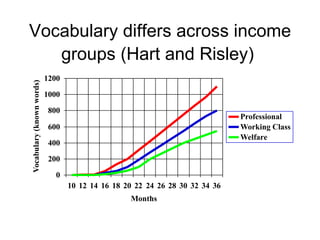
1. Teaching vocabulary is important for supporting content area learning and literacy. Explicit vocabulary instruction is needed as vocabulary differs across income groups.
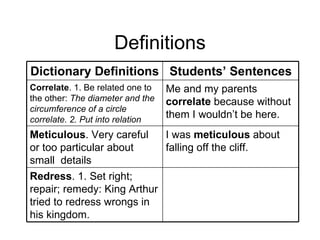
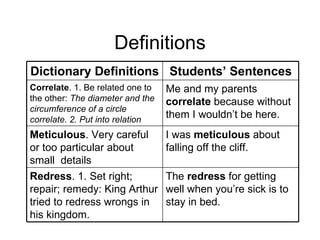
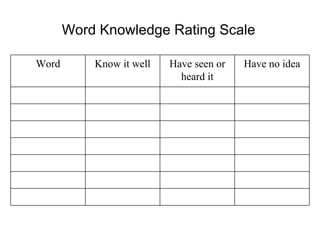
2. Less effective vocabulary instruction includes memorizing definitions without using words in context. More effective strategies include wide reading, using interesting words, playing with words, and returning student language with richer vocabulary.
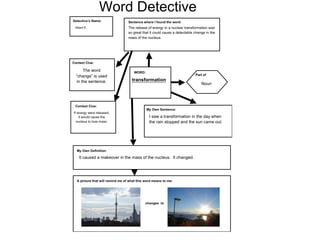
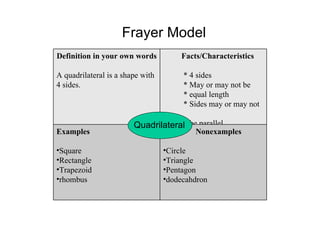
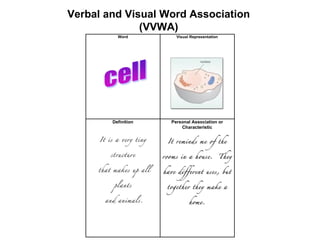
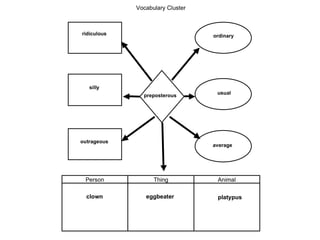
3. Explicit instruction in morphology helps students analyze word structure and meanings. Techniques include word sorts, word chains, and root word trees. Context clues and reference tools also aid word understanding.