Embed presentation
Download to read offline


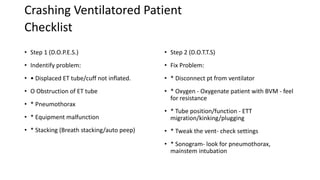
This document provides a checklist for addressing common ventilator alarms and troubleshooting a crashing ventilated patient. It lists potential causes and solutions for decreasing oxygen levels, high or low end-tidal carbon dioxide, and high or low airway pressures. It also outlines a two-step process for responding to a crashing ventilated patient by first identifying the problem using the mnemonic "DOPES" and then fixing the problem using "DOTTS".


