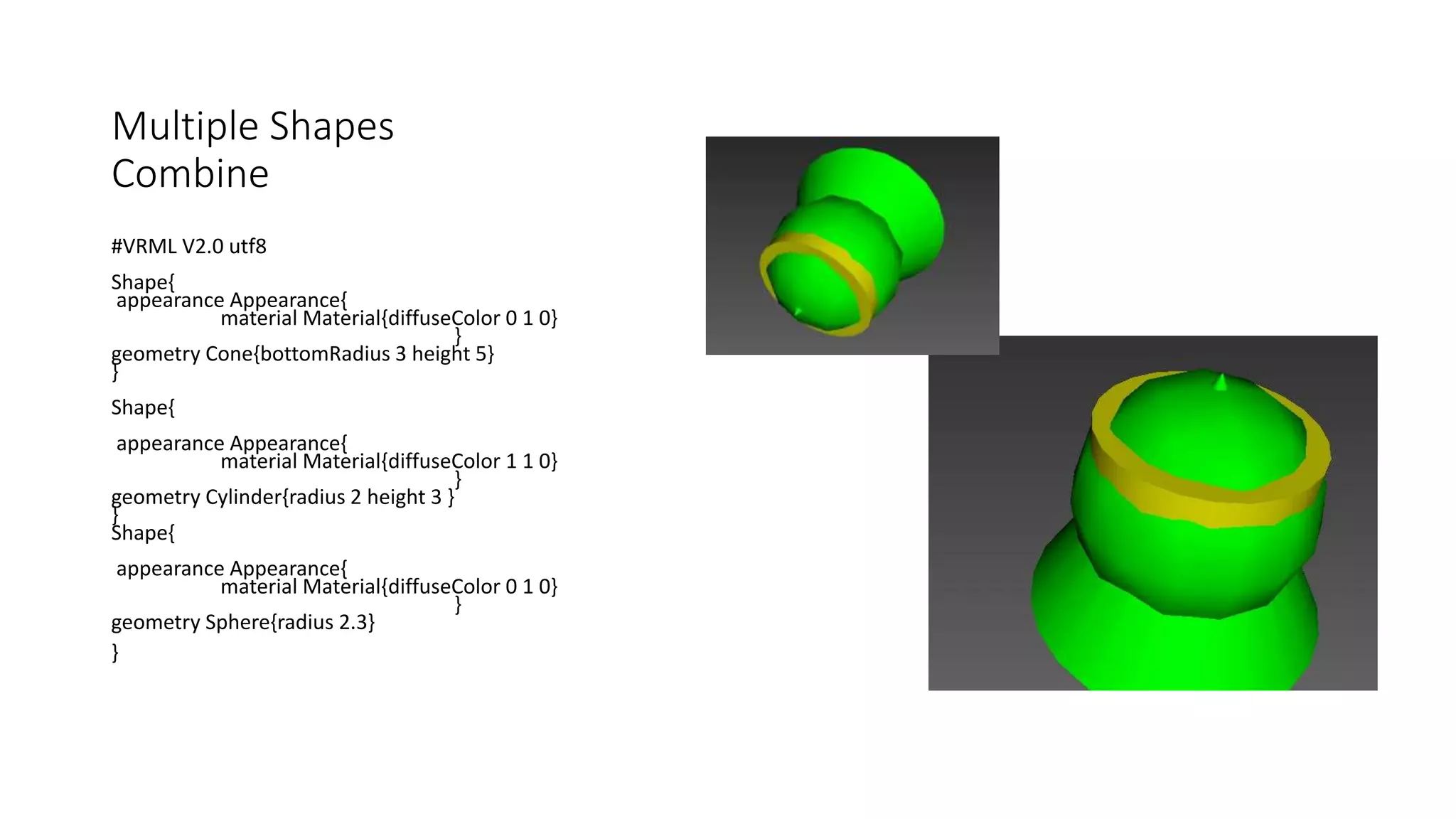
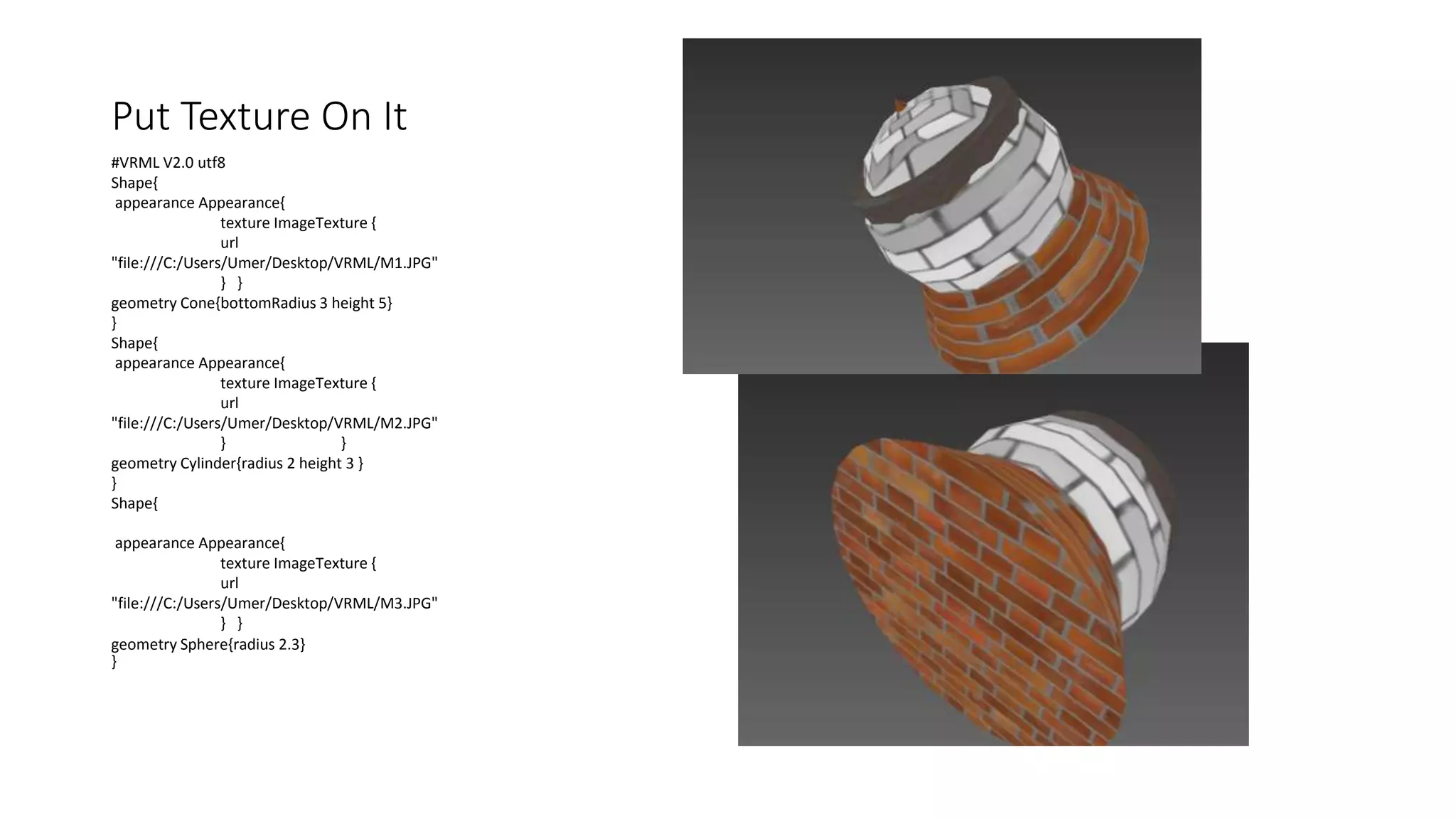
#VRML V2.0 utf8
Transform{
translation 0 0 0
rotation 0 0 0 0
children[
Shape{
appearance Appearance{
texture ImageTexture {
url
"file:///C:/Users/Umer/Desktop/VRML/M1.JPG"
} }
geometry Box {size 10 10 1}
}]}
Transform{
translation 0 0 3
rotation 1 1 1 90
children[
Shape{
appearance Appearance{
texture ImageTexture {
url
"file:///C:/Users/Umer/Desktop/VRML/M2.JPG"
} }
geometry Cone { height 5 bottomRadius 1}}]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vrml-copy-170521055553/75/Vrml-Language-Virtual-Reality-31-2048.jpg)
