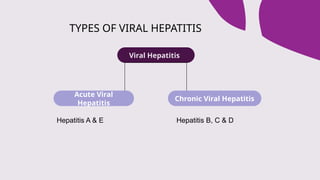
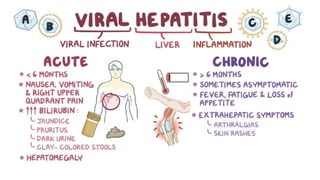
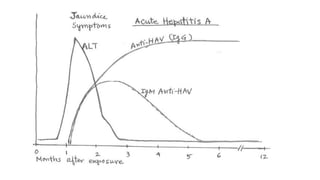
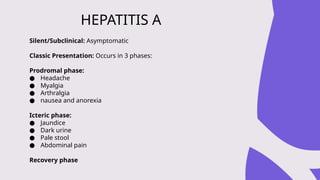
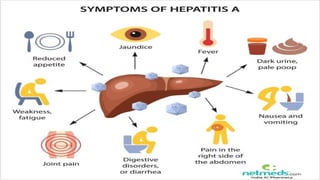
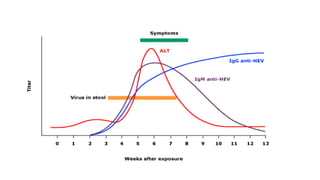
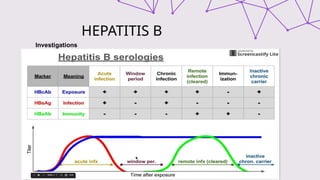
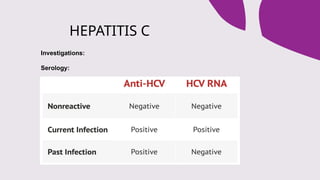
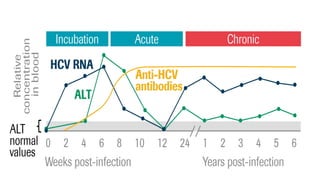
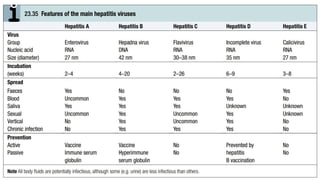
The document outlines the definitions, causes, and classifications of viral hepatitis, including the differences between acute and chronic types. It details specific types of viral hepatitis such as A, E, B, C, and D, along with their transmission, clinical features, investigations, treatments, and preventive measures. The focus is on the management of infections and the importance of supportive treatments and vaccination.