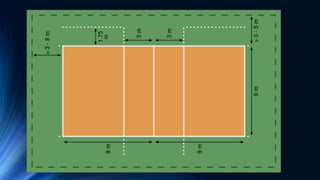
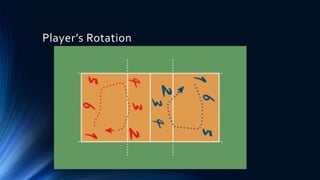
Volleyball is a team sport played by two teams of six players divided by a net. The objective is to ground the ball on the opponent's court after passing it over the net. Common faults include hitting the ball twice before passing over the net, catching/throwing the ball, and touching the net during play. Volleyball was invented in 1895 by William Morgan and has standardized rules for equipment like the ball and court dimensions. Players have designated positions and rotations, with specialized defensive libero positions introduced in 1998. Basic skills include serving to start a rally, passing the opponent's serve, setting up spikers, attacking over the net, blocking attacks, and digging hard-driven balls.