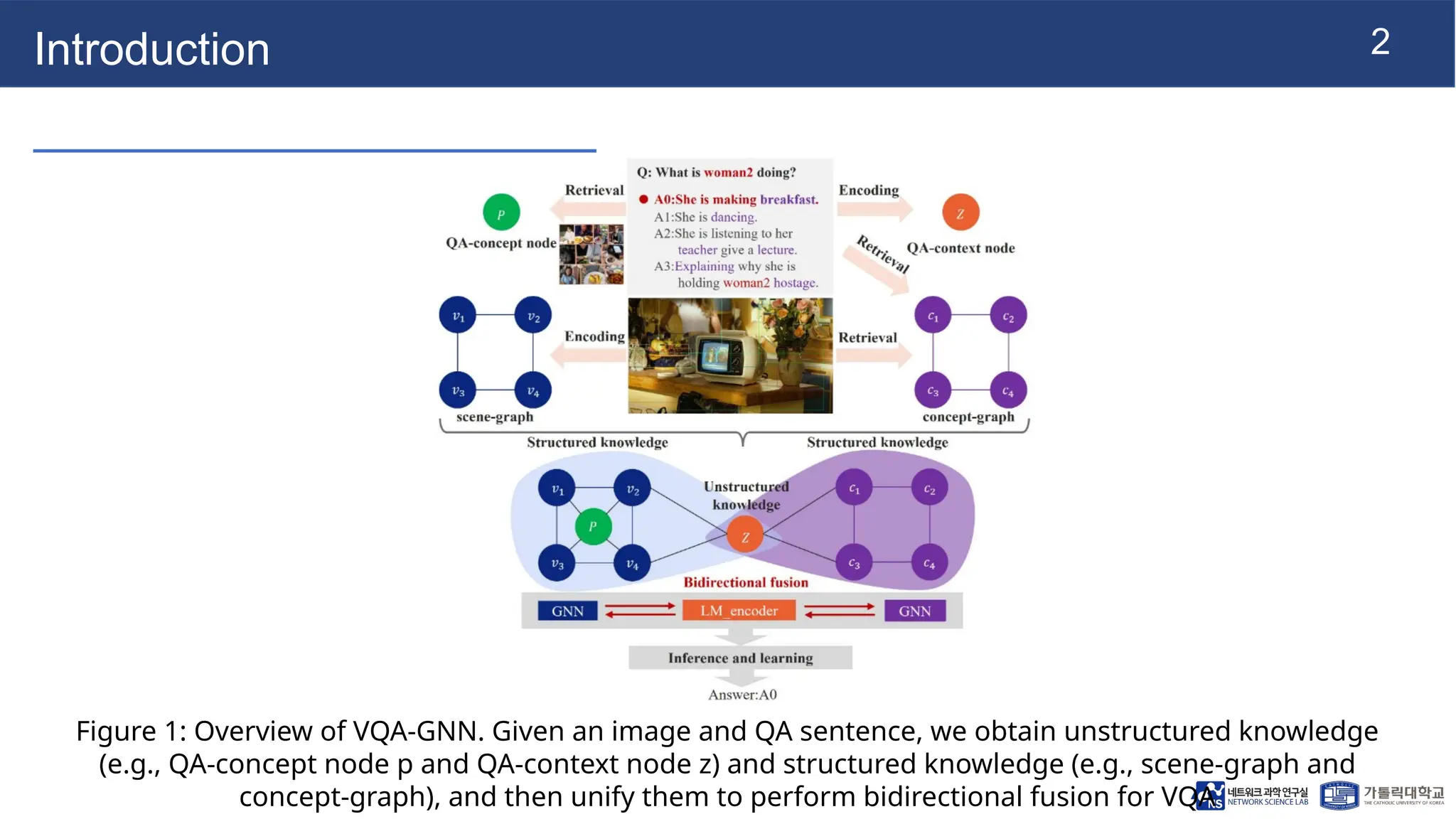
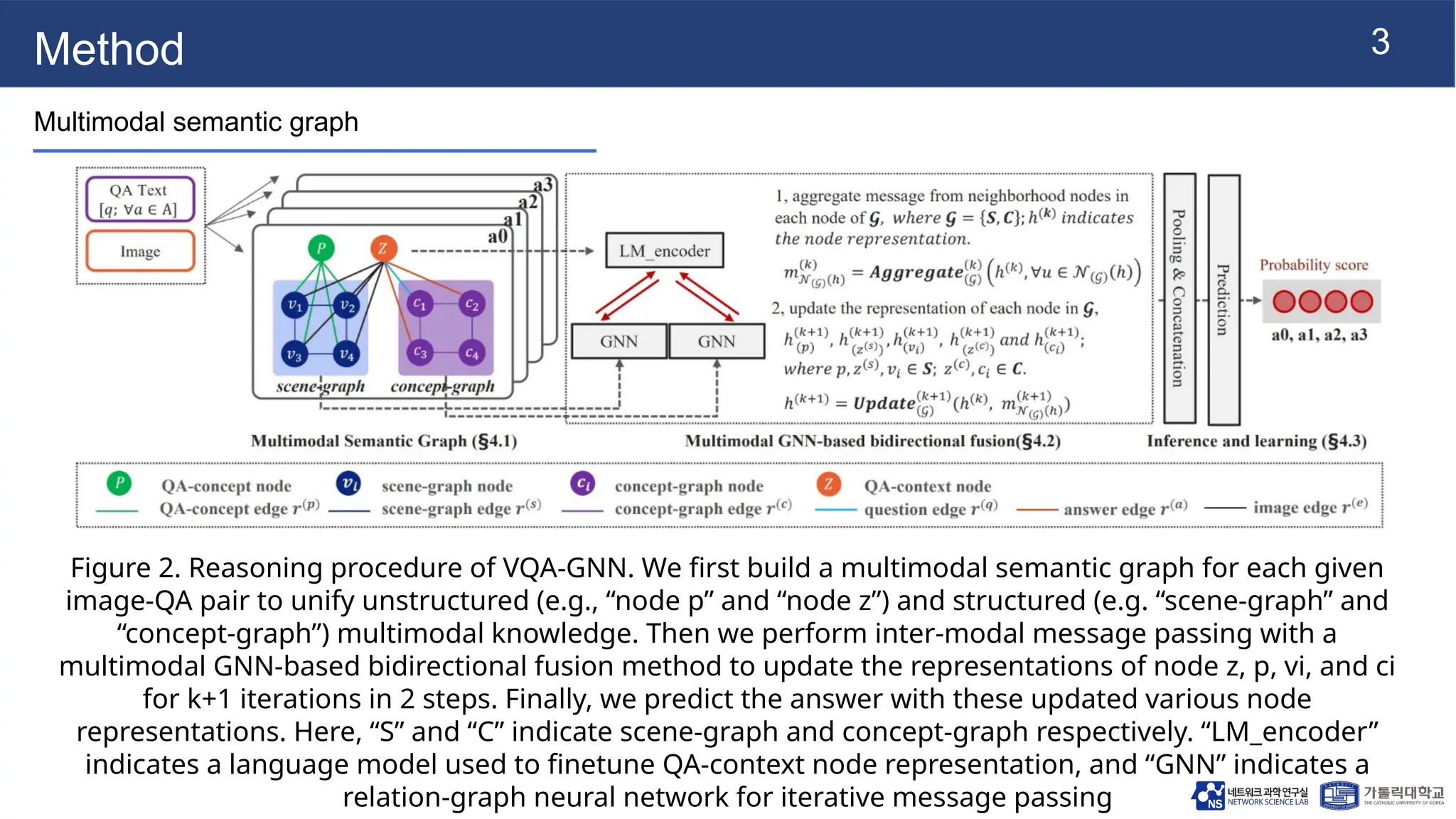
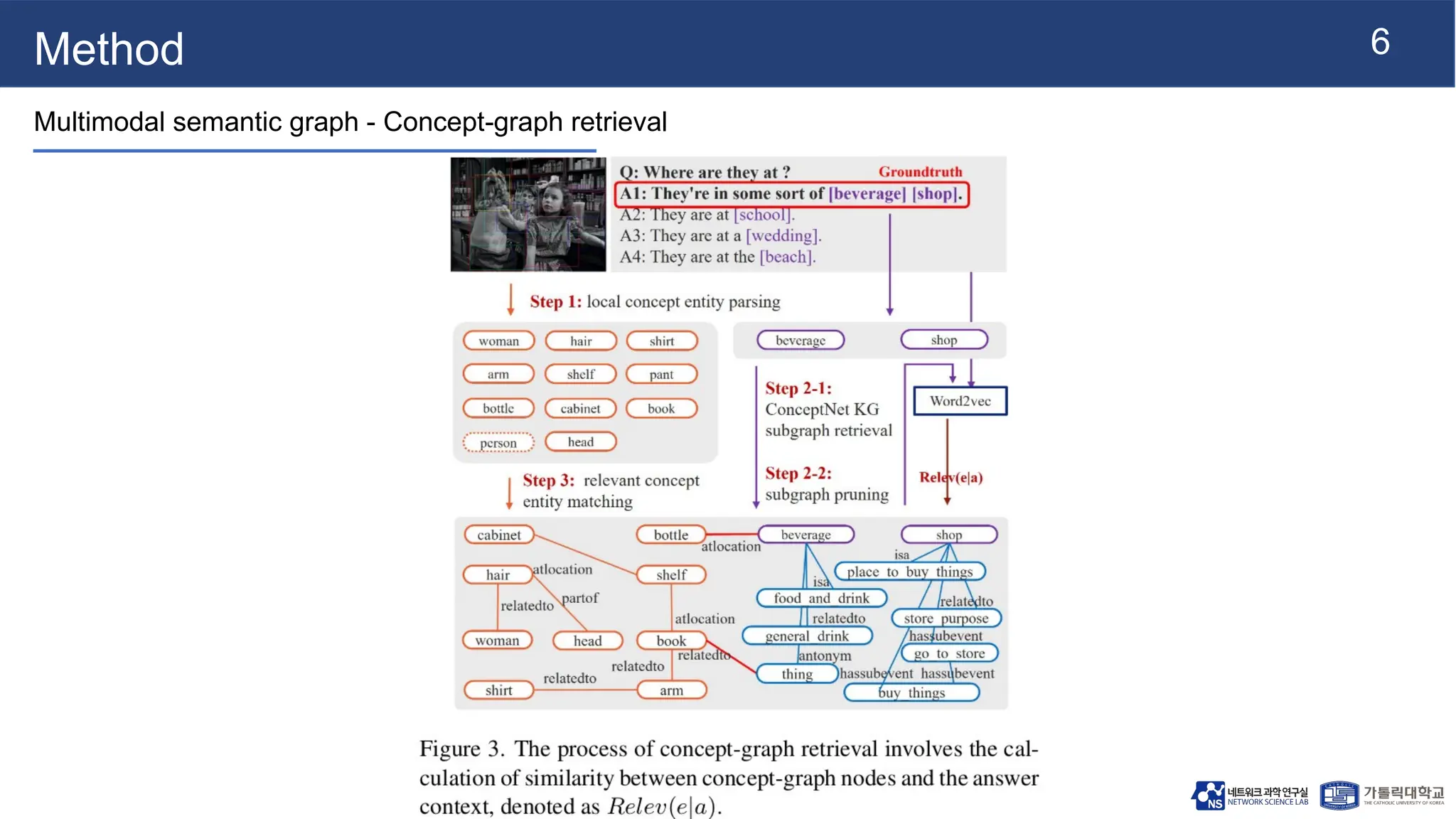
