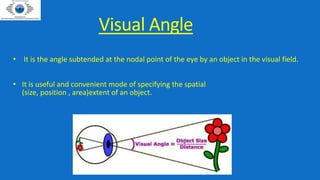
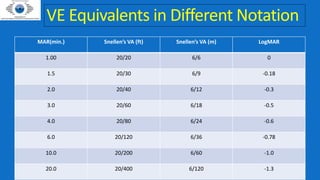
This document provides information about visual acuity and how it is assessed. It defines visual acuity as the ability to see fine detail and distinguish shapes. Visual acuity is measured using charts with letters, numbers, or symbols of decreasing size. It discusses different charts used to test visual acuity in infants, children, and adults. The document also describes procedures for assessing visual acuity and what is recorded if a patient cannot read the smallest line of a chart.