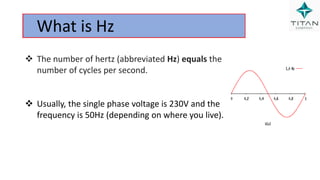
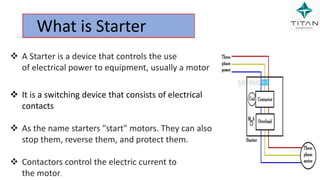
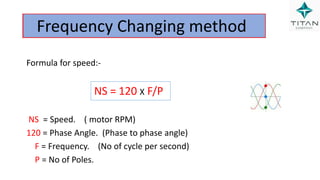
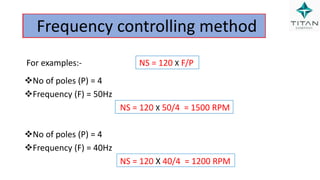
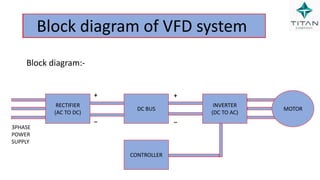
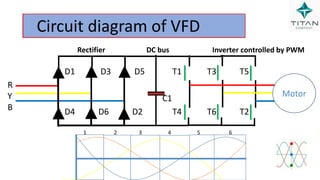
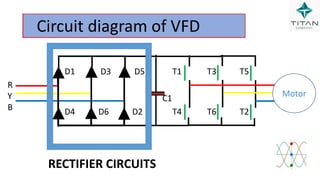
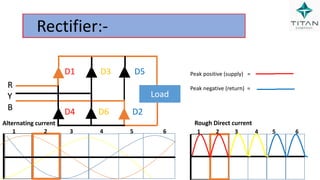
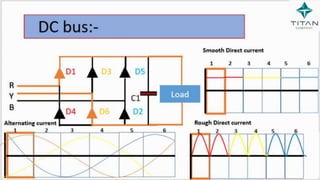
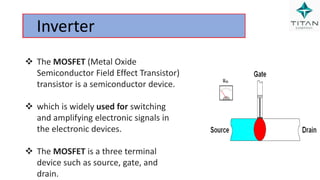
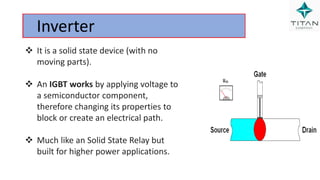
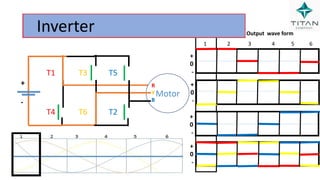
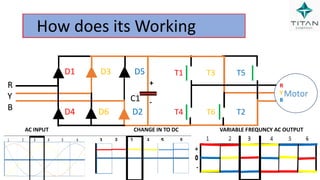
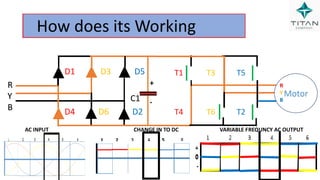
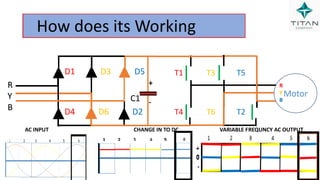
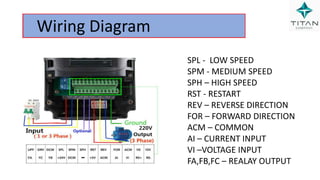
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Variable Frequency Drives (VFD), including definitions of AC and DC, sine wave generation, types of starters, speed control methods, and circuit diagrams. It explains the operation of VFDs in controlling motor functions through varying frequency and voltage, outlining components like rectifiers and inverters. Applications of VFDs in various industries such as cooling towers, compressors, and pumping systems are also discussed.