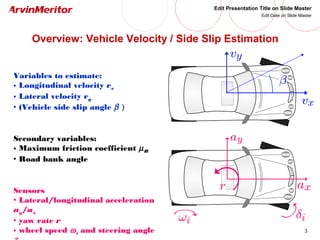
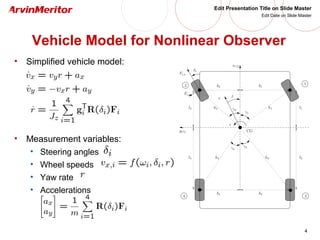
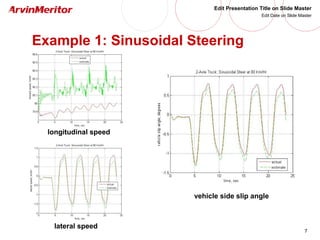
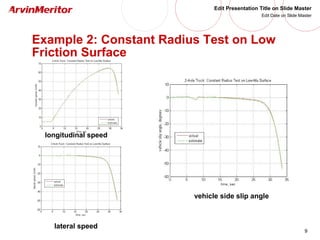
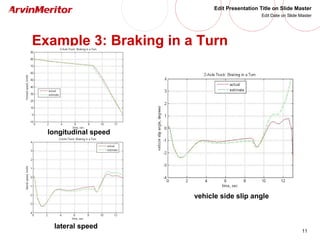
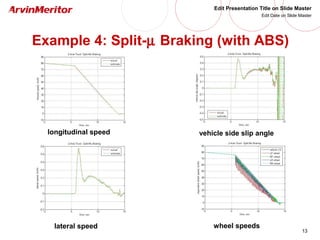
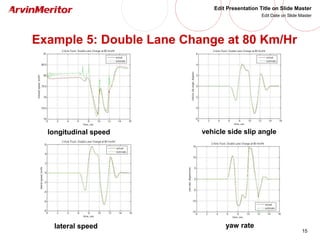
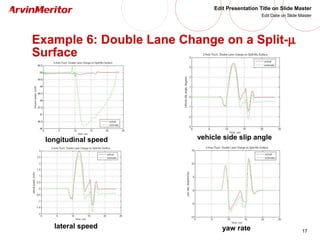
This document presents a nonlinear observer approach for estimating vehicle longitudinal and lateral velocity. It describes sensors used and a simplified vehicle model. A nonlinear observer is proposed using a tire-ground friction model. Examples are shown applying the observer to different vehicle maneuvers, like sinusoidal steering, braking in a turn, and lane changes. The next step is to develop an adaptive nonlinear observer that can estimate the maximum friction coefficient online without prior knowledge of road conditions.