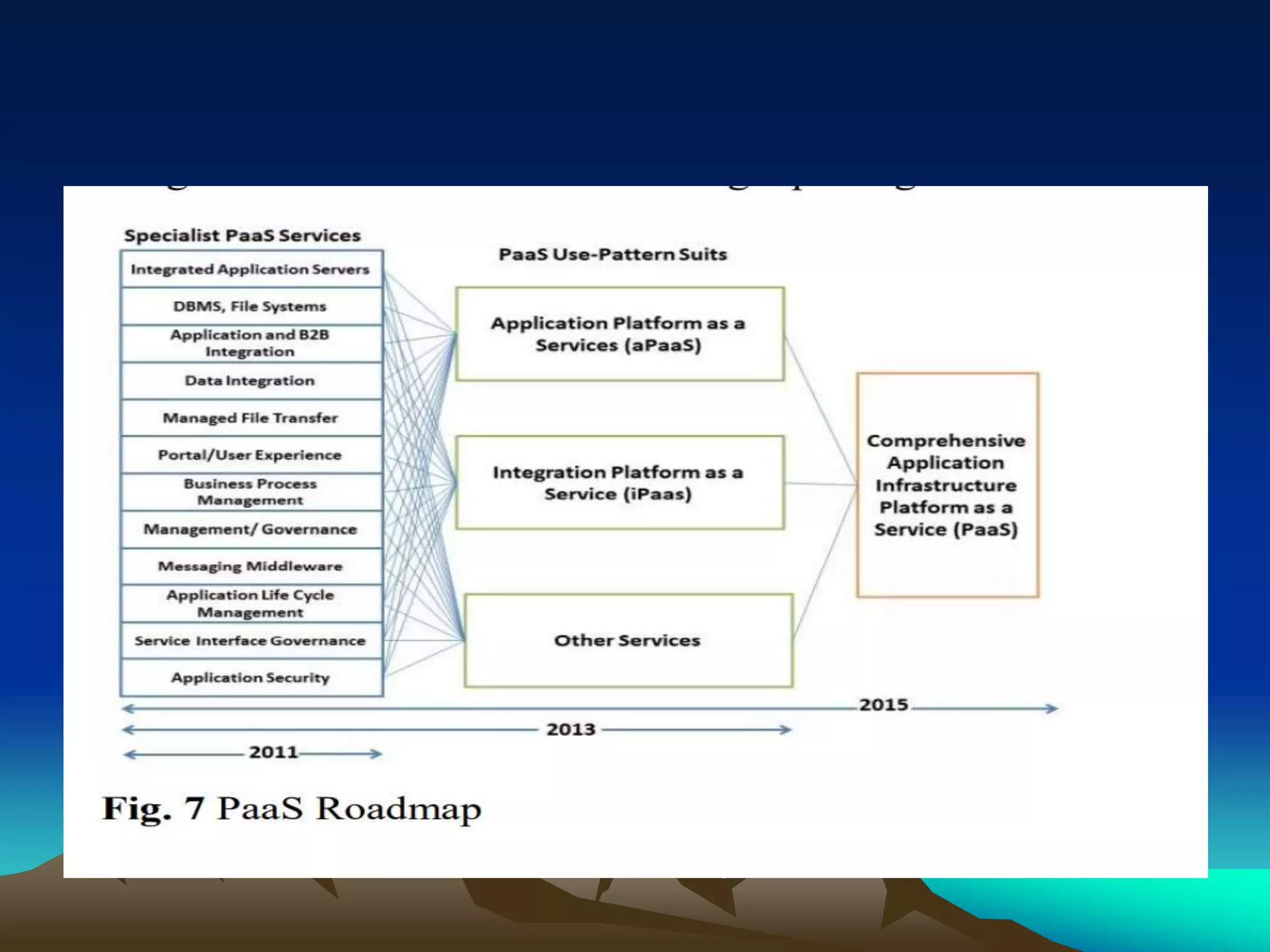
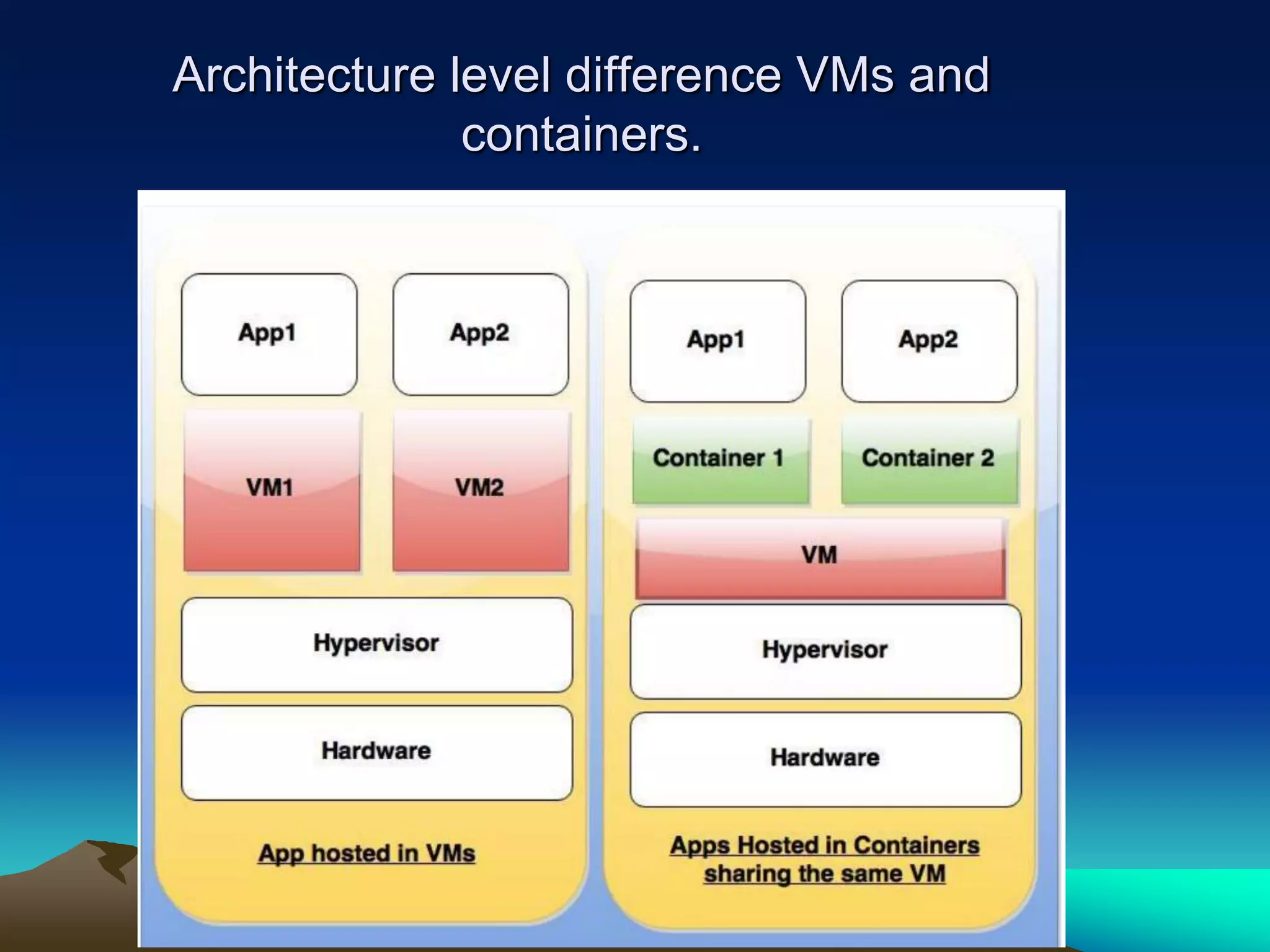
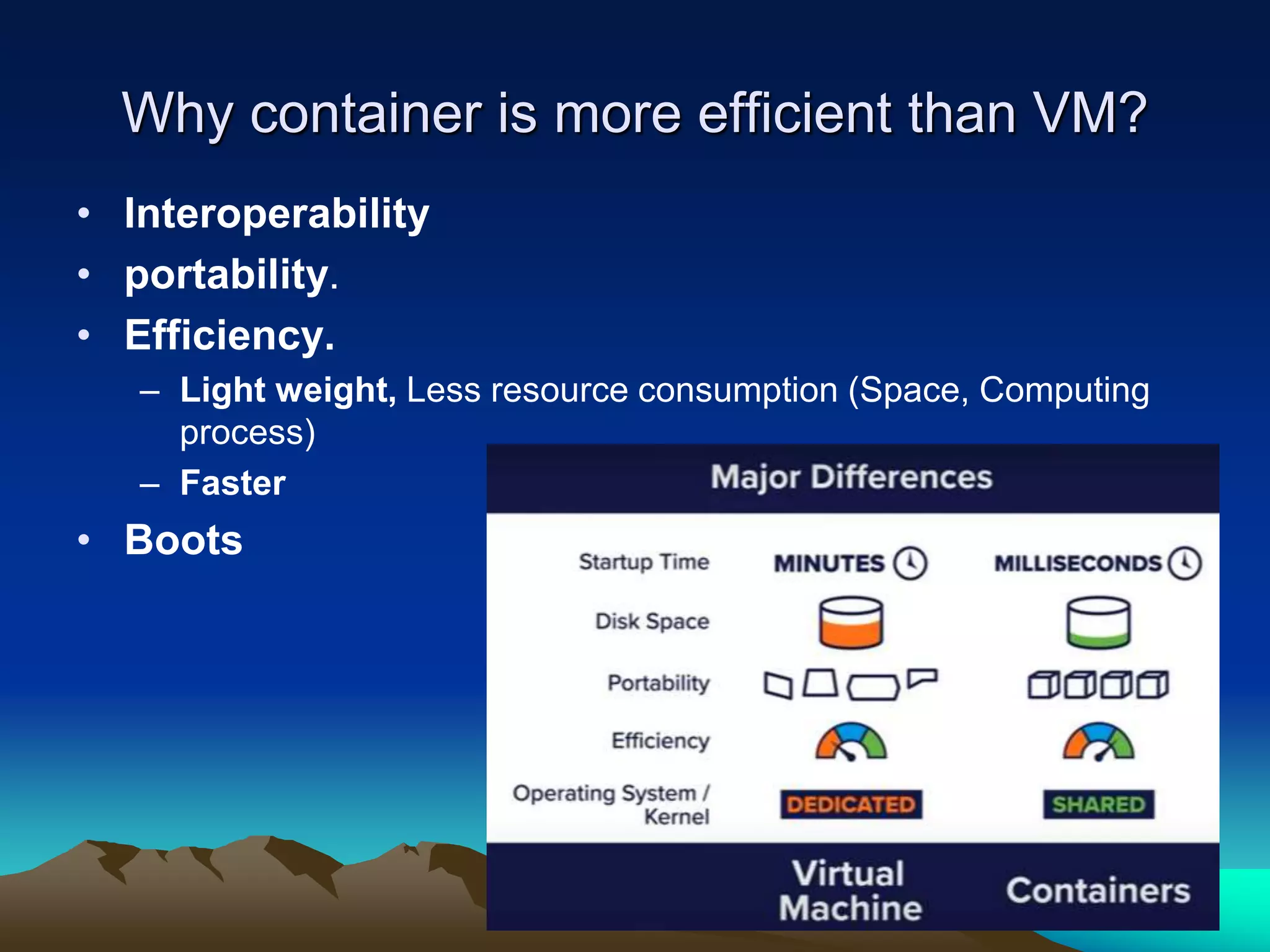
This document discusses the objective and future of Platform as a Service (PaaS) technology. It aims to assess and analyze the future of PaaS, discuss future market trends and competitors, and outline top PaaS service providers. The document covers what PaaS includes, why developers use PaaS, potential drawbacks, use cases, types of PaaS, core architectural transformations including containers replacing virtual machines, comparisons of providers like AWS, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure, and concludes that PaaS will enable faster and cheaper application development in the future.