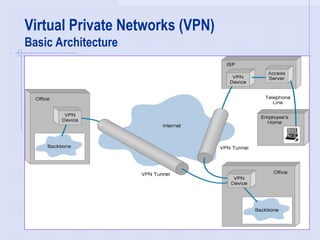
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) utilize public telecommunication systems, like the internet, to securely connect remote employees to private networks, allowing for cost-effective communication and scalability. Key functions of VPNs include authentication, access control, confidentiality, and data integrity, often implemented through various protocols such as PPTP, L2TP, and IPSec. While VPNs offer advantages like cost savings and flexibility, they also present challenges related to security, performance, and the need for comprehensive understanding and management of technology.

![Traditional Connectivity
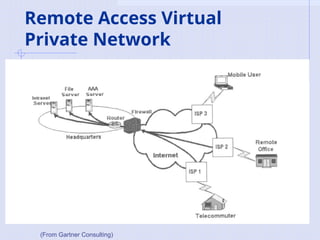
[From Gartner Consulting]
[From Gartner Consulting]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vpnbasics-240930103208-403d701b/85/Virtual-Private-Networks-VPN-basics-ppt-2-320.jpg)





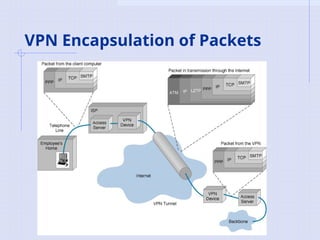
![Tunneling
A virtual point-to-point connection
made through a public network. It
transports
encapsulated datagrams.
Encrypted Inner Datagram
Datagram Header Outer Datagram Data Area
Original Datagram
Data Encapsulation [From Comer]
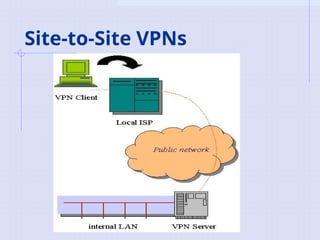
Two types of end points:
Remote Access
Site-to-Site](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vpnbasics-240930103208-403d701b/85/Virtual-Private-Networks-VPN-basics-ppt-9-320.jpg)