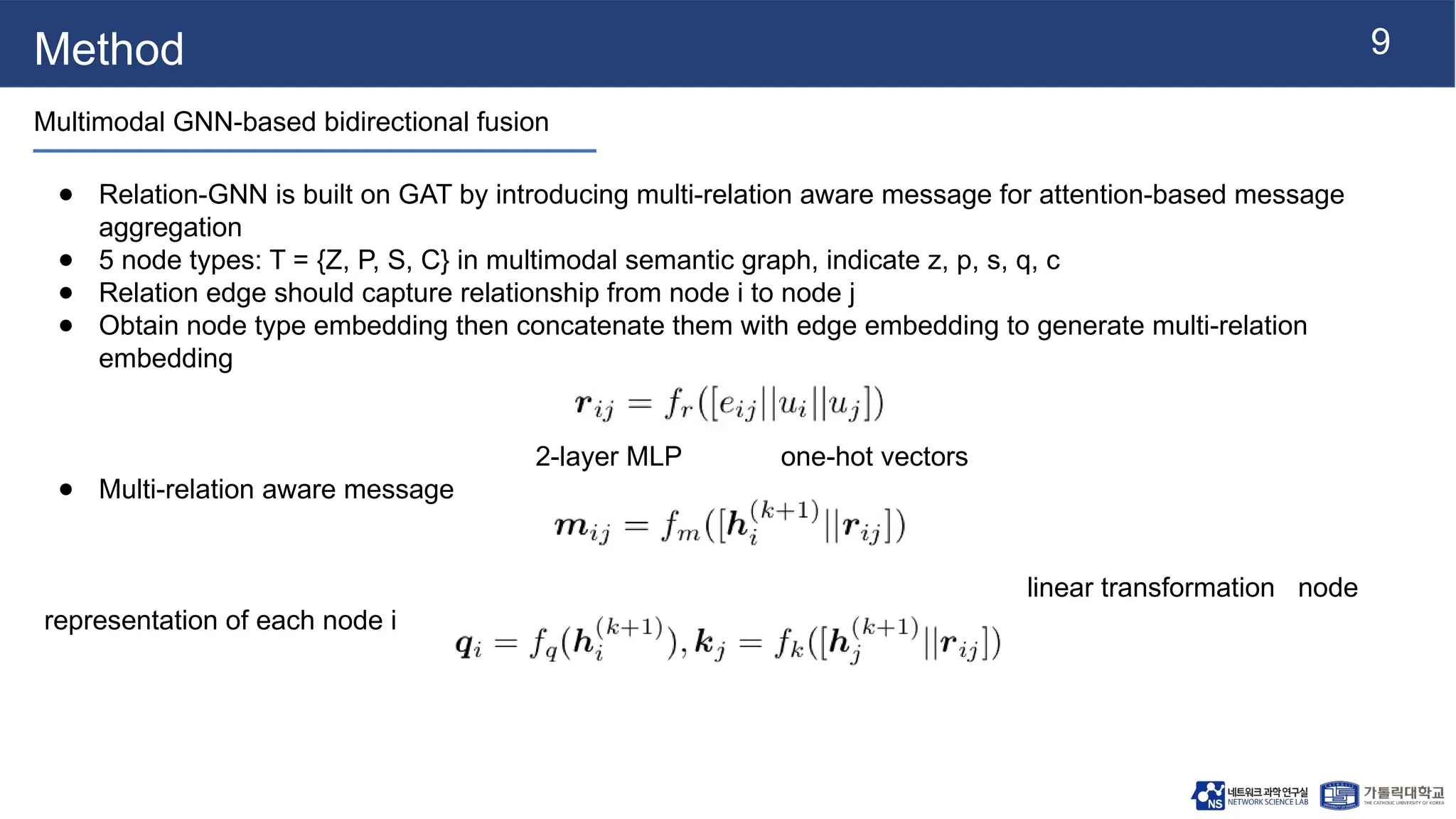
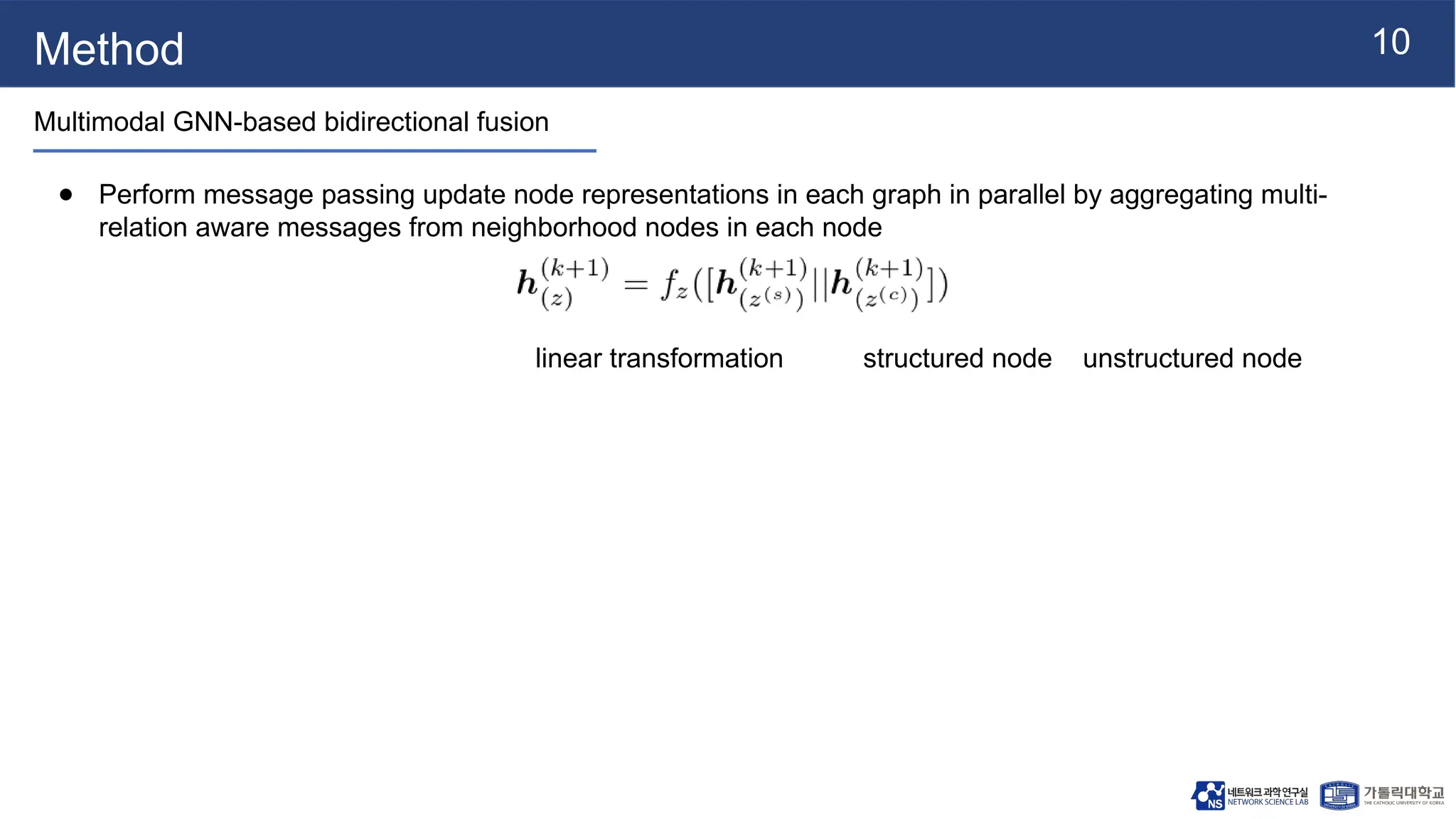
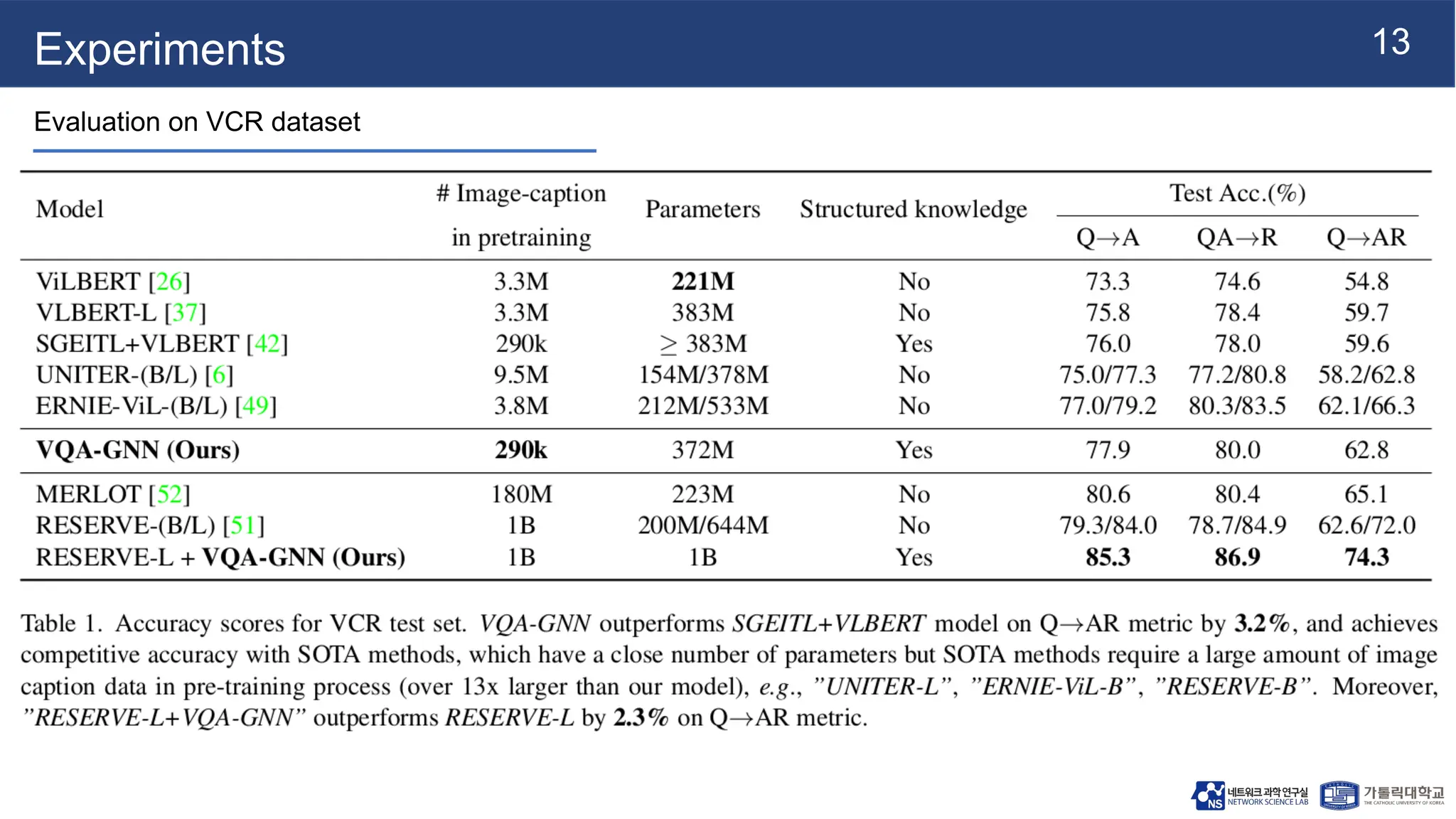
