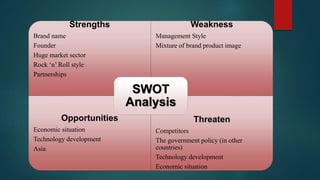
Virgin Group is one of the largest private companies in the UK founded by Richard Branson, operating in various sectors such as travel, financial services, and media. The company aims to deliver superior quality and customer service through an autonomous business model where each business is self-managed but tied together through shared ownership and values. While this decentralized approach provides flexibility, it also poses management challenges. Virgin addresses problems like losses in specific businesses by selling off mature operations and investing in new growth areas, demonstrating the adaptability of its brand-led business model.