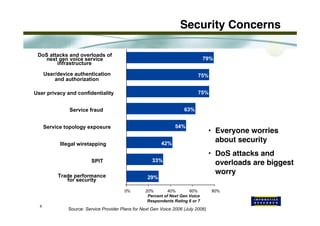
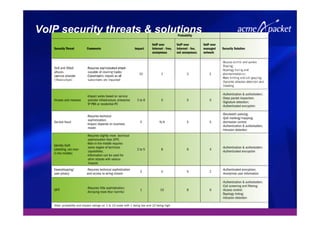
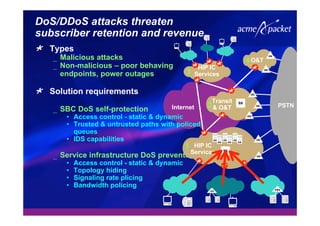
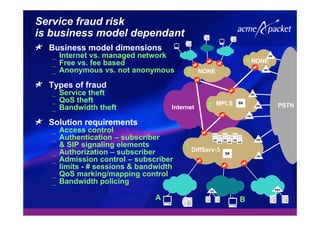
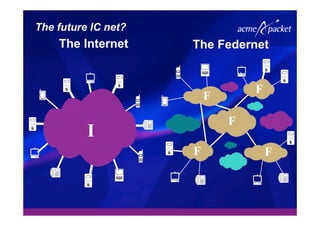
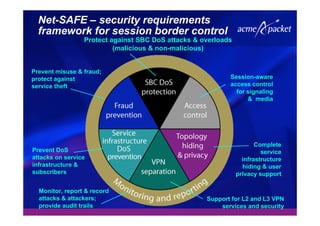
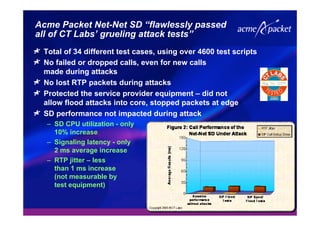
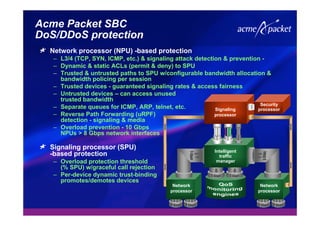
This document discusses security issues related to Voice over IP (VoIP) networks. It begins by noting some common security threats to VoIP like denial of service attacks, viruses, fraud, and eavesdropping. It then discusses how these threats can be addressed through techniques like access control, authentication, encryption, and admission control. The document argues that security is a complex issue and that investments should be made based on business needs and risk levels for different service providers and network types. It promotes session border controllers as a way for service providers to help ensure security.