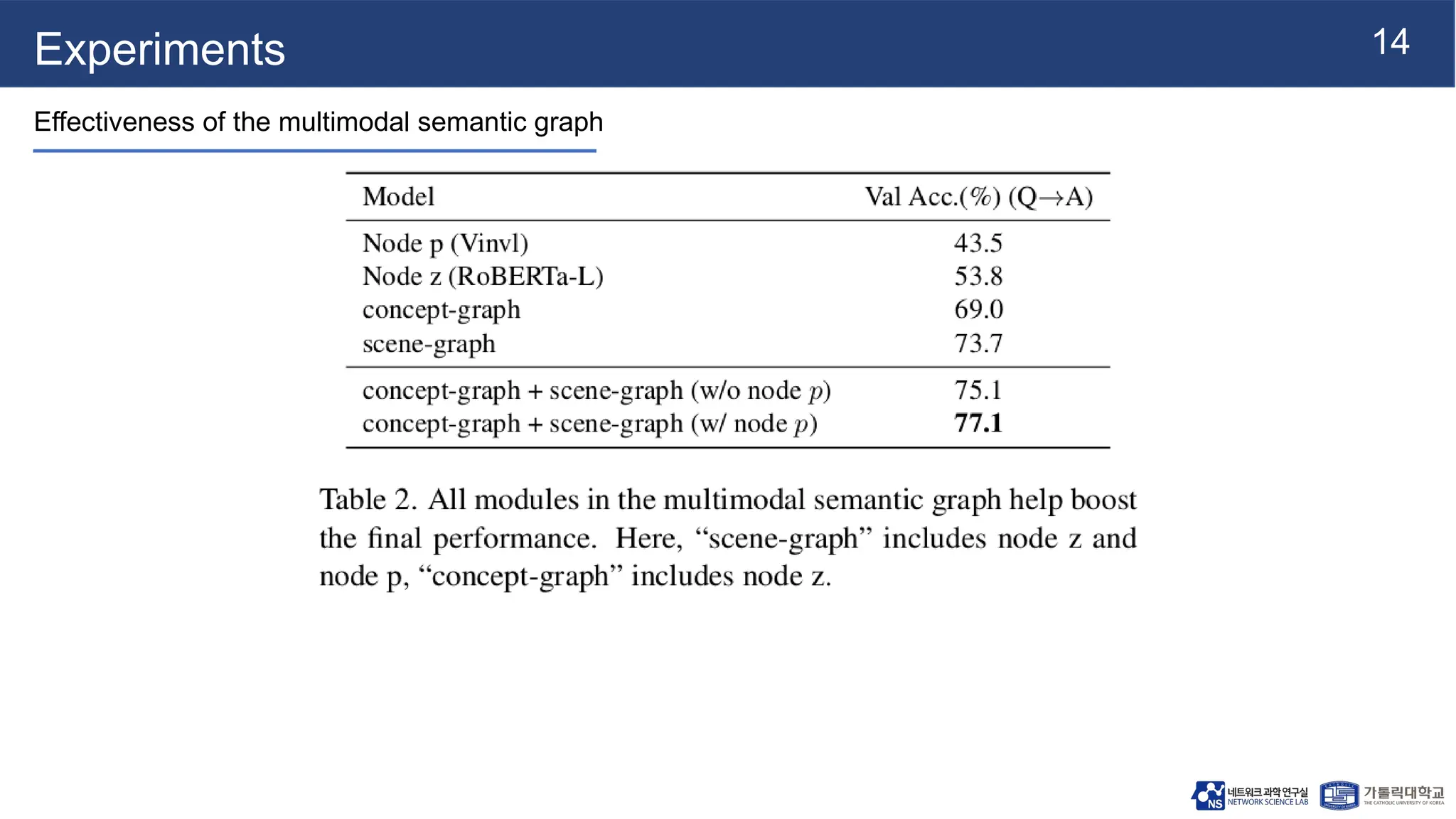
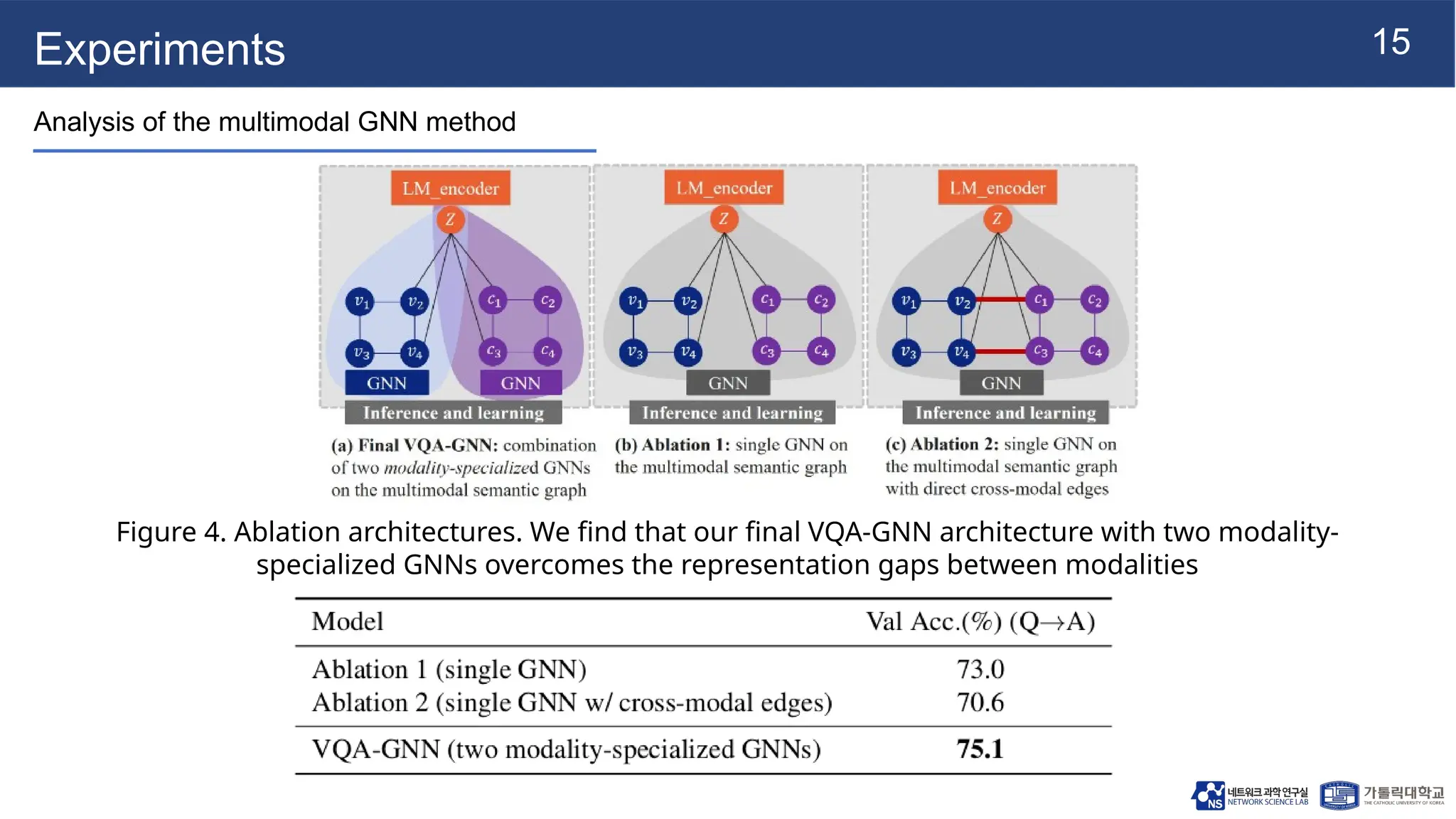
