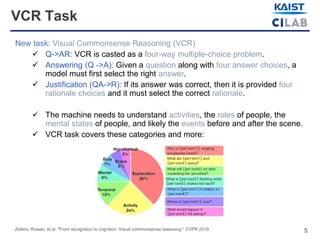
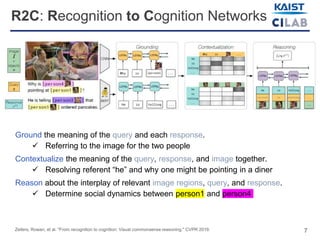
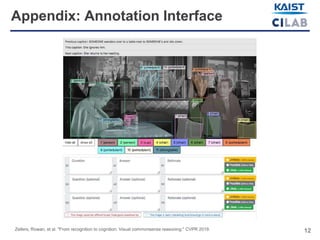
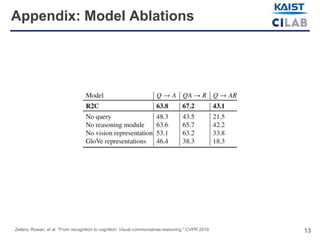
The document discusses visual commonsense reasoning (VCR), a new task combining visual question answering with rationales to improve machine understanding of images. It highlights the introduction of the VCR dataset containing 290k question-answer-rationale pairs, emphasizing the challenges faced by state-of-the-art models compared to human accuracy. A new model called R2C (recognition to cognition networks) aims to improve performance, successfully narrowing the gap between human and machine understanding.