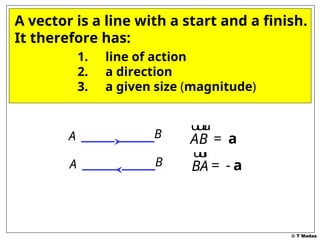
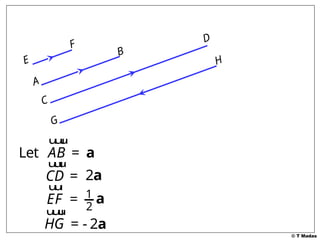
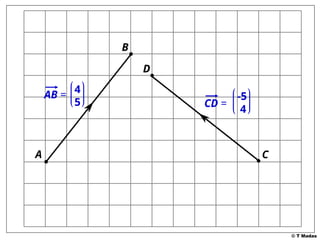
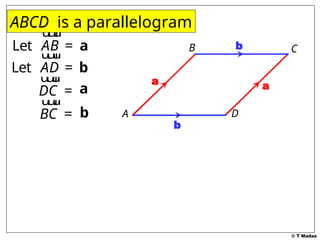
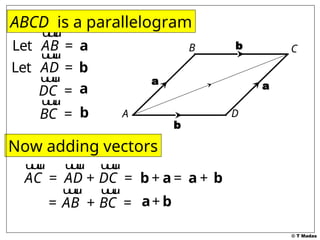
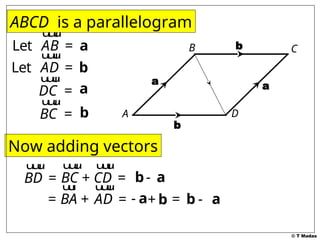
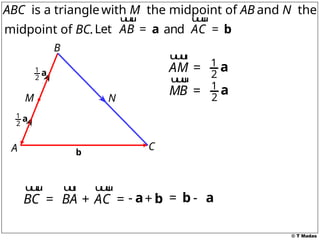
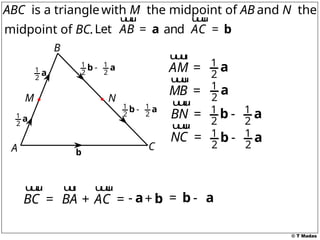
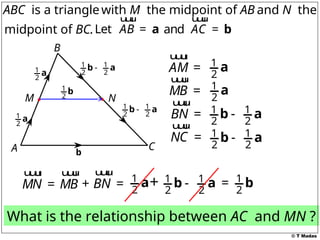
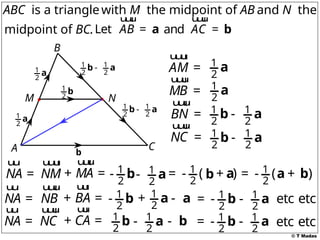
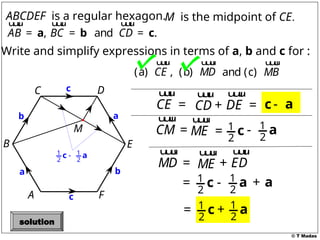
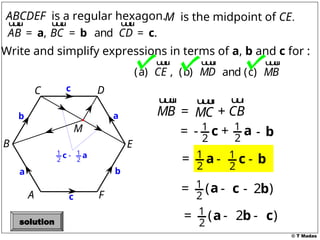
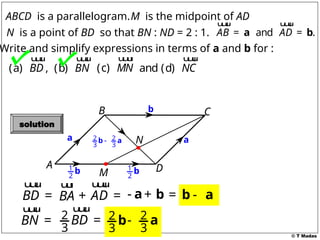
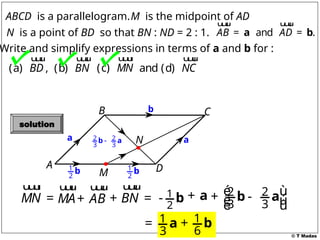
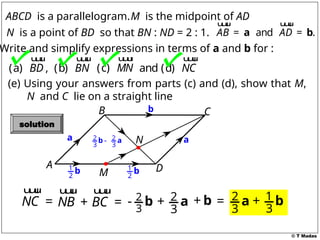
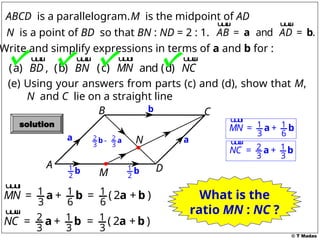
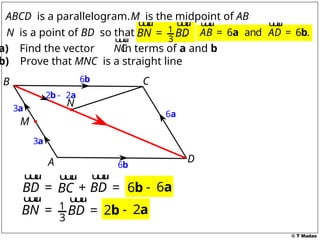
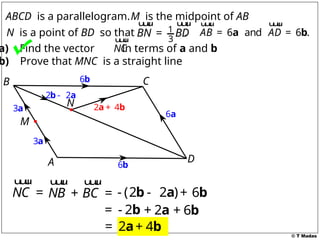
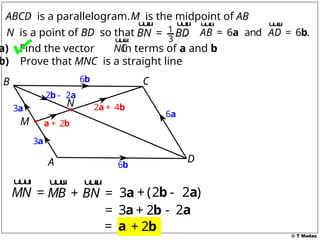
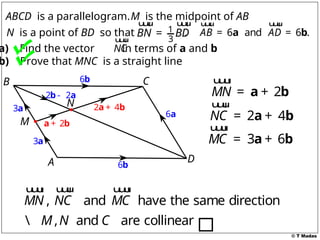
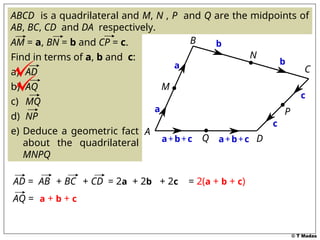
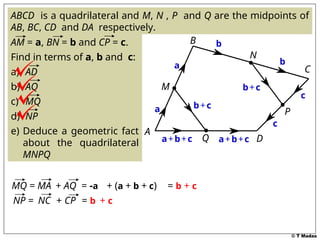
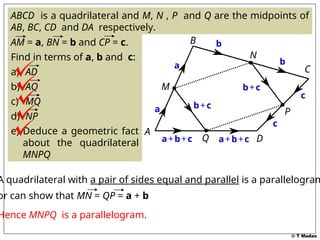
The document discusses vector concepts, focusing on their representation, addition, and the relationships between various geometric figures that can be formed with vectors. It covers specific cases such as parallelograms and triangles, emphasizing midpoints and vector notation in terms of components. Additionally, it presents exercises related to quadrilaterals and their properties, including conditions for parallelograms.