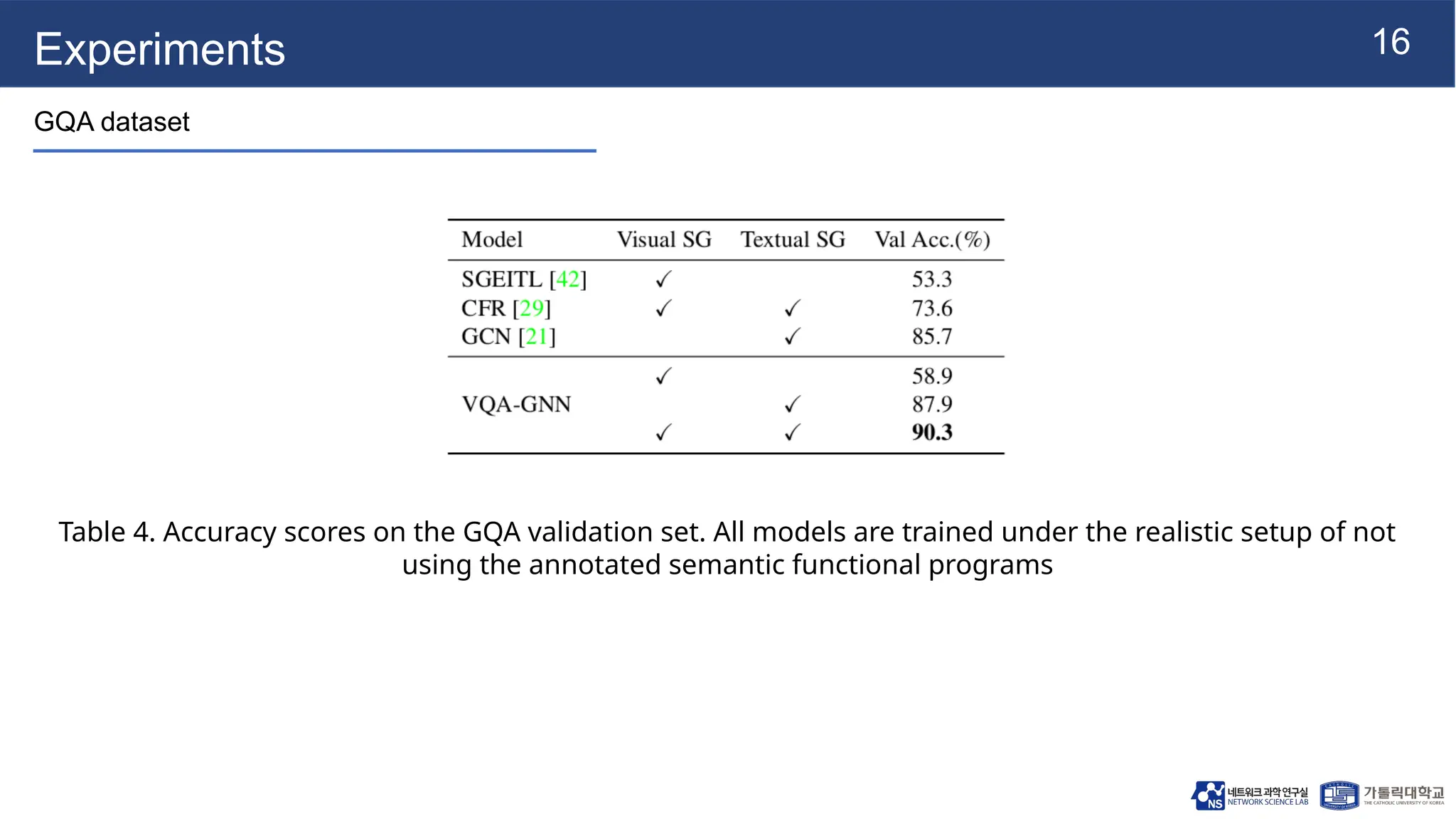
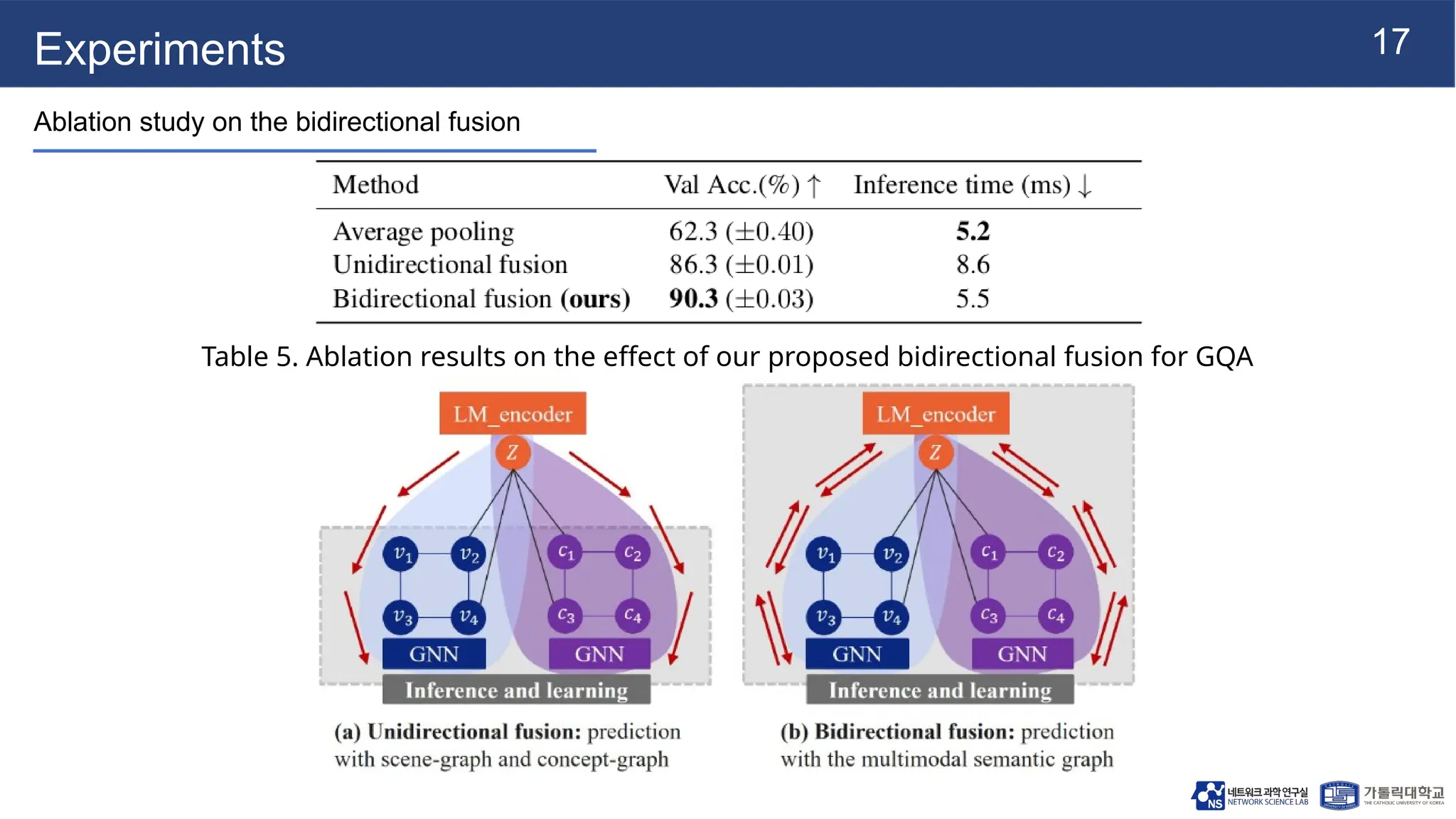
The document presents vqa-gnn, a method that integrates unstructured and structured multimodal knowledge using graph neural networks for visual question answering tasks. It details the construction of multimodal semantic graphs, the application of various graph encodings, and the use of bidirectional fusion to enhance reasoning capabilities. Experimental results indicate that vqa-gnn outperforms traditional VQA methods by significant margins, demonstrating its effectiveness in concept-level reasoning.